Abstract
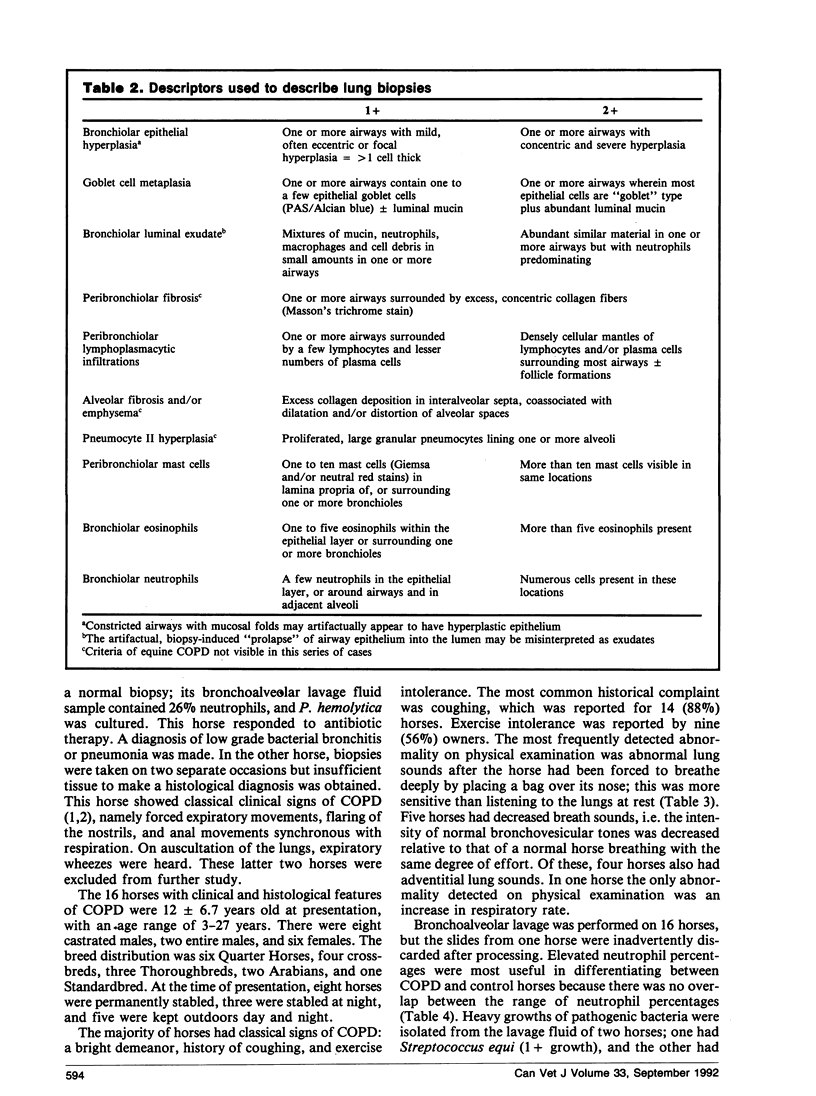
We examined 18 horses with clinical signs of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) using physical examination, cytological and bacteriological evaluation of bronchoalveolar fluid, and percutaneous lung biopsy. In 16 cases, histological examination of lung tissue confirmed the diagnosis of COPD. Two horses were excluded: one had uncomplicated bacterial pneumonia and in the other a satisfactory lung biopsy could not be obtained. In horses with COPD, the most common historical complaint was coughing, which was reported in 88%. The most frequently detected abnormal finding on physical examination was abnormal lung sounds; these were detected in 69% of horses at rest and in 88% of horses breathing deeply into a bag. A novel finding was that 29% of horses had lung sounds that were quieter than would be expected for the degree of respiratory effort. Horses with COPD had increased percentages of neutrophils and decreased percentages of lymphocytes and macrophages in their bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Bronchiolar neutrophil infiltration and peribronchiolar mast cell accumulation in lung biopsy tissue had the highest correlation with clinical condition. The severity of pathological changes in biopsies of lung did not predict whether the horse would die in the two to four year follow-up period. Horses that died in the follow-up period were more severely affected clinically at initial presentation than horses that were alive at the end of the follow-up period.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brain J. D., Frank R. Alveolar macrophage adhesion: wash electrolyte composition and free cell yield. J Appl Physiol. 1973 Jan;34(1):75–80. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. F., Madelin T. Technique for assessing respiratory health hazards from hay and other source materials. Equine Vet J. 1987 Sep;19(5):442–447. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1987.tb02639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darien B. J., Brown C. M., Walker R. D., Williams M. A., Derksen F. J. A tracheoscopic technique for obtaining uncontaminated lower airway secretions for bacterial culture in the horse. Equine Vet J. 1990 May;22(3):170–173. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1990.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen F. J., Robinson N. E., Scott J. S., Stick J. A. Aerosolized Micropolyspora faeni antigen as a cause of pulmonary dysfunction in ponies with recurrent airway obstruction (heaves). Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jun;49(6):933–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen F. J., Scott J. S., Miller D. C., Slocombe R. F., Robinson N. E. Bronchoalveolar lavage in ponies with recurrent airway obstruction (heaves). Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Nov;132(5):1066–1070. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.5.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogarty U. Evaluation of a bronchoalveolar lavage technique. Equine Vet J. 1990 May;22(3):174–176. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1990.tb04241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaup F. J., Drommer W., Damsch S., Deegen E. Ultrastructural findings in horses with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). II: Pathomorphological changes of the terminal airways and the alveolar region. Equine Vet J. 1990 Sep;22(5):349–355. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1990.tb04288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaup F. J., Drommer W., Deegen E. Ultrastructural findings in horses with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). I: Alterations of the larger conducting airways. Equine Vet J. 1990 Sep;22(5):343–348. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1990.tb04287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. H., McPherson E. A., Murphy J. R., Nicholson J. M., Wooding P., Breeze R. G., Pirie H. M. The presence of precipitating antibodies in the sera of horses with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Equine Vet J. 1979 Jul;11(3):172–176. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1979.tb01334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mair T. S., Stokes C. R., Bourne F. J. Cellular content of secretions obtained by lavage from different levels of the equine respiratory tract. Equine Vet J. 1987 Sep;19(5):458–462. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1987.tb02644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mair T. S., Sweeney C. R. Advances in the diagnosis of equine lung disease: sampling from the lower airways. Equine Vet J. 1990 May;22(3):147–148. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1990.tb04232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raphel C. F., Gunson D. E. Percutaneous lung biopsy in the horse. Cornell Vet. 1981 Oct;71(4):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier Y., Sweeney C. R., Ziemer E. L. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cytologic findings in horses with pneumonia or pleuropneumonia. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1991 Mar 15;198(6):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roudebush P. Lung sounds. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Jul 15;181(2):122–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viel L. Diagnostic procedures, prognosis and therapeutic approaches of chronic respiratory diseases in horses. Can Vet J. 1985 Jan;26(1):33–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder N. C., von Fellenberg R. Chronic small airway disease in the horse: immunohistochemical evaluation of lungs with mild, moderate and severe lesions. Vet Rec. 1988 Feb 20;122(8):181–183. doi: 10.1136/vr.122.8.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


