Abstract
A field trial of antimicrobial therapy for cases of undifferentiated bovine respiratory disease (UBRD) in beef calves was conducted at four Ontario feedlots. The primary purpose of the trial was to evaluate the efficacy of three different antimicrobials (oxytetracycline, penicillin, and trimethoprim-sulfadoxine) in the treatment of UBRD occurring within the first 28 days postarrival.
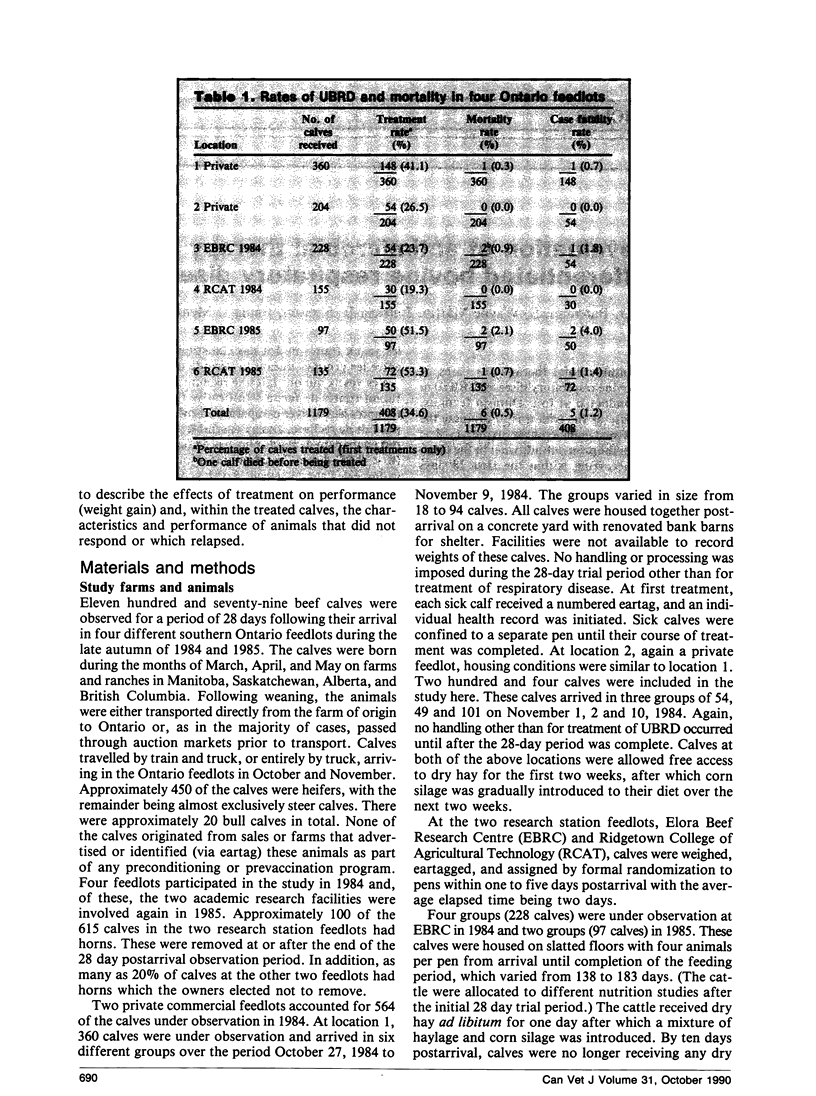
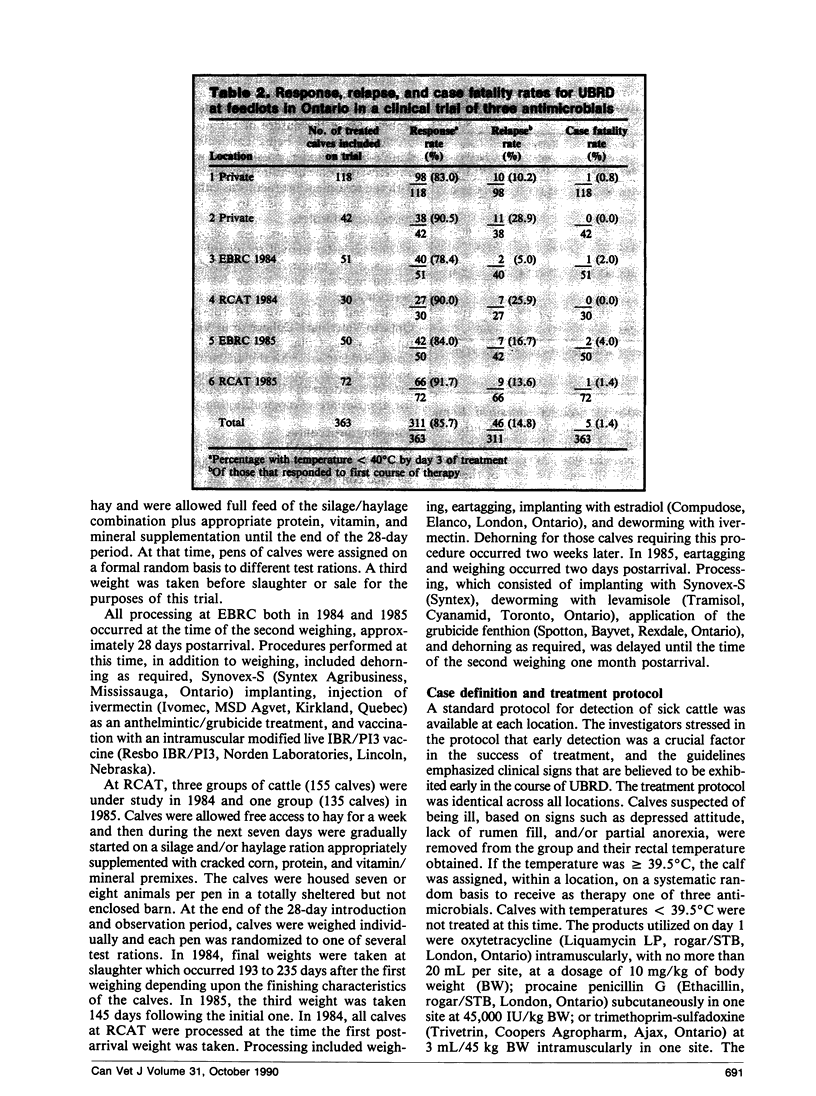
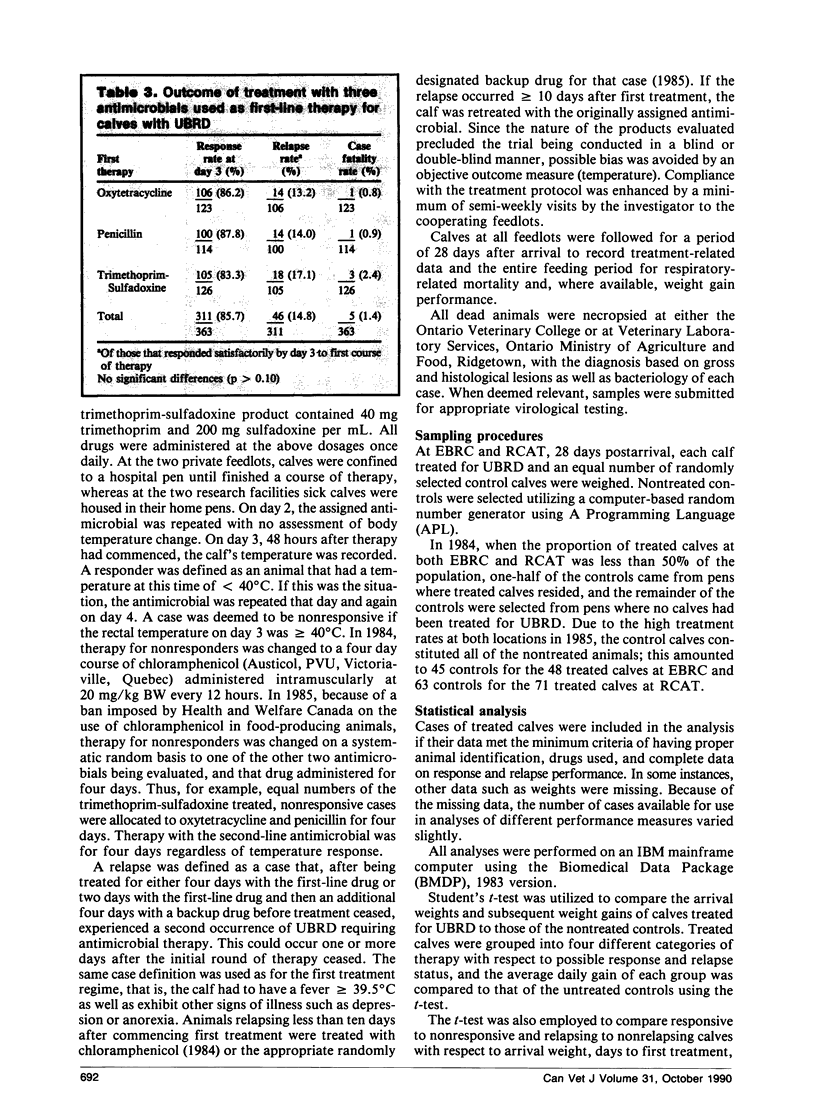
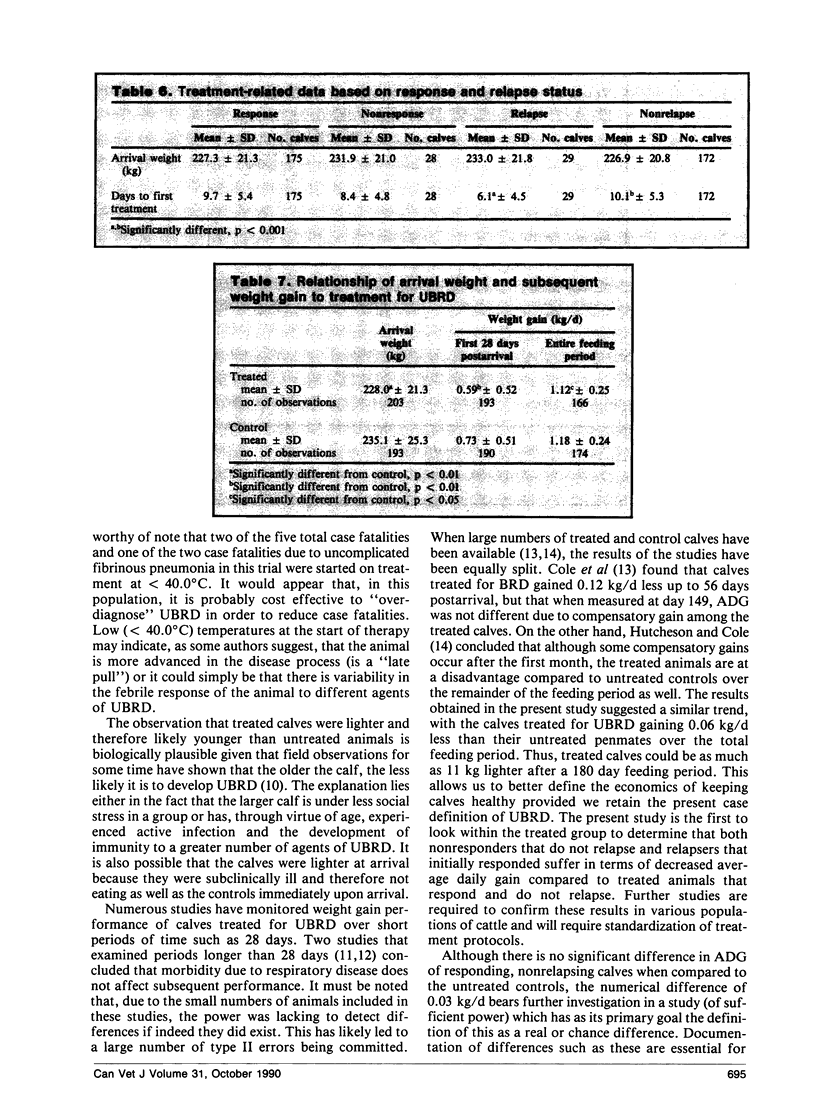
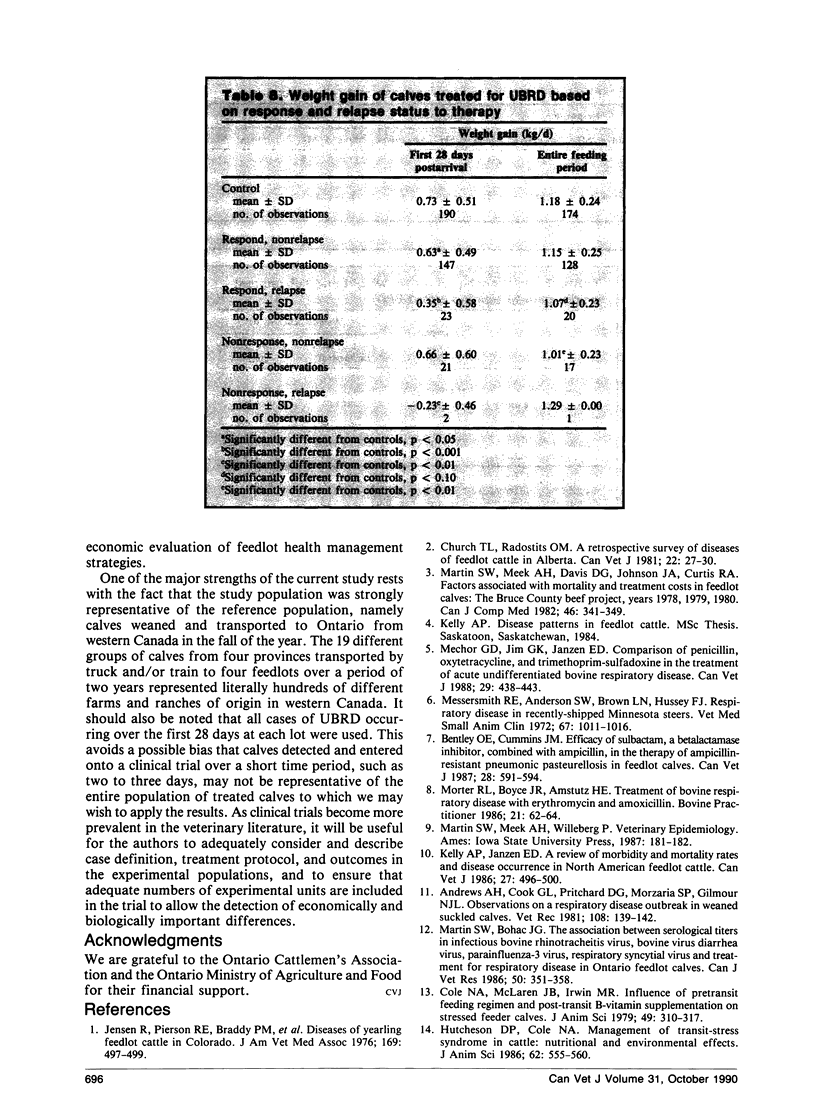
The response, relapse, and case fatality rates overall were 85.7%, 14.8%, and 1.4%, respectively, and were not significantly different among the three antimicrobials evaluated. Weight gains of calves treated with the different drugs were not statistically different over the feeding period. Calves that suffered a relapse posttreatment were first treated significantly earlier (p<0.001) in the postarrival period than those that did not relapse. Considered together, treated calves gained significantly less (p<0.05) over the first 28 days and throughout the entire feeding period than controls that were never sick. Cases of UBRD that responded to therapy and did not relapse had rates of gain that were not significantly different from the controls.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews A. H., Cook G. L., Pritchard D. G., Morzaria S. P., Gilmour N. J. Observations on a respiratory disease outbreak in weaned suckled calves. Vet Rec. 1981 Feb 14;108(7):139–142. doi: 10.1136/vr.108.7.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley O. E., Cummins J. M. Efficacy of Sulbactam, a B-lactamase Inhibitor, Combined with Ampicillin in the Therapy of Ampicillin-resistant Pneumonic Pasteurellosis in Feedlot Calves. Can Vet J. 1987 Sep;28(9):591–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church T. L., Radostits O. M. A retrospective survey of diseases of feedlot cattle in Alberta. Can Vet J. 1981 Feb;22(2):27–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole N. A., McLaren J. B., Irwin M. R. Influence of pretransit feeding regimen and posttransit B-vitamin supplementation on stressed feeder steers. J Anim Sci. 1979 Aug;49(2):310–317. doi: 10.2527/jas1979.492310x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Pierson R. E., Braddy P. M., Saari D. A., Lauerman L. H., England J. J., Horton D. P., McChesney A. E. Diseases of yearling feedlot cattle in Colorado. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Sep 1;169(5):497–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A. P., Janzen E. D. A review of morbidity and mortality rates and disease occurrence in north american feedlot cattle. Can Vet J. 1986 Dec;27(12):496–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Bohac J. G. The association between serological titers in infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus, bovine virus diarrhea virus, parainfluenza-3 virus, respiratory syncytial virus and treatment for respiratory disease in Ontario feedlot calves. Can J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;50(3):351–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Johnson J. A., Curtis R. A. Factors associated with mortality and treatment costs in feedlot calves: the Bruce County Beef Project, years 1978, 1979, 1980. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Oct;46(4):341–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechor G. D., Jim G. K., Janzen E. D. Comparison of penicillin, oxytetracycline, and trimethoprim-sulfadoxine in the treatment of acute undifferentiated bovine respiratory disease. Can Vet J. 1988 May;29(5):438–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messersmith R. E., Anderson S. W., Brown L. N., Hussey F. J. Respiratory disease in recently-shipped Minnesota steers (a clinical study). Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Sep;67(9):1011–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


