Abstract
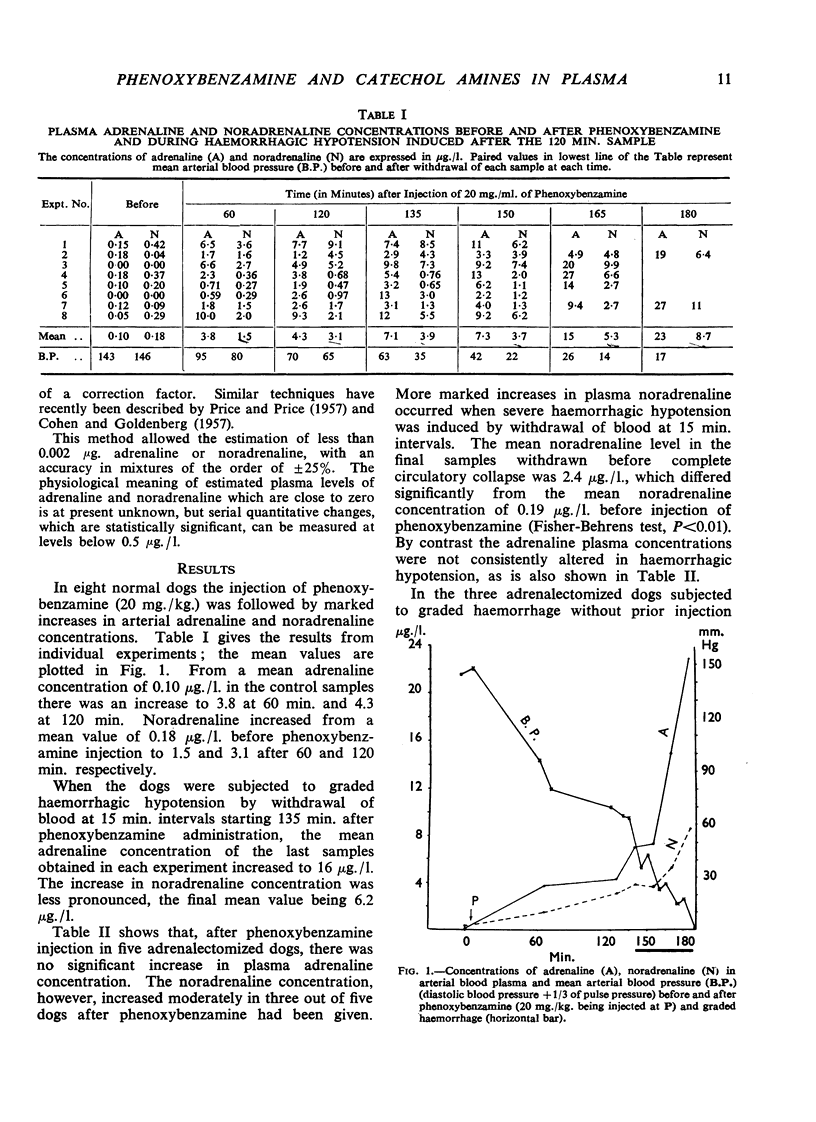
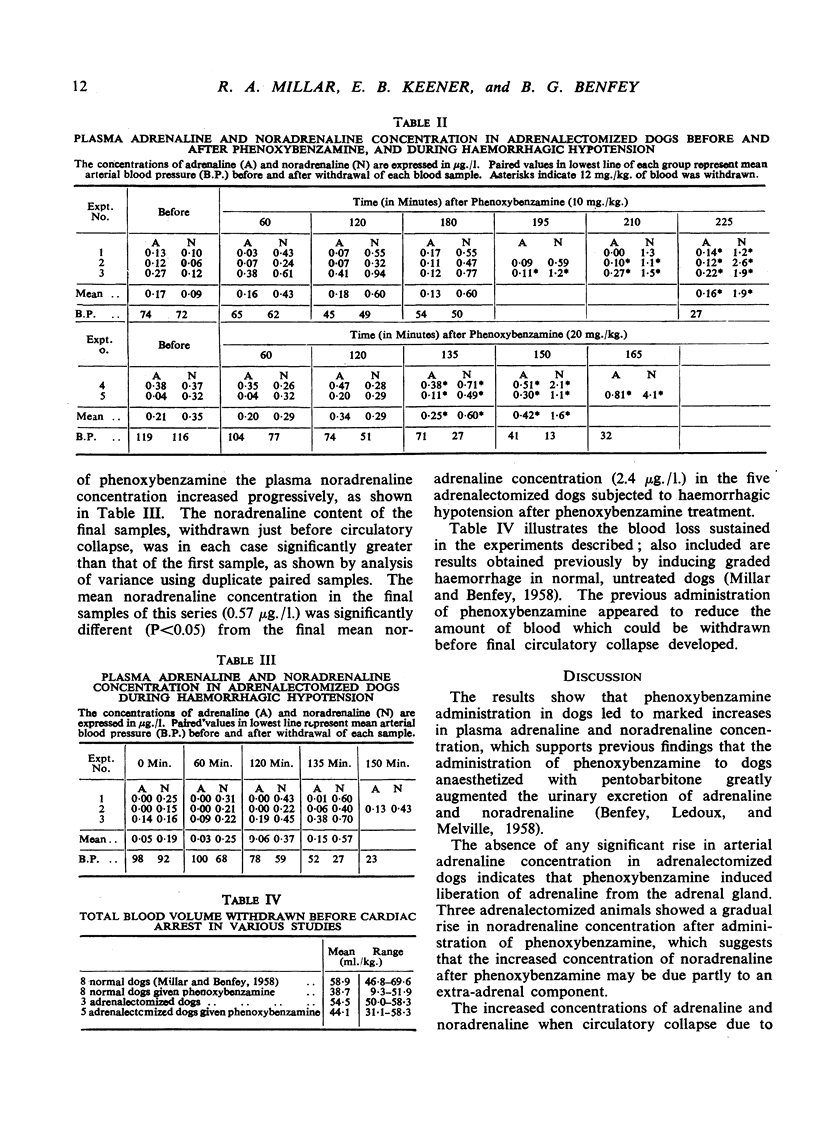
The intravenous administration of the antiadrenaline drug phenoxybenzamine (Dibenzyline) markedly raised the arterial adrenaline and noradrenaline concentration in dogs lightly anaesthetized with thiopentone. Graded haemorrhage led to a further rise in the amounts of amine. In adrenalectomized dogs, phenoxybenzamine moderately increased the plasma noradrenaline concentration. During haemorrhagic hypotension, previous treatment of adrenalectomized animals with phenoxybenzamine led to a significantly greater rise in plasma noradrenaline compared with that of adrenalectomized animals subjected to haemorrhage without treatment with phenoxybenzamine. Thus, phenoxybenzamine (1) raised plasma amine concentration largely due to adrenal medullary stimulation, and (2) led to increased plasma noradrenaline concentrations during sympathetic stimulation in adrenalectomized animals. The previous administration of phenoxybenzamine reduced the amount of blood which could be withdrawn before final circulatory collapse in both normal and adrenalectomized dogs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN G. L., GILLESPIE J. S. The output of sympathetic transmitter from the spleen of the cat. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):81–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE H. L., PRICE M. L. The chemical estimation of epinephrine and norepinephrine in human and canine plasma. II. A critique of the trihydroxylndole method. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Nov;50(5):769–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


