Abstract
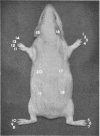
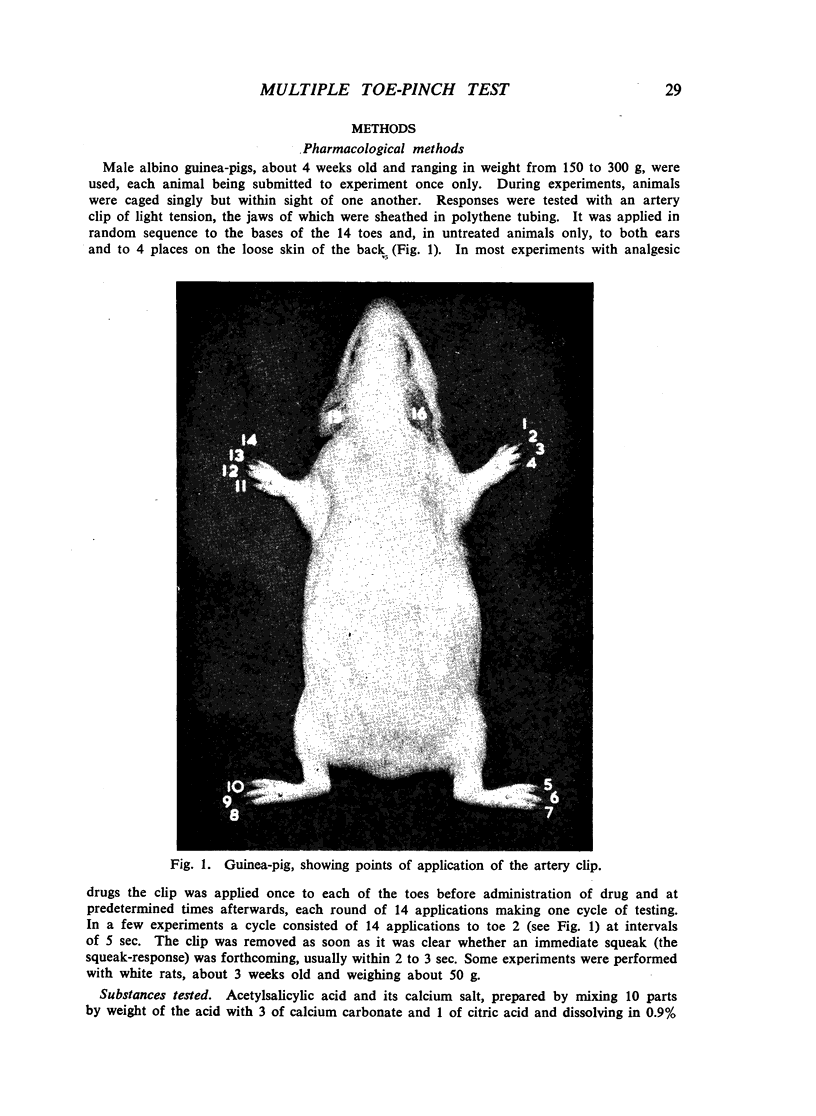
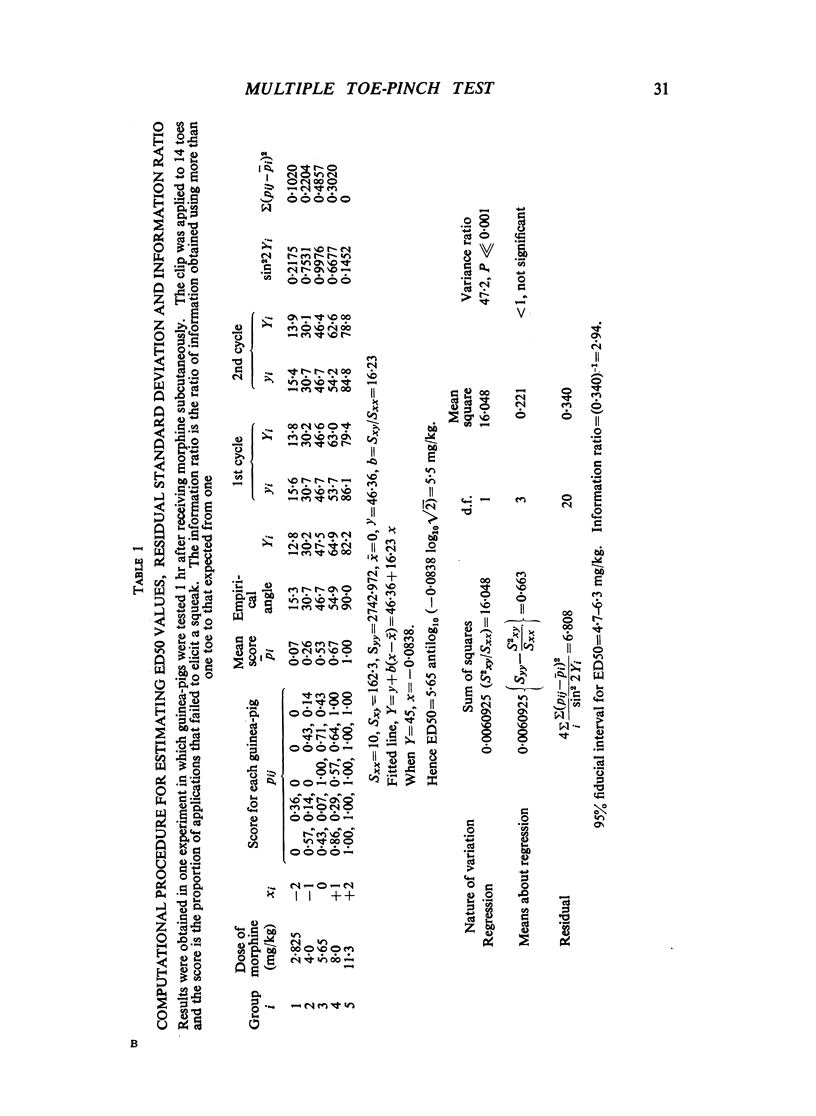
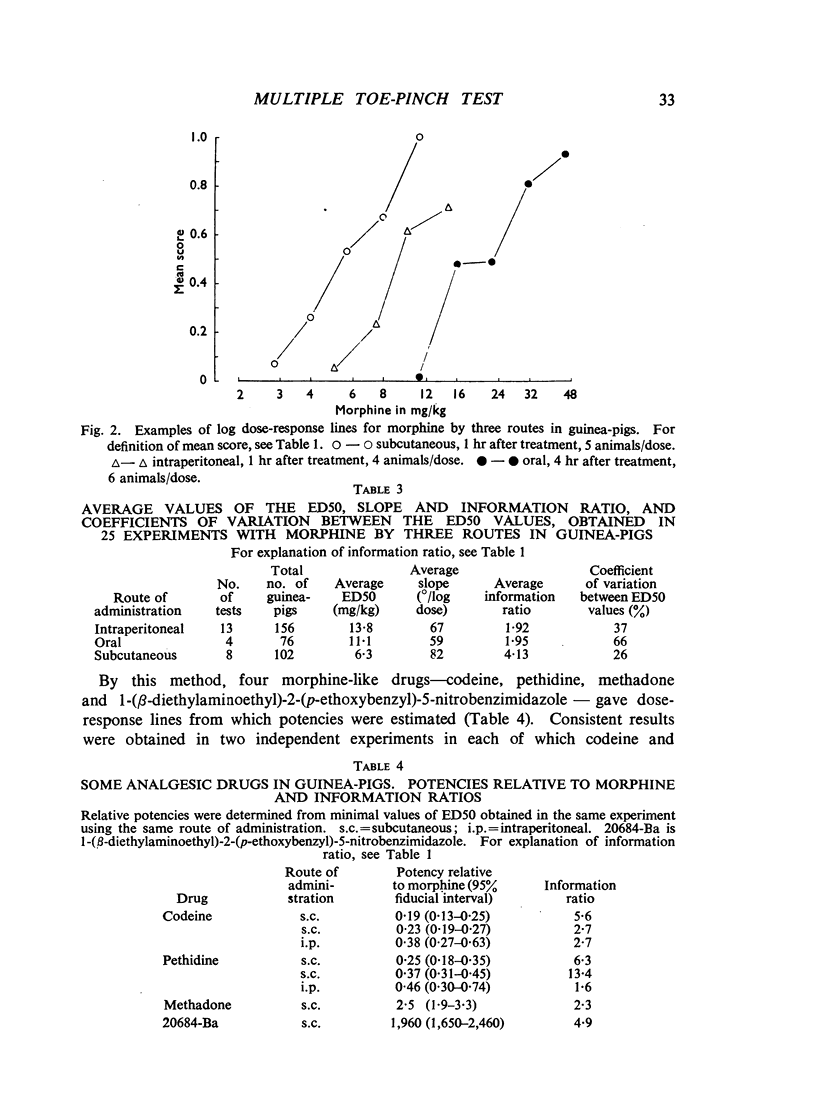
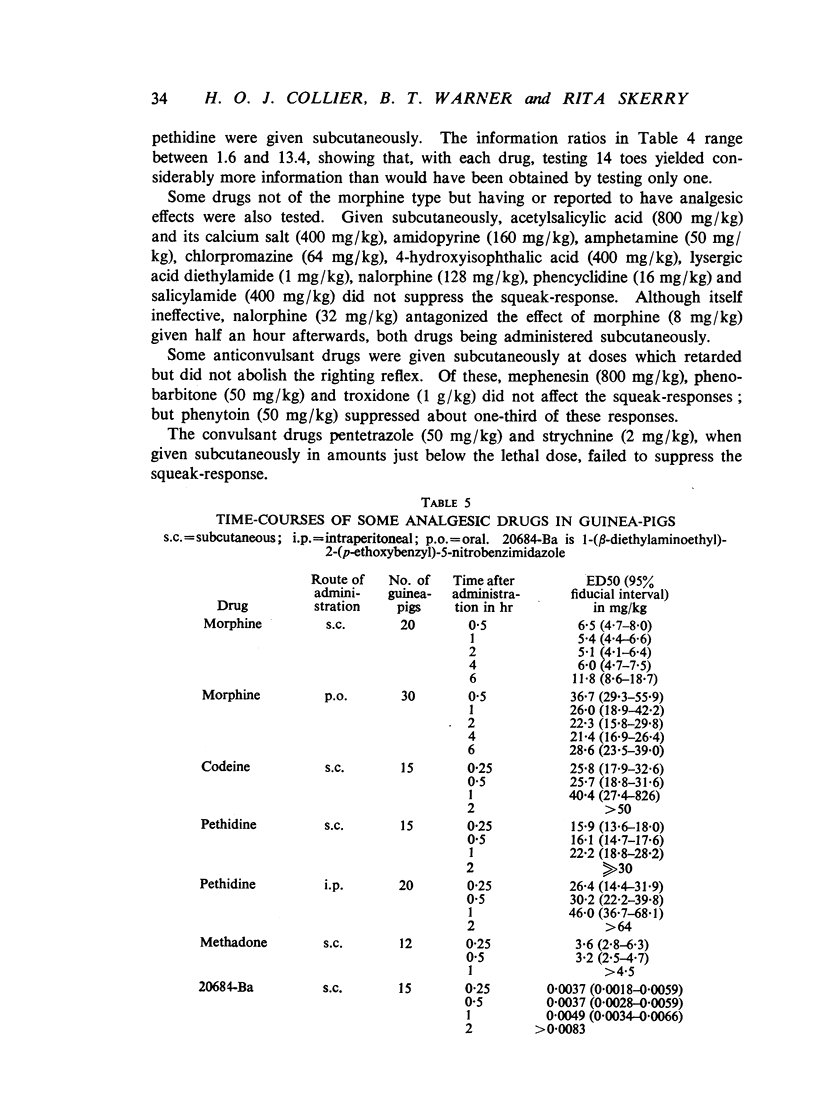
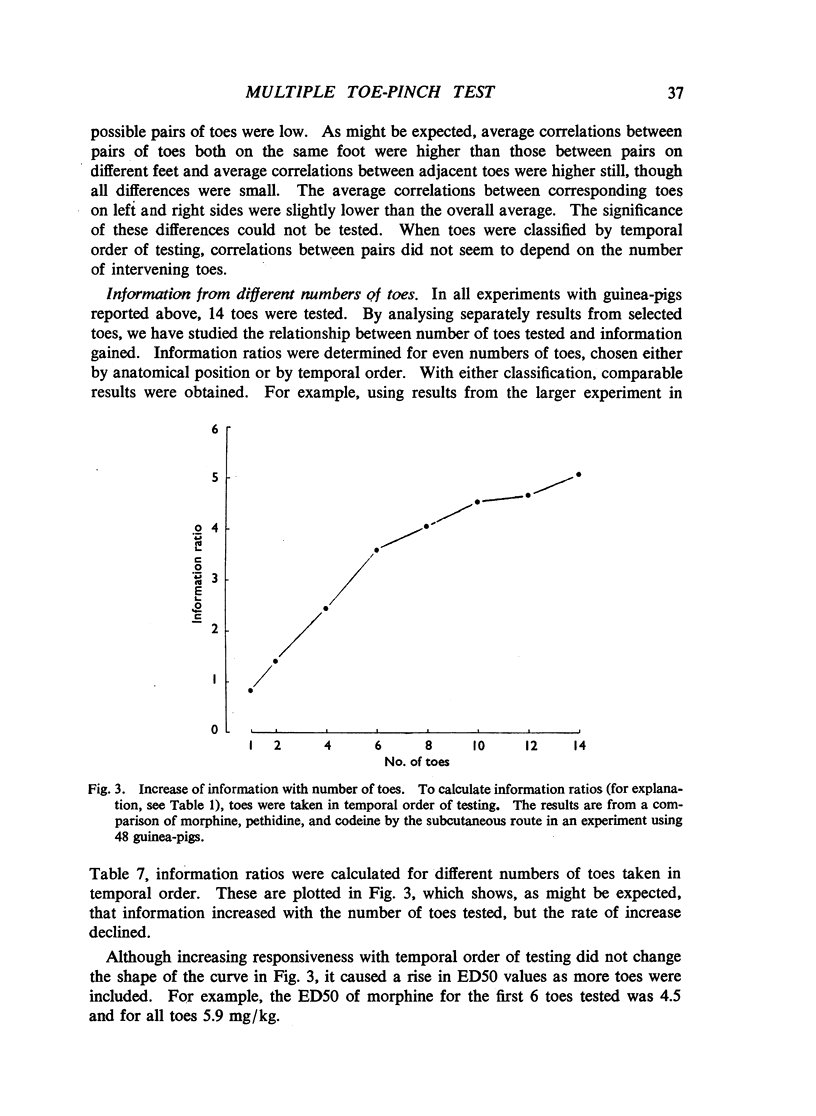
In guinea-pigs and rats, an immediate squeak was one of the most consistent and readily observed responses to application of a light artery clip to the base of a toe. Morphine and related drugs suppressed this response. Squeak-responses from each toe of an experimental animal formed the basis of a technique for measuring activity of analgesic drugs. A statistical method was developed to analyse the correlated quantal observations obtained. It provided an estimate of the increase of information from several toes compared with one. Testing all toes of each animal yielded a substantial increase of information, because the correlation between responses of different toes was low. Among drugs having an analgesic action in man, 1-(β-diethyl-aminoethyl)-2-(p-ethoxybenzyl)-5-nitrobenzimidazole, methadone, morphine, pethidine and codeine (in descending order of potency) were active in this test in guinea-pigs. Acetylsalicylic acid, amidopyrine, amphetamine, chlorpromazine, 4-hydroxyisophthalic acid, lysergic acid diethylamide, mephenesin, nalorphine, pentetrazole, phenobarbitone, phencyclidine, phenytoin, salicylamide, strychnine and troxidone showed little or no activity. The time-courses of active drugs were estimated, and morphine had the longest action.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIANCHI C., FRANCESCHINI J. Experimental observations on Haffner's method for testing analgesic drugs. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Sep;9(3):280–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN G. M., WESTON J. K. The analgesic and anesthetic effect of 1-(1-phenylcyclohexyl) piperidine HCl on the monkey. Anesth Analg. 1960 Mar-Apr;39:132–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDER C. V. Aspirin and algesimetry. Nature. 1959 Aug 15;184:494–497. doi: 10.1038/184494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]