Abstract
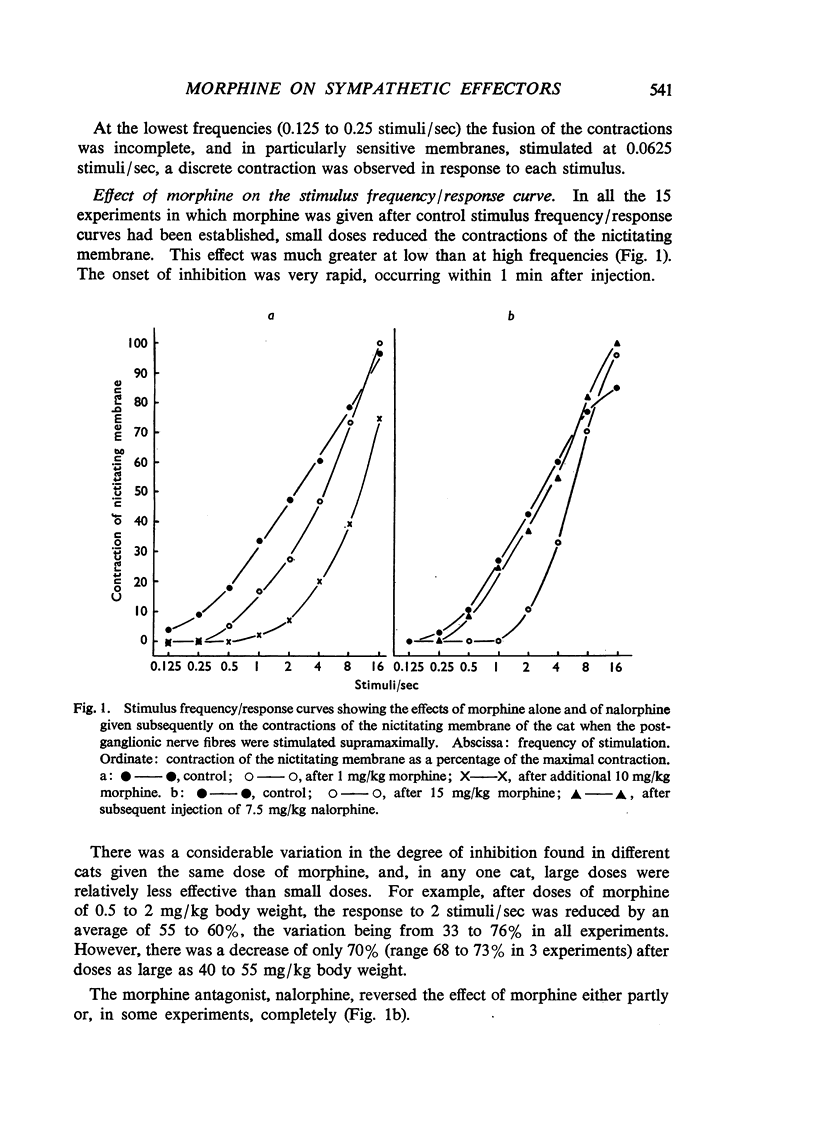
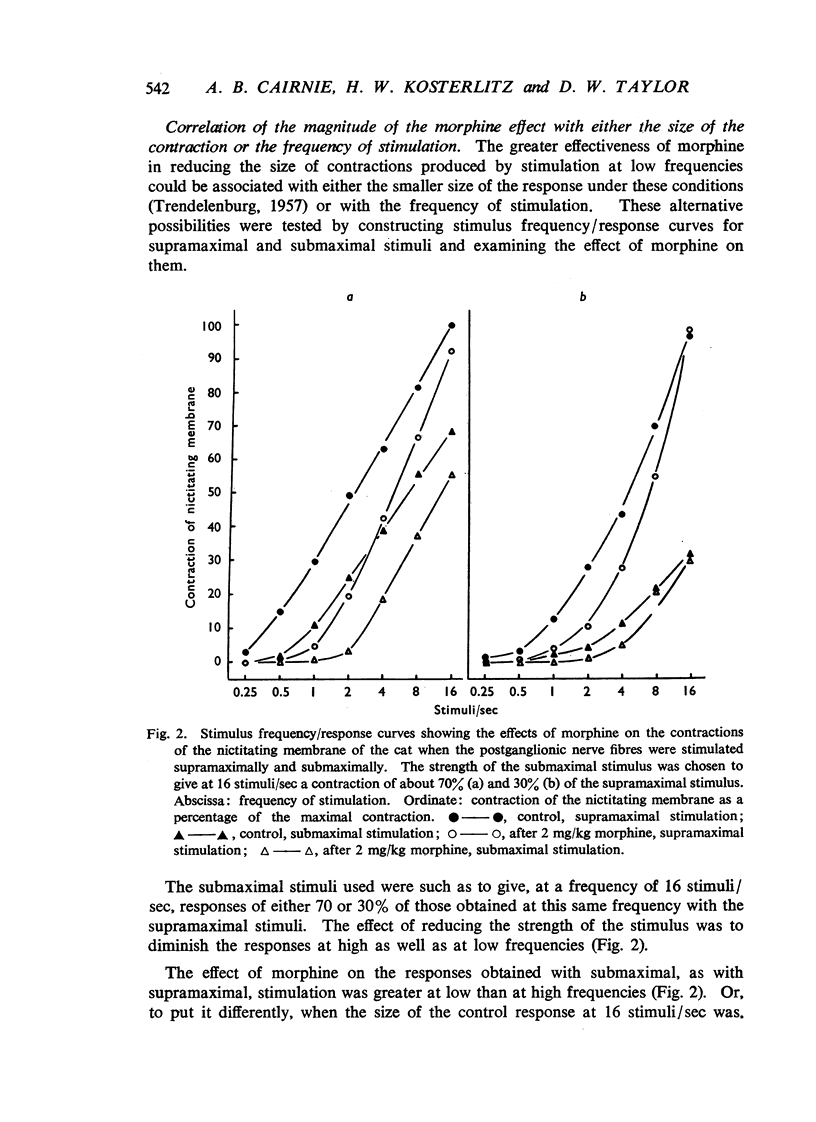
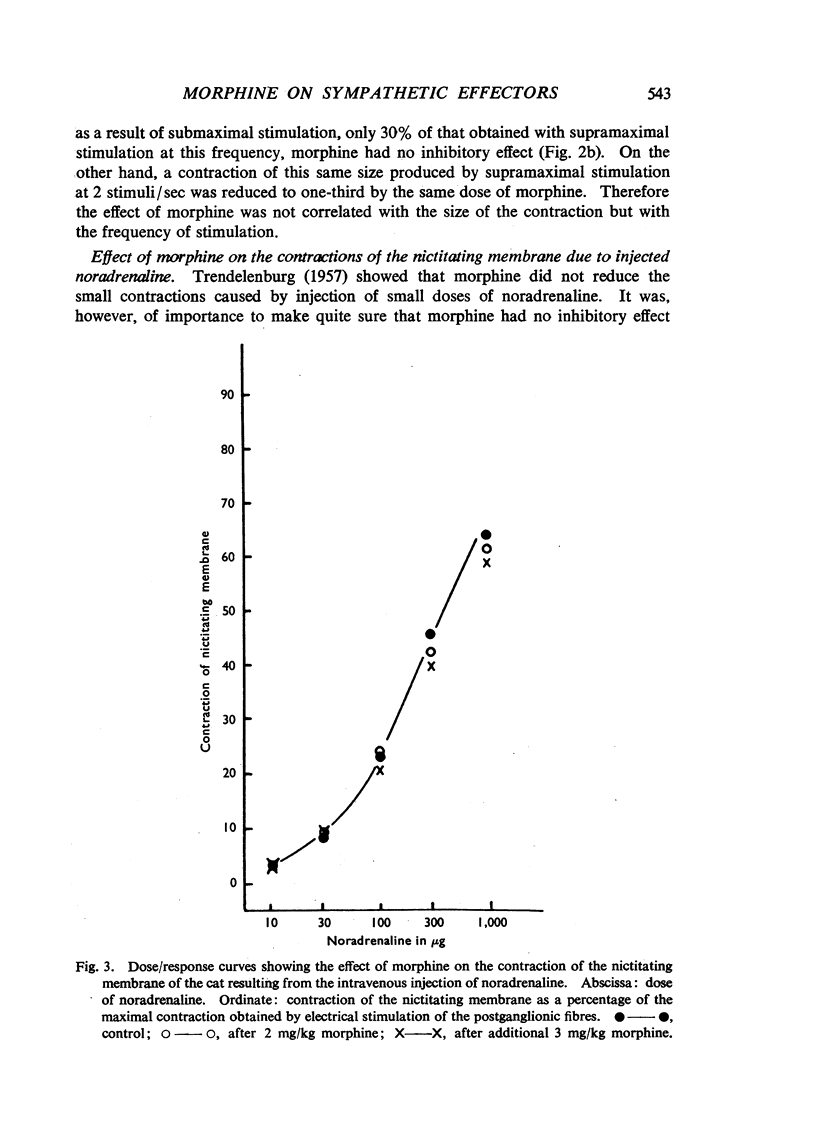
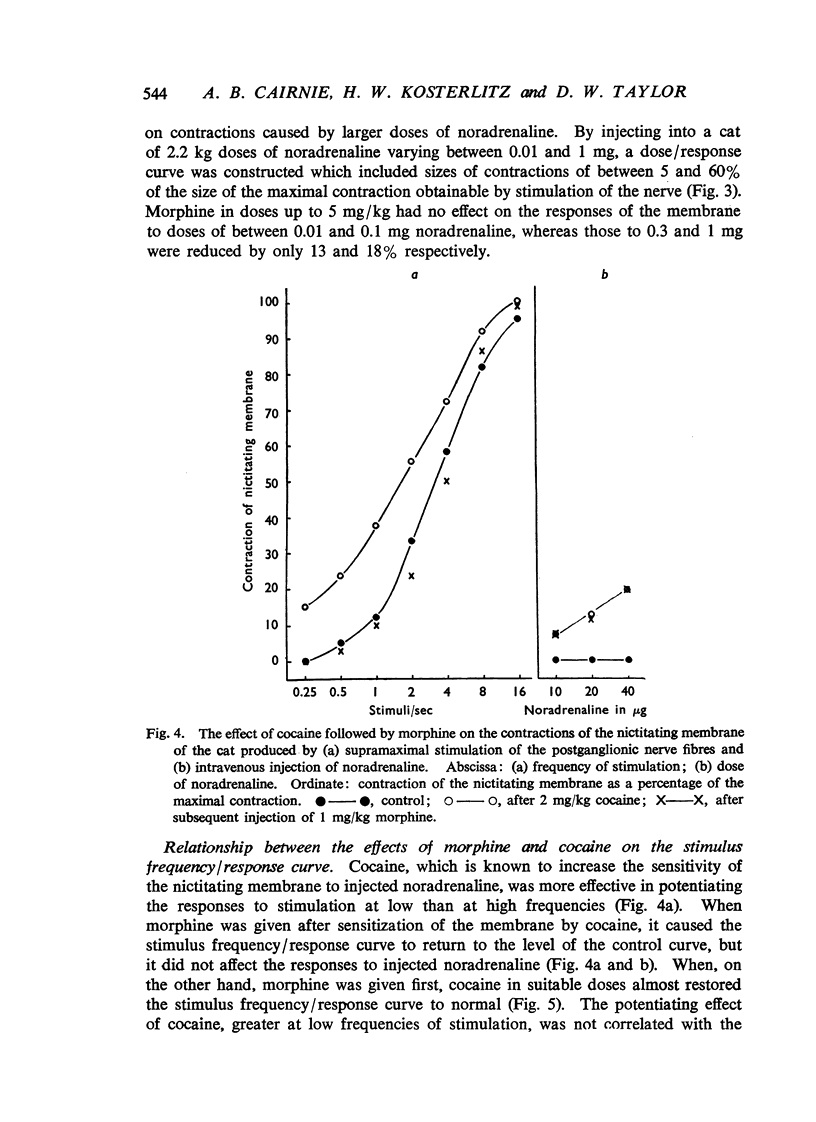
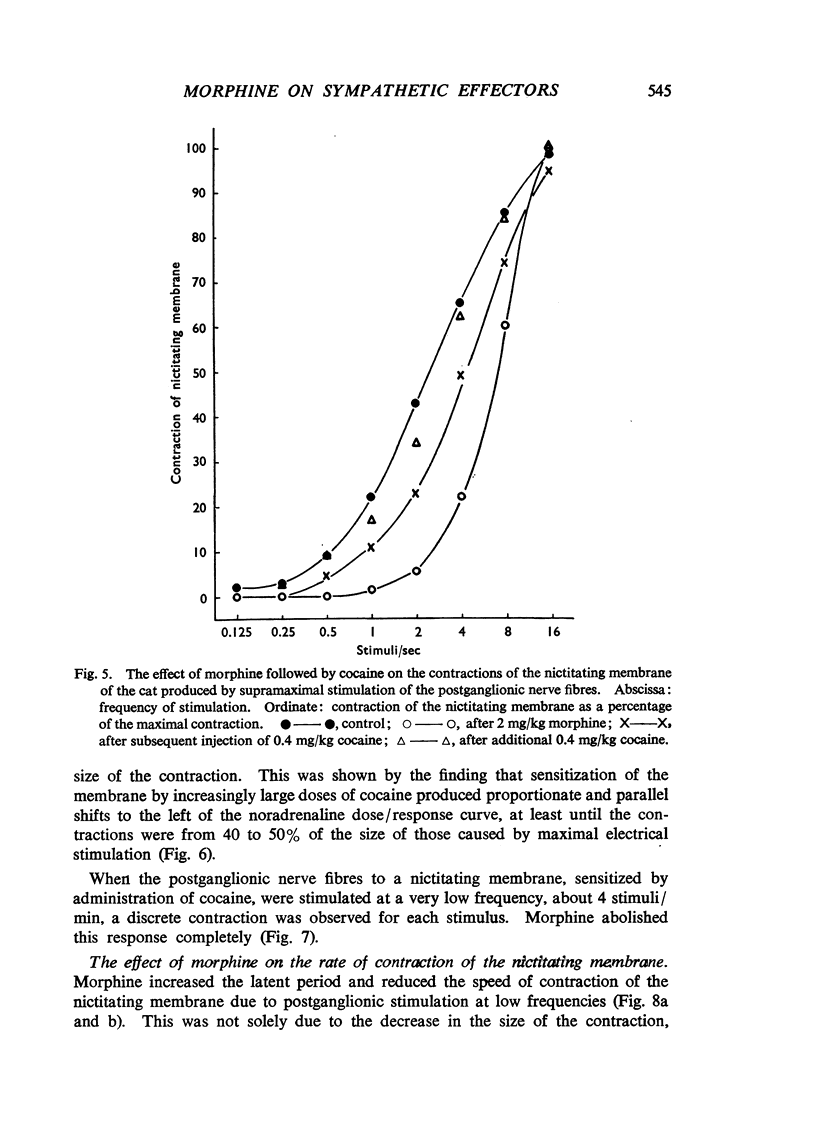
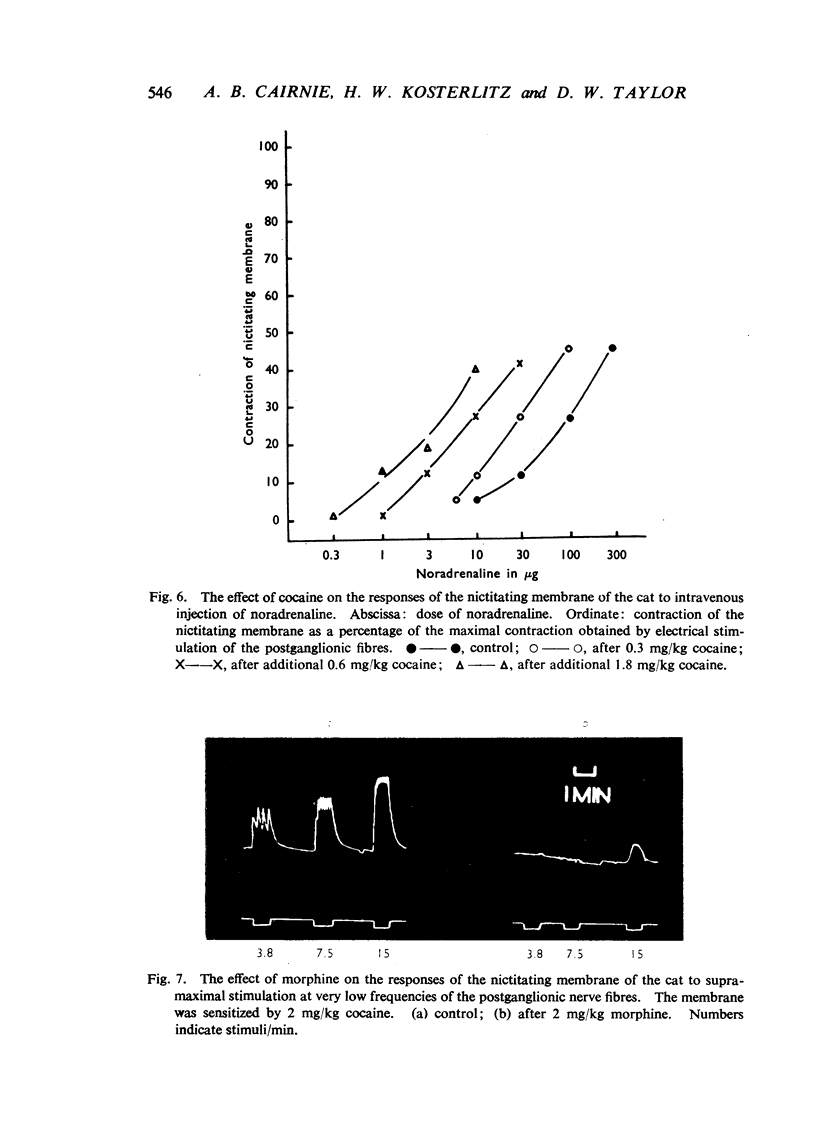
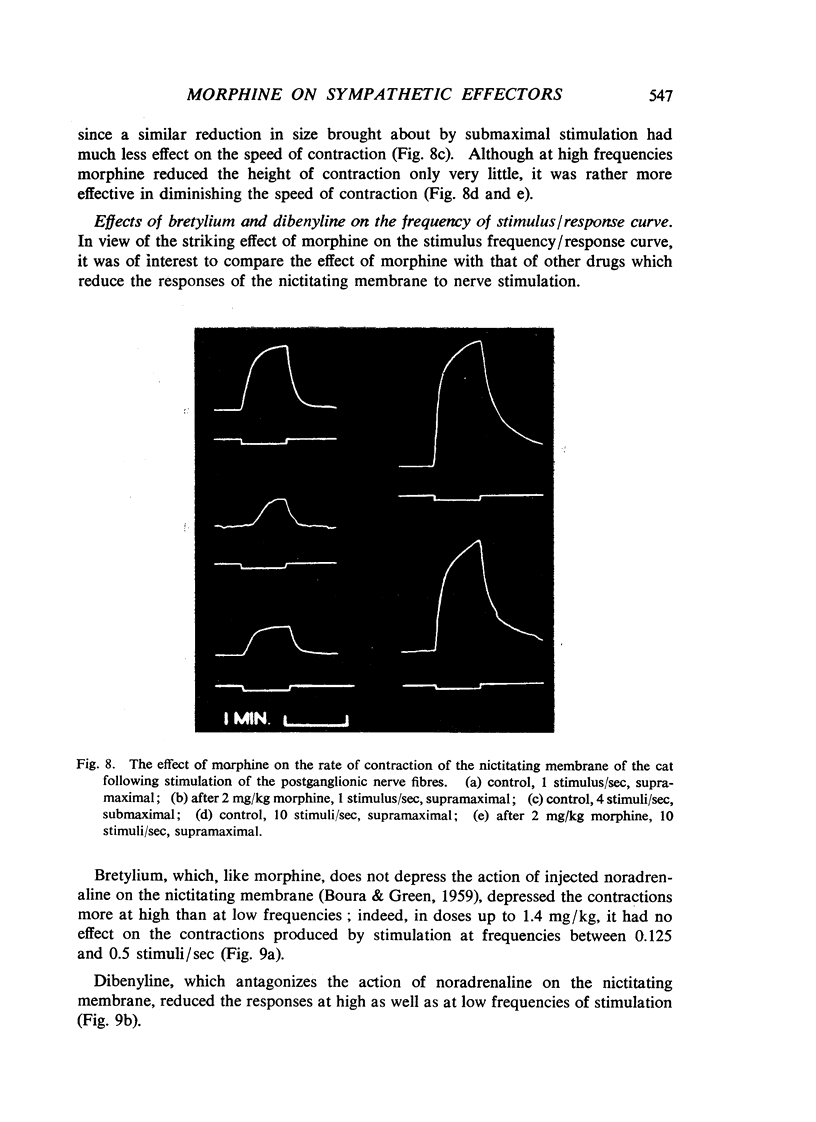
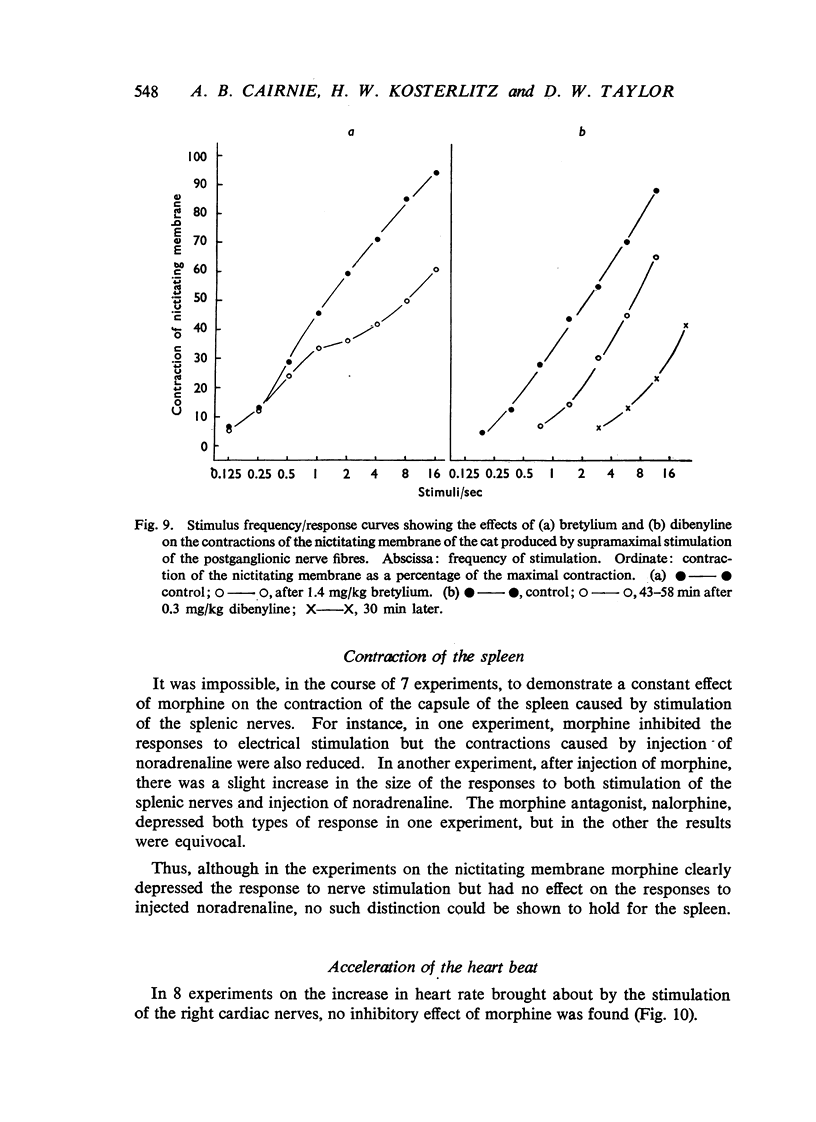
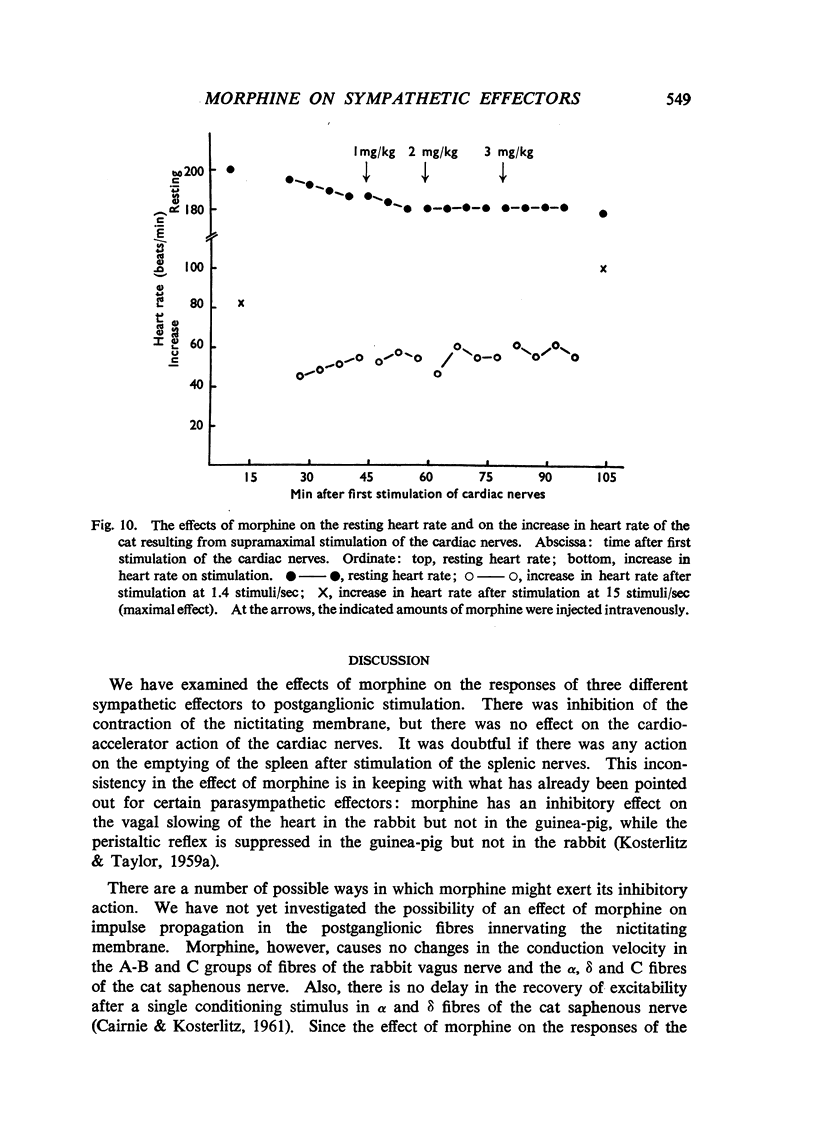
Morphine, in doses of 0.5 to 55 mg/kg, inhibited contraction of the nictitating membrane of the cat following stimulation of the postganglionic sympathetic nerve fibres. Morphine was more effective at low than at high frequencies of stimulation, independently of the size of contraction of the membrane; the speed of contraction was reduced at all frequencies. Cocaine potentiated the contraction of the nictitating membrane following nerve stimulation more at low than at high frequencies, and antagonized the action of morphine. These findings, and the absence of an effect of morphine on the action of injected noradrenaline, make it likely that morphine interferes with the release of noradrenaline from the postganglionic nerve endings in the nictitating membrane. Morphine had no effect on the cardioaccelerator action of the cardiac nerves and inconsistent results were obtained on the emptying of the spleen after stimulation of the splenic nerves.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMETT C. J., HUNSPERGER R. W. Excitation of receptors in the pad of the cat by single and double mechanical pulses. J Physiol. 1961 Sep;158:15–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURA A. L., GREEN A. F. The actions of bretylium: adrenergic neurone blocking and other effects. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Dec;14:536–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., KRAYER O., MATALLANA A. Studies on veratrum alkaloids, XXII. Periodic activity of the sino-auricular node of the denervated cat heart caused by veratramine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Apr;113(4):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., ROBINSON J. A. Inhibition of the peristaltic reflex of the isolated guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 30;136(2):249–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., ROBINSON J. A. Mechanism of the contraction of the longitudinal muscle of the isolated guinea-pig ileum, caused by raising the pressure in the lumen. J Physiol. 1955 Jul 28;129(1):18–9P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., TAYLOR D. W. The effect of morphine on vagal inhibition of the heart. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Jun;14(2):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb01385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAUMANN W. Influence of atropine and morphine on the liberation of acetylcholine from the guinea pig's intestine. Nature. 1956 Nov 17;178(4542):1121–1122. doi: 10.1038/1781121b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZERB J. C. The effect of morphine on the adrenergic nerves of the isolated guinea-pig jejunum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Feb;16:23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRENDELENBURG U. The action of morphine on the superior cervical ganglion and on the nictitating membrane of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


