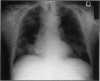
Abstract
Q or “query” fever is a zoonosis caused by the organism Coxiella burnetii. Cattle, sheep and goats are the most common reservoirs of this organism. The placenta of infected animals contains high numbers (up to 109/g) of C. burnetii. Aerosols occur at the time of parturition and man becomes infected following inhalation of the microorganism. The spectrum of illness in man is wide and consists of acute and chronic forms. Acute Q fever is most often a self-limited flu-like illness but may include pneumonia, hepatitis, or meningoencephalitis. Chronic Q fever almost always means endocarditis and rarely osteomyelitis. Chronic Q fever is not known to occur in animals other than man. An increased abortion and stillbirth rate are seen in infected domestic ungulates.
Four provinces (Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Ontario and Alberta) reported cases of Q fever in 1989.
A vaccine for Q fever has recently been licensed in Australia.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABINANTI F. R., LENNETTE E. H., WINN J. F., WELSH H. H. Q fever studies. XVIII. Presence of Coxiella burnetii in the birth fluids of naturally infected sheep. Am J Hyg. 1953 Nov;58(3):385–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABINANTI F. R., WELSH H. H., LENNETTE E. H., BRUNETTI O. Q fever studies. XVI. Some aspects of the experimental infection induced in sheep by the intratracheal route of inoculation. Am J Hyg. 1953 Mar;57(2):170–184. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABINANTI F. R., WELSH H. H., WINN J. F., LENNETTE E. H. Q fever studies. XIX. Presence and epidemiologic significance of Coxiella burnetii in sheep wool. Am J Hyg. 1955 May;61(3):362–370. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALKAN W. J., EVENCHIK Z., ESHCHAR J. QFEVER AND INFECTIOUS HEPATITIS. Am J Med. 1965 Jan;38:54–61. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken I. D. Clinical aspects and prevention of Q fever in animals. Eur J Epidemiol. 1989 Dec;5(4):420–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00140132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken I. D. Q fever in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Nov;267(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arechaga Uriarte S., Martín Peña G., Alonso Gordo J. M., San Román Terán C., Serrano Ríos M. Paniculitis mesentérica. Rev Clin Esp. 1983 Dec 15;171(5):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL J. F., LACKMAN D. B., MEIS A., HADLOW W. J. RECURRENT REACTION OF SITE OF Q FEVER VACCINATION IN A SENSITIZED PERSON. Mil Med. 1964 Jul;129:591–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON W. W., BROCK D. W., MATHER J. SEROLOGIC ANALYSIS OF A PENITENTIARY GROUP USING RAW MILK FROM A Q FEVER INFECTED HERD. Public Health Rep. 1963 Aug;78:707–710. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Q fever and Coxiella burnetii: a model for host-parasite interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):127–149. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.127-149.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs B. A., Douglas J. G., Grant I. W., Crompton G. K. Prolonged Q fever associated with inappropriate secretion of anti-diuretic hormone. J Infect. 1984 Jan;8(1):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)93381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brada M., Bellingham A. J. Bone-marrow necrosis and Q fever. Br Med J. 1980 Oct 25;281(6248):1108–1109. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6248.1108-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks R. G., Licitra C. M., Peacock M. G. Encephalitis caused by Coxiella burnetii. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jul;20(1):91–93. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Varma M. G. Trans-stadial and transovarial development of disease agents in arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol. 1967;12:347–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.12.010167.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATROS A., HOEL J. [Bilateral axial optic neuritis caused by Q fever]. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr. 1960 Apr;5:325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK W. H., LENNETTE E. H., RAILSBACK O. C., ROMER M. S. Q fever in California. VII. Clinical features in one hundred eighty cases. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1951 Aug;88(2):155–167. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1951.03810080023003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK W. H., ROMER M. S., HOLMES M. A., WELSH H. H., LENNETTE E. H., ABINANTI F. R. Q fever in California VIII. An epidemic of Q fever in a small rural community in northern California. Am J Hyg. 1951 Jul;54(1):25–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey J. E. Pleuropericardial lesion in Q fever. Br Med J. 1977 Jun 4;1(6074):1447–1447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6074.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conget I., Mallolas J., Mensa J., Rovira M. Erythema nodosum and Q fever. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Jul;123(7):867–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. H. Q fever in Northern Ireland. Br Med J. 1968 Mar 2;1(5591):547–552. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5591.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha B. A., Quintiliani R. The atypical pneumonias: a diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Postgrad Med. 1979 Sep;66(3):95–102. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1979.11715248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curet L. B., Paust J. C. Transmission of Q fever from experimental sheep to laboratory personnel. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Oct 15;114(4):566–568. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Angelo L. J., Hetherington R. Q fever treated with erythromycin. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 4;2(6185):305–306. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6185.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DERRICK E. H., POPE J. H., SMITH D. J. Outbreak of Q fever in Queensland associated with sheep. Med J Aust. 1959 May 2;46(18):585–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delsol G., Pellegrin M., Familiades J., Auvergnat J. C. Bone marrow lesions in Q fever. Blood. 1978 Sep;52(3):637–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont H. L., Hornick R. B., Levin H. S., Rapoport M. I., Woodward T. E. Q fever hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Feb;74(2):198–206. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-2-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis G., Petite J., Péter O., Vouilloz M. An important outbreak of human Q fever in a Swiss Alpine valley. Int J Epidemiol. 1987 Jun;16(2):282–287. doi: 10.1093/ije/16.2.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis G., Péter O., Peacock M., Burgdorfer W., Haller E. Immunoglobulin responses in acute Q fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):484–487. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.484-487.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlinger E. A. Q fever in France. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Nov;267(1):26–29. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. E., Dunbar E. M. In vivo response of acute Q fever to erythromycin. Thorax. 1982 Nov;37(11):867–868. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.11.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. E., Smith C. C., Moffat M. A. Chronic or fatal Q-fever infection: a review of 16 patients seen in North-East Scotland (1967-80). Q J Med. 1983 Winter;52(205):54–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Delahaye F., Raoult D., Frieh J. P., Loire R., Delaye J. Acute heart failure due to Q fever endocarditis. Eur Heart J. 1988 Aug;9(8):923–926. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FONTAN P., DESBORDES P. [Optic neuritis and "Q" fever]. Ann Ocul (Paris) 1961 Nov;194:971–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan M. Y., Walker D. H., Yu S. R., Liu Q. H. Epidemiology and ecology of rickettsial diseases in the People's Republic of China. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9(4):823–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Guerrero M. L., Muelas J. M., Aguado J. M., Renedo G., Fraile J., Soriano F., De Villalobos E. Q fever endocarditis on porcine bioprosthetic valves. Clinicopathologic features and microbiologic findings in three patients treated with doxycycline, cotrimoxazole, and valve replacement. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Feb;108(2):209–213. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field P. R., Hunt J. G., Murphy A. M. Detection and persistence of specific IgM antibody to Coxiella burnetii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: a comparison with immunofluorescence and complement fixation tests. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):477–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A., Silberman R., Peacock M., Spielman S. H. A microagglutination technique for detection and measurement of rickettsial antibodies. Acta Virol. 1969 Jan;13(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE J. H., BAKER J. A. Experimental Q fever in cats. Am J Vet Res. 1952 Jan;13(46):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Marrie T. J. Serological Evidence of Coxiella burnetii Infection in Horses in Atlantic Canada. Can Vet J. 1987 Jul;28(7):425–426. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerth H. J., Leidig U., Riemenschneider T. Q-Fieber-Epidemie in einem Institut für Humanpathologie. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1982 Sep 17;107(37):1391–1395. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1070136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. D., MacKeen A. D., Marrie T. J., Fraser D. B. The radiographic features of epidemic and sporadic Q fever pneumonia. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1984 Sep;35(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. G., Ascher M. S., Bernard K. W., Ruppanner R., Vellend H. Q fever and experimental sheep. From the International Council for Laboratory Animal Science. Infect Control. 1985 Mar;6(3):122–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grist N. R., Ross C. A. Q fever. Br Med J. 1968 Apr 13;2(5597):119–120. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5597.119-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARMAN J. B. Q fever in Great Britain; clinical account of eight cases. Lancet. 1949 Dec 3;2(6588):1028–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(49)91600-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEBNER R. J., BELL J. A. Q fever studies in Southern California; summary of current results and a discussion of possible control measures. J Am Med Assoc. 1951 Feb 3;145(5):301–passim. doi: 10.1001/jama.1951.02920230025005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Peacock M. G., Hitchcock P. J., Cole R. L. Lipopolysaccharide variation in Coxiella burnetti: intrastrain heterogeneity in structure and antigenicity. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):359–365. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.359-365.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldane E. V., Marrie T. J., Faulkner R. S., Lee S. H., Cooper J. H., MacPherson D. D., Montague T. J. Endocarditis due to Q fever in Nova Scotia: experience with five patients in 1981-1982. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):978–985. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. J., Richmond S. J., Caul E. O., Pearce N. H., Silver I. A. Laboratory outbreak of Q fever acquired from sheep. Lancet. 1982 May 1;1(8279):1004–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard S. R., Ronalds C. J., Heath R. B. Coxiella burnetii infection in immunocompromised patients. J Infect. 1985 Jul;11(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)90870-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Templeton J. L., Wilkinson A. J. Spontaneous splenic rupture: a unique presentation of Q fever. Ulster Med J. 1988 Oct;57(2):218–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C. E., Heaton J. W., Jr Q fever hepatitis: clinical manifestations and pathological findings. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):474–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. G., Field P. R., Murphy A. M. Immunoglobulin responses to Coxiella burnetii (Q fever): single-serum diagnosis of acute infection, using an immunofluorescence technique. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):977–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.977-981.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON G., DENLINGER R. B., CARTER R. A. Roentgen manifestations of Q fever. Radiology. 1949 Nov;53(5):739-49, illust. doi: 10.1148/53.5.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Kadull P. J. Laboratory-acquired Q fever. A report of fifty cases. Am J Med. 1966 Sep;41(3):391–403. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. M., BERTAGNA P. The geographical distribution of Q fever. Bull World Health Organ. 1955;13(5):829–860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanfer E., Farrag N., Price C., MacDonald D., Coleman J., Barrett A. J. Q fever following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1988 Mar;3(2):165–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosatsky T. Household outbreak of Q-fever pneumonia related to a parturient cat. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1447–1449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91633-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F. T., Williams J. C., Goodwin J. S. Cellular immunity in Q fever: specific lymphocyte unresponsiveness in Q fever endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1283–1289. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss H., Schmeer N., Schiefer H. G. Epidemiology and significance of Q fever in the Federal Republic of Germany. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Nov;267(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKMAN D. B., BELL E. J., BELL J. F., PICKENS E. G. Intradermal sensitivity testing in man with a purified vaccine for Q fever. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1962 Jan;52:87–93. doi: 10.2105/ajph.52.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUOTO L., CASEY M. L., PICKENS E. G. Q FEVER STUDIES IN MONTANA. DETECTION OF ASYMPTOMATIC INFECTION AMONG RESIDENTS OF INFECTED DAIRY PREMISES. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 May;81:356–369. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUOTO L., HUEBNER R. J. Q fever studies in southern California; IX. Isolation of Q fever organisms from parturient placenta; of naturally infected dairy cows. Public Health Rep. 1950 Apr 21;65(16):541–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUOTO L., PICKENS E. G. A resume of recent research seeking to define the Q fever problem. Am J Hyg. 1961 Jul;74:43–49. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladurner G., Stünzner D., Lechner H., Sixl W. Q-Fieber-Meningoencephalitis. Ein Fallbericht. Nervenarzt. 1976 May;46(5):274–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer D., Lew P. D., Oberhansli I., Cox J. N., Longson M. Chronic Q fever endocarditis with massive splenomegaly in childhood. J Pediatr. 1986 Apr;108(4):535–539. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80828-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev B. I., Shachar A., Segev S., Weiss P., Rubinstein E. Quiescent Q fever endocarditis exacerbated by cardiac surgery and corticosteroid therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Jul;148(7):1531–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loudon M. M., Thompson E. N. Severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome, tissue transplant, leukaemia, and Q fever. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Feb;63(2):207–209. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMION B. P., STOKER M. G. The epidemiology of Q fever in Great Britain; an analysis of the findings and some conclusions. Br Med J. 1958 Oct 4;2(5100):809–816. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5100.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMION B. P., STOKER M. G., WALKER C. B., CARPENTER R. G. Q fever in Great Britain; epidemiological information from a serological survey of healthy adults in Kent and East Anglia. J Hyg (Lond) 1956 Mar;54(1):118–140. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASBERNARD A. LES LOCALISATIONS NEUROLOGIQUES DES RICKETTSIOSES. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1963 Jul-Aug;56:714–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. S., Douglas J. G., Inglis J. M., Leitch A. G. Q fever: person to person transmission within a family. Thorax. 1986 Dec;41(12):974–975. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.12.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmion B. P., Ormsbee R. A., Kyrkou M., Wright J., Worswick D., Cameron S., Esterman A., Feery B., Collins W. Vaccine prophylaxis of abattoir-associated Q fever. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1411–1414. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Durant H., Williams J. C., Mintz E., Waag D. M. Exposure to parturient cats: a risk factor for acquisition of Q fever in Maritime Canada. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):101–108. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Durant H., Yates L. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization: 5-year prospective study. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11(4):586–599. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.4.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Fraser J. Prevalence of Antibodies to Coxiella burnetii Among Veterinarians and Slaughterhouse Workers in Nova Scotia. Can Vet J. 1985 Jun;26(6):181–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Haldane E. V., Faulkner R. S., Kwan C., Grant B., Cook F. The importance of Coxiella burnetii as a cause of pneumonia in Nova Scotia. Can J Public Health. 1985 Jul-Aug;76(4):233–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Haldane E. V., Noble M. A., Faulkner R. S., Lee S. H., Gough D., Meyers S., Stewart J. Q fever in maritime Canada. Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Jun 1;126(11):1295–1300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Haldane E. V., Noble M. A., Faulkner R. S., Martin R. S., Lee S. H. Causes of atypical pneumonia: results of a 1-year prospective study. Can Med Assoc J. 1981 Nov 15;125(10):1118–1123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Langille D., Papukna V., Yates L. Truckin' pneumonia--an outbreak of Q fever in a truck repair plant probably due to aerosols from clothing contaminated by contact with newborn kittens. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Feb;102(1):119–127. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J. Pneumonia and meningo-encephalitis due to Coxiella burnetii. J Infect. 1985 Jul;11(1):59–61. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)91066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J. Q fever pneumonia. Semin Respir Infect. 1989 Mar;4(1):47–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Schlech W. F., 3rd, Williams J. C., Yates L. Q fever pneumonia associated with exposure to wild rabbits. Lancet. 1986 Feb 22;1(8478):427–429. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Van Buren J., Fraser J., Haldane E. V., Faulkner R. S., Williams J. C., Kwan C. Seroepidemiology of Q fever among domestic animals in Nova Scotia. Am J Public Health. 1985 Jul;75(7):763–766. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.7.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaul T. F., Williams J. C. Developmental cycle of Coxiella burnetii: structure and morphogenesis of vegetative and sporogenic differentiations. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1063–1076. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1063-1076.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiklejohn G., Reimer L. G., Graves P. S., Helmick C. Cryptic epidemic of Q fever in a medical school. J Infect Dis. 1981 Aug;144(2):107–113. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. K. The chest film findings in 'Q' fever--a series of 35 cases. Clin Radiol. 1978 Jul;29(4):371–375. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(78)80092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. M., Field P. R. The persistence of complement-fixing antibodies to Q-fever (Coxiella burneti) after infection. Med J Aust. 1970 Jun 6;1(23):1148–1150. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1970.tb84481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A. A method of purifying Coxiella burnetii and other pathogenic Rickettsiae. J Immunol. 1962 Jan;88:100–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A., BELL E. J., LACKMAN D. B., TALLENT G. THE INFLUENCE OF PHASE ON THE PROTECTIVE POTENCY OF Q FEVER VACCINE. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:404–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okun D. B., Sun N. C., Tanaka K. R. Bone marrow granulomas in Q fever. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;71(1):117–121. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL O. "Q" fever: clinical features in 72 cases. Australas Ann Med. 1960 Aug;9:214–223. doi: 10.1111/imj.1960.9.3.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer N. C., Kierstead M., Key D. W., Williams J. C., Peacock M. G., Vellend H. Placentitis and Abortion in Goats and Sheep in Ontario Caused by Coxiella burnetii. Can Vet J. 1983 Feb;24(2):60–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S. R., Young S. E. Q-fever endocarditis in England and Wales, 1975-81. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1448–1449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrin M., Delsol G., Auvergnat J. C., Familiades J., Faure H., Guiu M., Voigt J. J. Granulomatous hepatitis in Q fever. Hum Pathol. 1980 Jan;11(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polydorou K. Q fever in Cyprus: a short review. Br Vet J. 1981 Sep-Oct;137(5):470–477. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)31584-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polydorou K. Q-fever control in Cyprus--recent progress. Br Vet J. 1985 Jul-Aug;141(4):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0007-1935(85)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Dupuis G., Burgdorfer W., Peacock M. Evaluation of the complement fixation and indirect immunofluorescence tests in the early diagnosis of primary Q fever. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;4(4):394–396. doi: 10.1007/BF02148690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Dupuis G., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and complement fixation and indirect fluorescent-antibody tests for detection of Coxiella burnetii antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1063–1067. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1063-1067.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qizilbash A. H. The pathology of Q fever as seen on liver biopsy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1983 Jul;107(7):364–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju N. R., Collings D. F., Saville P. H. Abortion in black belly Barbados sheep in Fiji caused by Coxiella burnetii. Aust Vet J. 1988 Jul;65(7):225–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1988.tb14465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Etienne J., Massip P., Iaocono S., Prince M. A., Beaurain P., Benichou S., Auvergnat J. C., Mathieu P., Bachet P. Q fever endocarditis in the south of France. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):570–573. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Piquet P., Gallais H., de Micco C., Drancourt M., Casanova P. Coxiella burnetii infection of a vascular prosthesis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 20;315(21):1358–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardus J. H., Donkers A., Dumas A. M., Schaap G. J., Akkermans J. P., Huisman J., Valkenburg H. A. Q fever in the Netherlands: a sero-epidemiological survey among human population groups from 1968 to 1983. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Apr;98(2):211–219. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800061938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. J., JacobsoJn J., Muir J. R. Q fever endocarditis of porcine xenograft valves. Am Heart J. 1983 Jan;105(1):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(83)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDWELL R. W., THORPE B. D., GEBHARDT L. P. STUDIES OF LATENT Q FEVER INFECTIONS. II. EFFECTS OF MULTIPLE CORTISONE INJECTIONS. Am J Hyg. 1964 May;79:320–327. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDWELL R. W., THORPE B. D., GEBHARDT L. P. STUDIES ON LATENT Q FEVER INFECTIONS. I. EFFECTS OF WHOLE BODY X-IRRADIATION UPON LATENTLY INFECTED GUINEA PIGS, WHITE MICE AND DEER MICE. Am J Hyg. 1964 Jan;79:113–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOENNER H. G. Experimental Q fever in cattle--epizootiologic aspects. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1951 Mar;118(888):170–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M. G. P., THOMPSON J. F. An explosive outbreak of Q fever. Lancet. 1953 Jan 17;1(6751):137–139. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90855-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M. G., MARMION B. P. The spread of Q fever from animals to man; the natural history of a rickettsial disease. Bull World Health Organ. 1955;13(5):781–806. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M. G. Q fever down the drain. Br Med J. 1957 Feb 23;1(5016):425–427. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5016.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYRUCEK L., SOBESLAVSKY O., GUTVIRTH I. Isolation of Coxiella burneti from human placentas. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1958;2(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saginur R., Silver S. S., Bonin R., Carlier M., Orizaga M. Q-fever endocarditis. CMAJ. 1985 Dec 15;133(12):1228–1230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. A., Fishbein D. B., McDade J. E. Q fever: current concepts. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9(5):935–946. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.5.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Mayer H. Different sugar compositions of lipopolysaccharides isolated from phase I and pure phase II cells of Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):53–57. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.53-57.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuil J., Richardus J. H., Baarsma G. S., Schaap G. J. Q fever as a possible cause of bilateral optic neuritis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1985 Aug;69(8):580–583. doi: 10.1136/bjo.69.8.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. B. Manic psychosis in connection with Q-fever. Br J Psychiatry. 1974 Feb;124(579):140–143. doi: 10.1192/bjp.124.2.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seggev J. S., Levin S., Schey G. Unusual radiological manifestations of Q fever. Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;69(2):120–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan P., MacCaig J. N., Hart R. J. Myocarditis complicating Q fever. Br Med J. 1974 Apr 20;2(5911):155–156. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5911.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlo F., Kovalik M. Acute thyroiditis in a patient with Q fever. Can Med Assoc J. 1966 Nov 19;95(21):1091–1093. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somma-Moreira R. E., Caffarena R. M., Somma S., Pérez G., Monteiro M. Analysis of Q fever in Uruguay. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9(2):386–387. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.2.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelman D. W. Q fever: a study of 111 consecutive cases. Med J Aust. 1982 Jun 26;1(13):547-8, 551, 553. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb124169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer D. S., DeSanctis A. N. Preparation of phase 1Q fever antigen suitable for vaccine use. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):85–88. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.85-88.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring W. J., Hampson J. Chronic Q fever endocarditis causing massive splenomegaly and hypersplenism. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 30;285(6350):1244–1244. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6350.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tellez A., Sainz C., Echevarria C., de Carlos S., Fernandez M. V., Leon P., Brezina R. Q fever in Spain: acute and chronic cases, 1981-1985. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):198–202. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin M. J., Cahill N., Gearty G., Maurer B., Blake S., Daly K., Hone R. Q fever endocarditis. Am J Med. 1982 Mar;72(3):396–400. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis L. B., Travis W. D., Li C. Y., Pierre R. V. Q fever. A clinicopathologic study of five cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Nov;110(11):1017–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck W. P., Howitt G., Turnberg L. A., Fox H., Longson M., Matthews M. B., Das Gupta R. Chronic Q fever. Q J Med. 1976 Apr;45(178):193–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tylewska-Wierzbanowska S. K., Kruszewska D. Q fever--sexually transmitted infection? J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):368–369. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma M. P., Adgey A. A., Connolly J. H. Chronic Q fever endocarditis. Br Heart J. 1980 Jun;43(6):695–699. doi: 10.1136/hrt.43.6.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C., Stephenson E. H. Genetic heterogeneity among isolates of Coxiella burnetii. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):455–463. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt J. J., Delsol G., Fabre J. Liver and bone marrow granulomas in Q fever. Gastroenterology. 1983 Apr;84(4):887–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSH H. H., LENNETTE E. H., ABINANTI F. R., WINN J. F. Air-borne transmission of Q fever: the role of parturition in the generation of infective aerosols. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):528–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt A. H., Fraser A. G., Stephens M. R. Q fever endocarditis presenting as myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1986 Dec;112(6):1333–1335. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(86)90374-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willeberg P., Ruppanner R., Behymer D. E., Haghighi S., Kaneko J. J., Franti C. E. Environmental exposure to Coxiella burnetii: a sero-epidemiologic survey among domestic animals. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Apr;111(4):437–443. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. F., Matthews M. B., Peutherer J. F., Marmion B. P. Chronic cryptic Q-fever infection of the heart. Lancet. 1979 Aug 11;2(8137):270–272. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. G., Neilson G. H., Galea E. G., Stafford G., O'Brien M. F. Q fever endocarditis in Queensland. Circulation. 1976 Apr;53(4):680–684. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.53.4.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worswick D., Marmion B. P. Antibody responses in acute and chronic Q fever and in subjects vaccinated against Q fever. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Jun;19(3):281–296. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-3-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]