Abstract
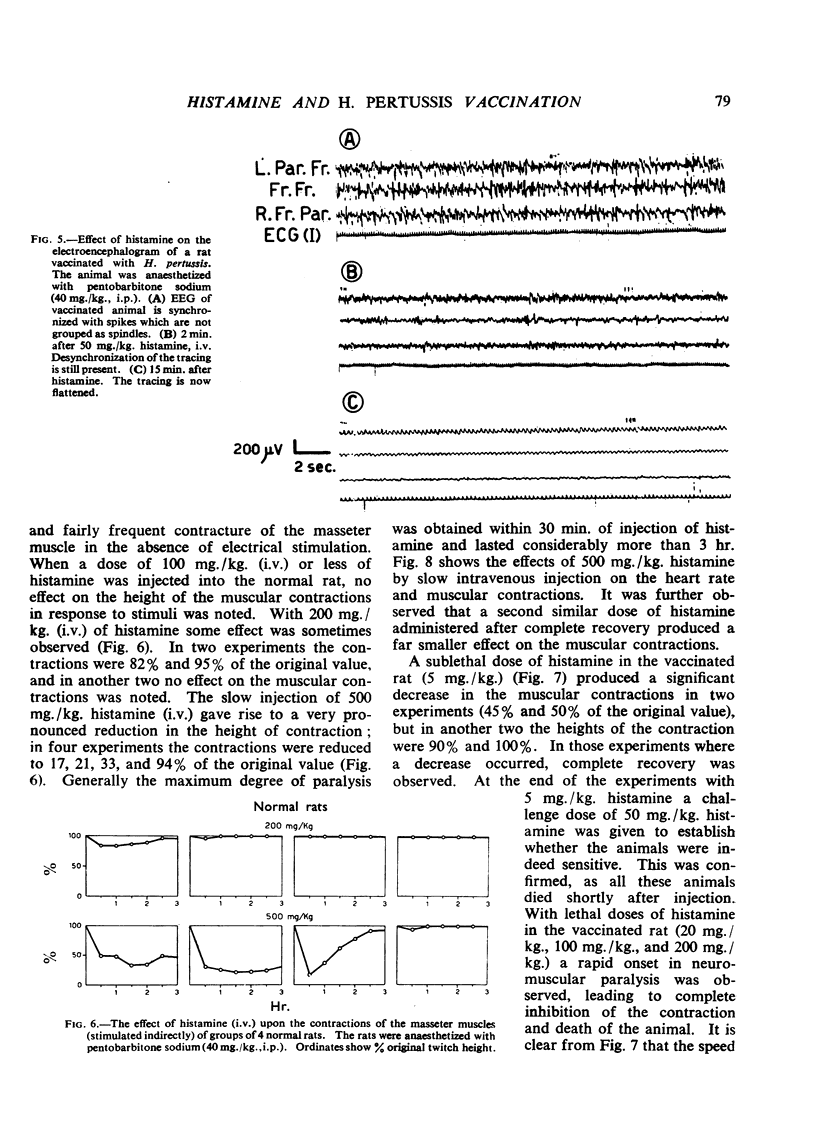
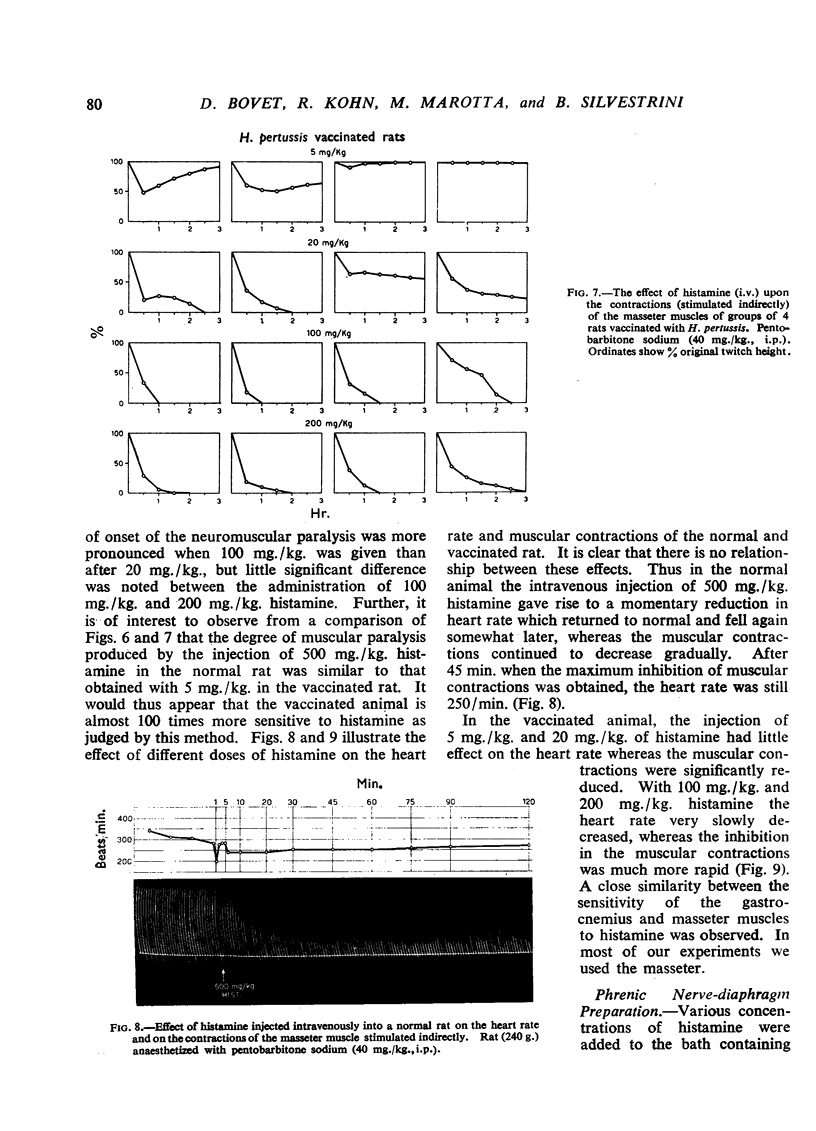
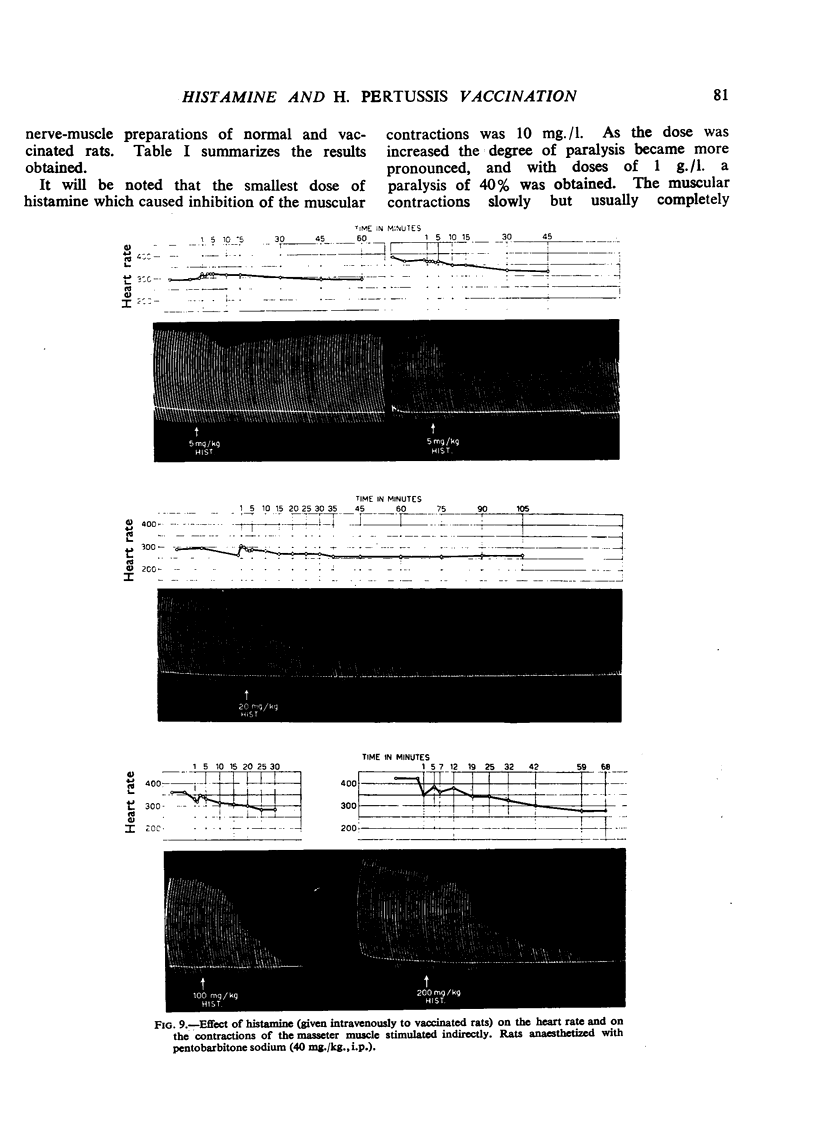
The effects of histamine in the normal and H. pertussis vaccinated rat have been investigated. In the normal animal small doses of histamine (from 1 to 30 mg./kg., i.v.) produced significant, reversible alterations in the blood pressure, electrocardiogram and electroencephalogram. Doses of 100 mg./kg. or more caused bronchoconstriction and doses of 200 mg./kg. or more an effect on the muscular contractions after electrical stimulation of the nerve. Acute histamine intoxication resulted on rapid injection of 500 mg./kg. intravenously; death was probably due to cardiovascular collapse. In the vaccinated rat, a distinction could be made between the immediate and delayed effects of histamine. With a sublethal dose of histamine (5 mg./kg.) alterations in the blood pressure, electrocardiogram and electroencephalogram were noted. The neuromuscular system, which in the normal animal was the least reactive to histamine, showed the most marked increase in sensitivity in the vaccinated rat. The delayed effects of histamine observed after an interval of 5 to 30 min. were characteristic and irreversible, leading to death of the animal. The mechanism of death in the vaccinated rat after histamine appears to differ from that of the normal animal and has been discussed in the light of present knowledge.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FRANK M., LONGO V. G. Un nuovo manometro elettrico atto alla misurazione di pressioni arteriose e venose. Rend Ist Sup Sanit. 1955;18(11):1045–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUTHIER G. F., LOEW E. R., JENKINS H. J. Histamine sensitivity of adrenalectomized and pertussis-treated mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Dec;90(3):726–728. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., BENACERRAF B., BRIOT M. The roles of cortisone, desoxycorticosterone, and adrenaline in protecting adrenalectomized animals against heemorrhagic, traumatic, and histaminic shock. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Jun;7(2):287–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISE E., KIMBEL K. H. Das normale Elektrokardiogramm der Ratte. Z Kreislaufforsch. 1955 Mar;44(5-6):212–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUSSAY R. H. Sensibilidad a la histamina de las ratas con suprarrenales accesorias o desmedulizadas. Rev Soc Argent Biol. 1955 Aug-Sep;31(5-6):131–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIND L. S. The altered reactivity of mice after immunization with Hemophilus pertussis vaccine. J Immunol. 1953 Apr;70(4):411–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACMILLAN W. H., VANE J. R. The effects of histamine on the plasma potassium levels of cats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 Oct;118(2):182–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAITLAND H. B., KOHN R., MACDONALD A. D. The histamine-sensitizing property of Haemophilus pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Jun;53(2):196–211. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400000668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALKIEL S., HARGIS B. J. Histamine sensitivity and anaphylaxis in the pertussis-vaccinated rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Dec;81(3):689–691. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMJEN G., UYLDERT I. E. The effect of compound 48/80 on mammalian skeletal muscle. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Dec;10(4):413–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIELE E. H., SCHUCHARDT L. F. The inhibition of the development of histamine sensitivity in mice immunized with Hemophilus pertussis. Science. 1952 Jan 4;115(2975):8–9. doi: 10.1126/science.115.2975.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


