Abstract
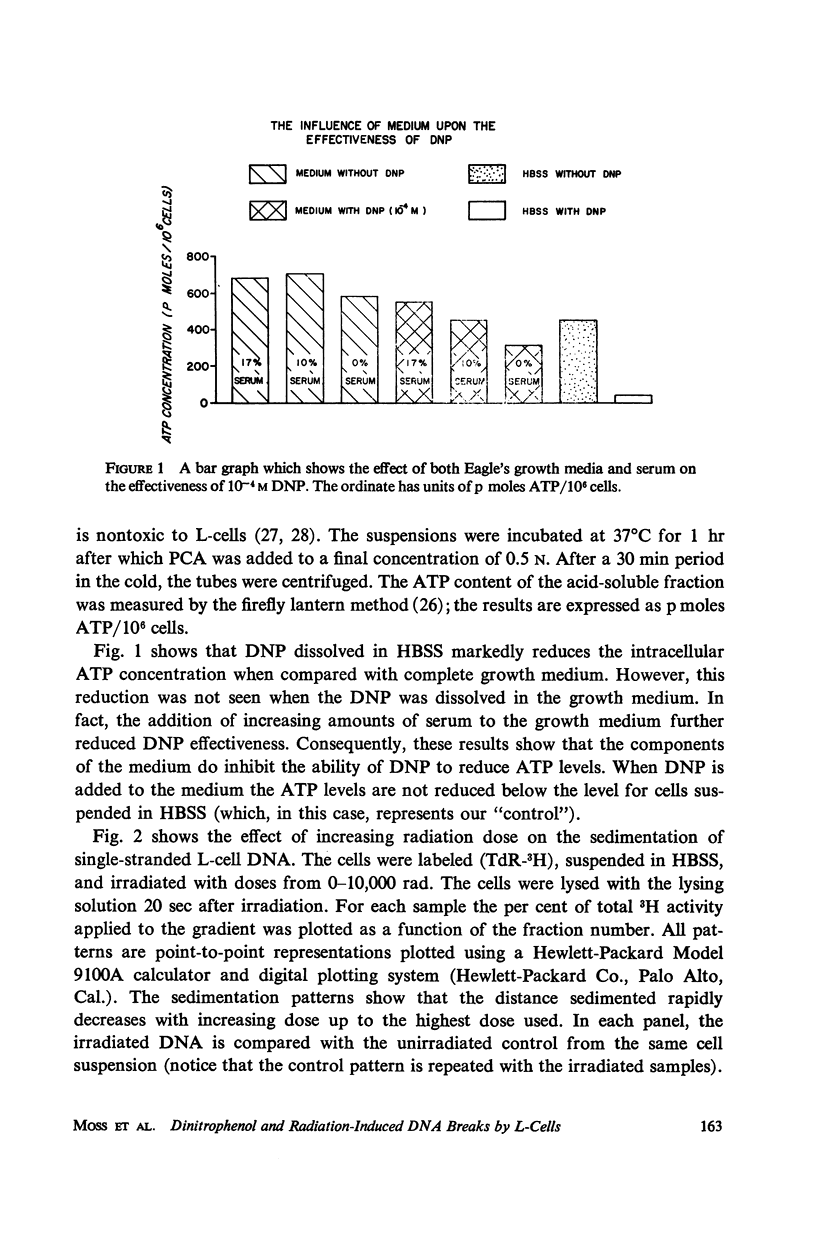
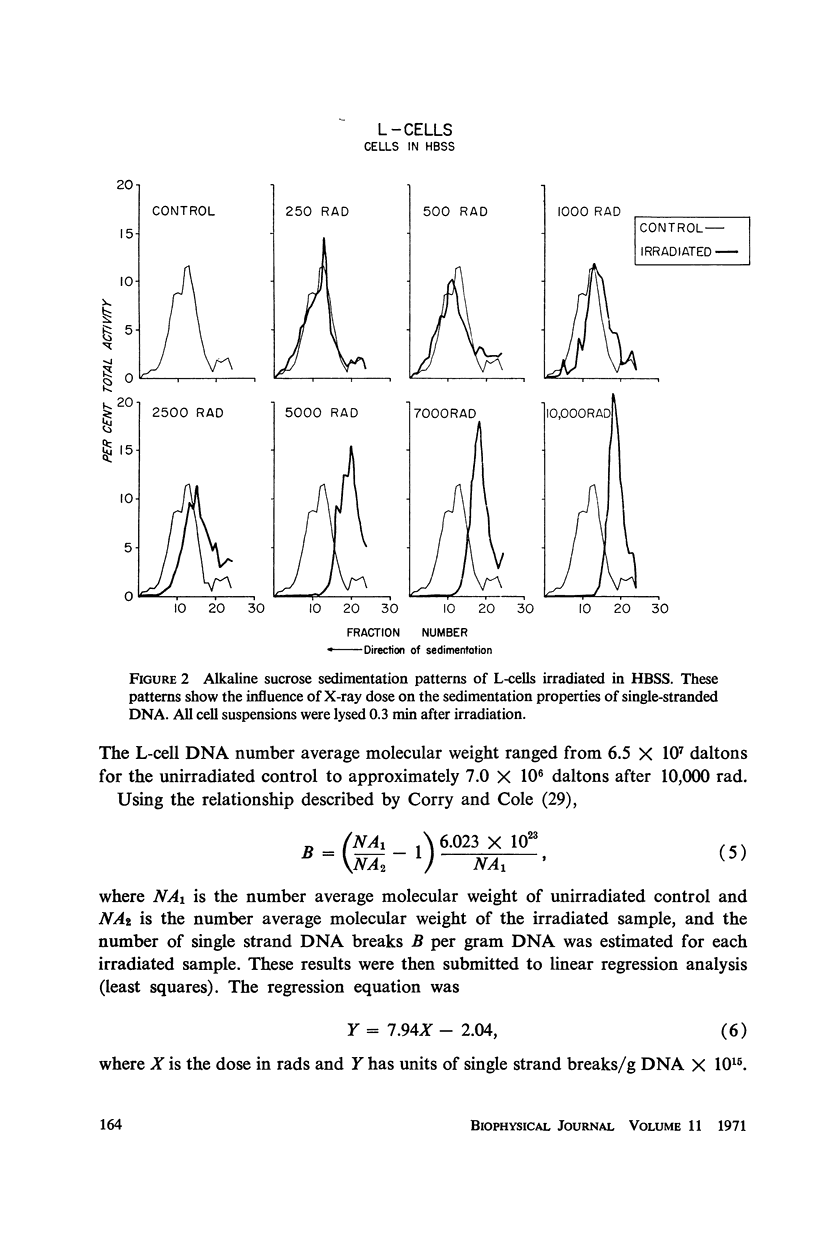
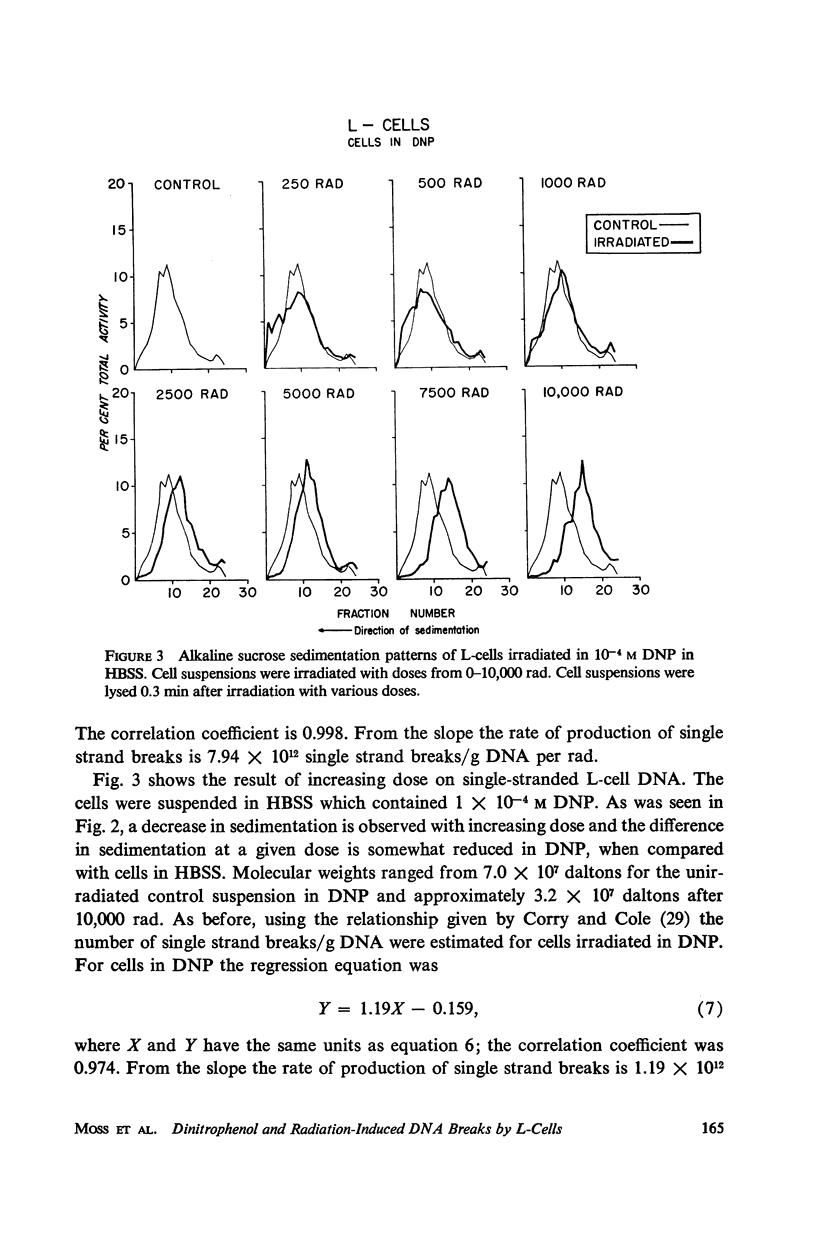
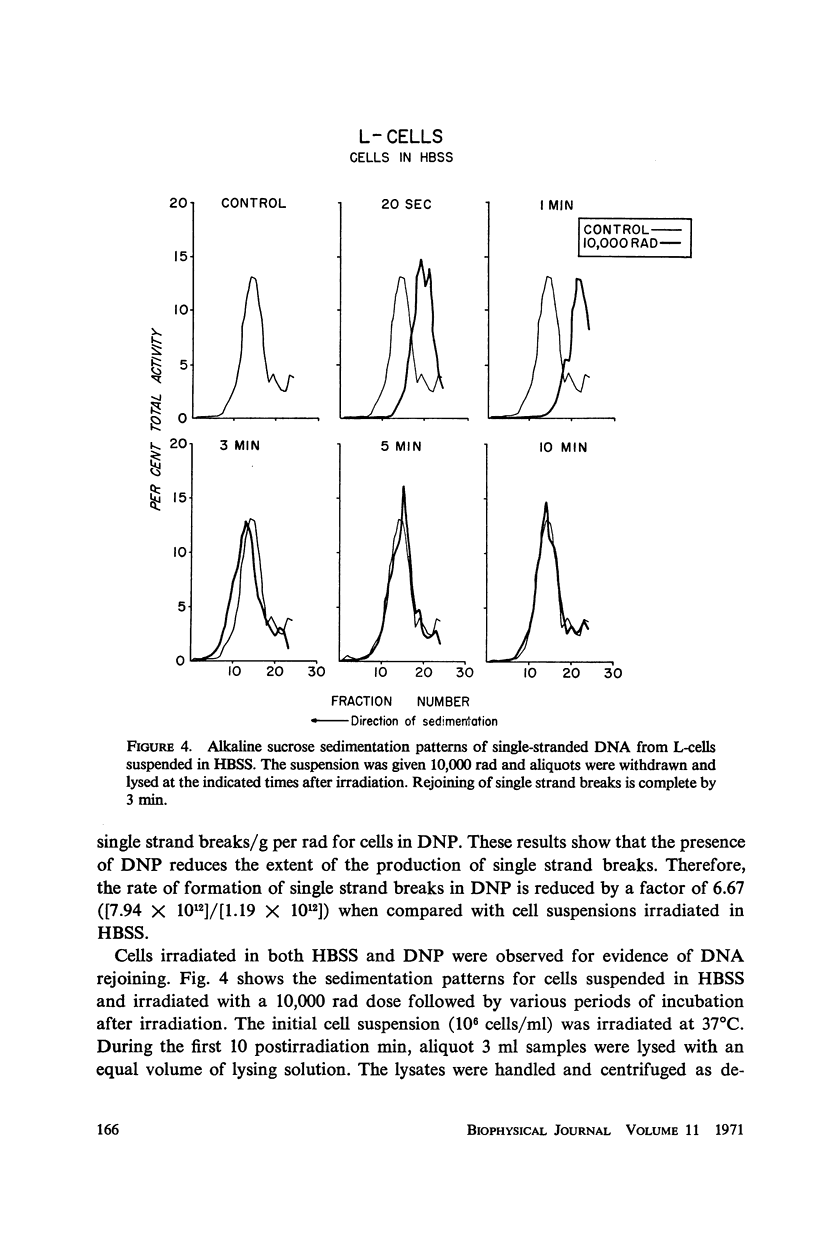
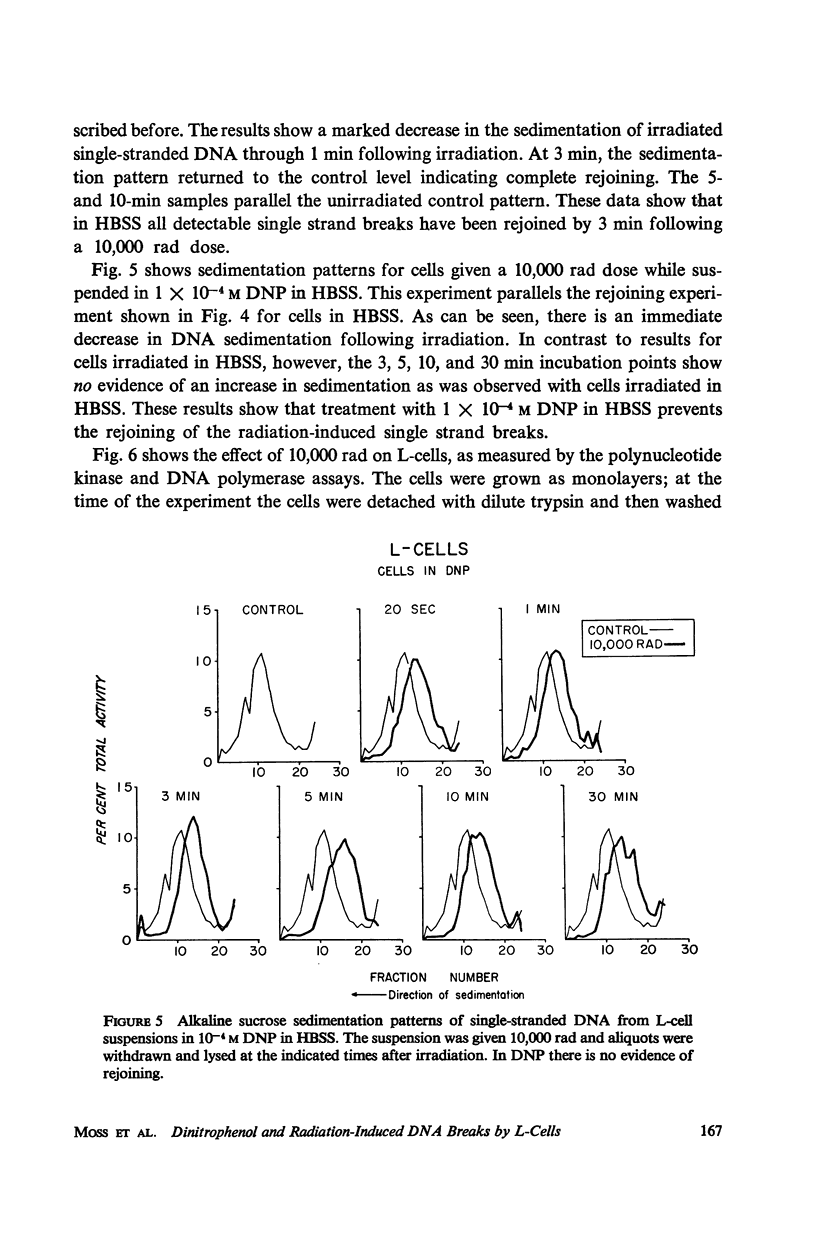
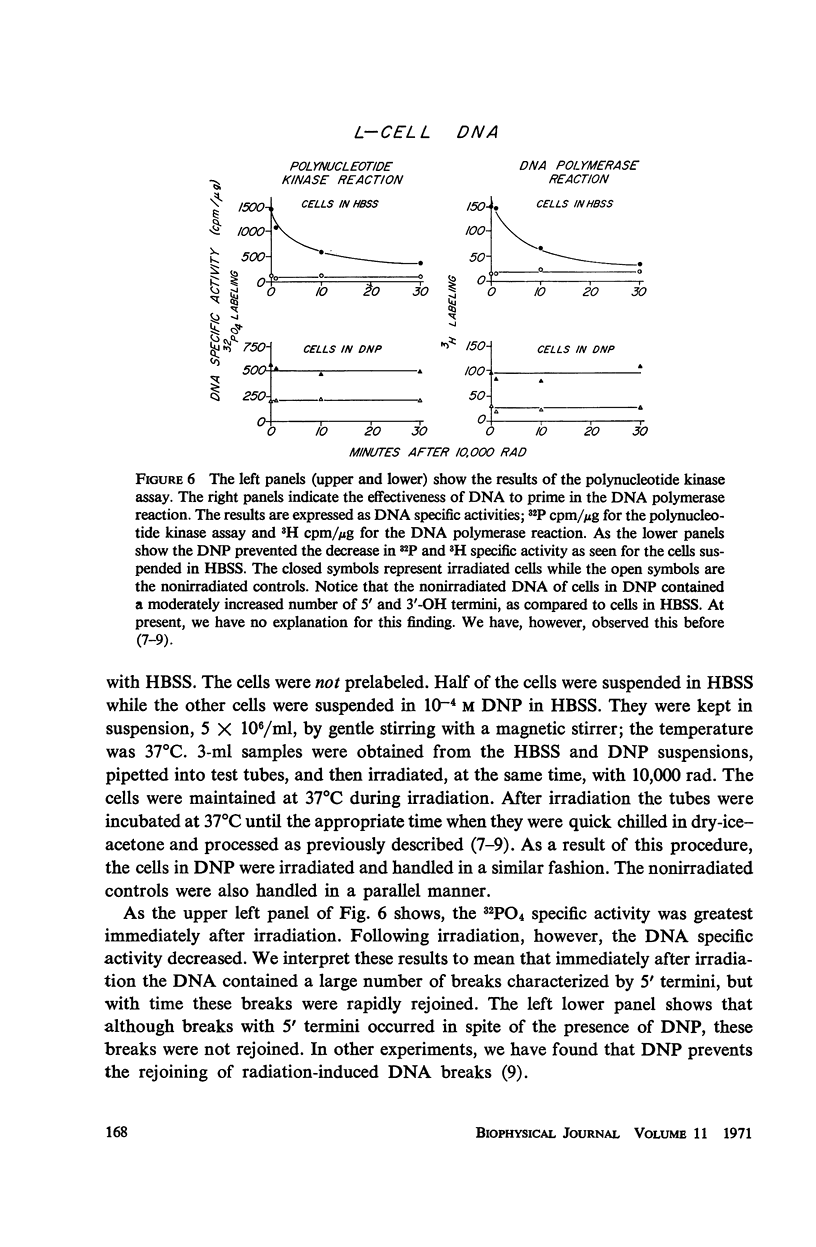
The production and rejoining of X-ray-induced single-stranded DNA breaks was studied using the alkaline sucrose density gradient technique and by measuring the disappearance of both 5′ termini and 3′-OH termini using polynucleotide kinase and DNA polymerase, respectively. All studies were conducted using L-cell suspensions irradiated both in the presence and absence of 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP), an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation. Results show that the induction of single-stranded DNA breaks probably includes a nucleolytic component in addition to indirect free radical effects. A greater number of breaks were produced in the absence of DNP, suggesting that depressed adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels reduce endogenous nucleolytic activity. The rejoining mechanism is enzymatic and requires an available ATP supply for operation. In the presence of DNP no DNA rejoining was observed following 30 min incubation after 10,000 rad. These results suggest that DNA breaks produced may be characterized by 5′-PO4-3′-OH termini and are rejoined by DNA ligase.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APOSHIAN H. V., KORNBERG A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. IX. The polymerase formed after T2 bacteriophage infection of Escherichia coli: a new enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:519–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achey P. M., Pollard E. C. Studies on the radiation-induced breakdown of deoxyribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli 15 T L. Radiat Res. 1967 May;31(1):47–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Addanki S., Sotos J. F., Rearick P. D. Rapid determination of picomole quantities of ATP with a liquid scintillation counter. Anal Biochem. 1966 Feb;14(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. Sedimentation rate as a measure of molecular weight of DNA. Biophys J. 1963 Jul;3:309–321. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86823-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry P. M., Cole A. Radiation-induced double-strand scission of the DNA of mammalian metaphase chromosomes. Radiat Res. 1968 Dec;36(3):528–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Baker M. L., Sanders J. L., Moss A. J., Jr, Nash J. C., Wilkinson K. P. Do mammalian cells repair radiation injury by the "cut-and-patch" mechanism? II. An extension of the original model. J Theor Biol. 1970 Jul;28(1):121–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(70)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Baker M. L. Dinitrophenol decreases the radiation sensitivity of L cells. Nature. 1967 Nov 18;216(5116):708–709. doi: 10.1038/216708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Baker M. L. Do cultured mammalian cells repair radiation injury by the "cut-and-patch" mechanism? J Theor Biol. 1968 Dec;21(3):368–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Baker M. L., Wilkinson K. P. The effect of 2,4-dinitrophenol on the repair of radiation injury by L cells. Radiat Res. 1969 Jan;37(1):90–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Baker M. L., Wilknson K. P., Walls R. A. The relation of DNA degradation to the repair of radiation injury by L cells. Radiat Res. 1969 Oct;40(1):112–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Moss A. J., Jr, Baker M. L., Wilkinson K. P. Energy dependent nucleolytic processes are responsible for the production of many post-irradiation breaks in L cell DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 23;36(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Moss A. J., Jr, Baker M. L., Wilkinson K. P. Radiation produces breaks in L cell and mouse liver DNA characterized by 5' phosphoryl termini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):300–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple G. V., Sanders J. L., Moss A. J., Jr, Wilkinson K. P. Radiation induced breaks increase the priming activity of rat sarcoma DNA in the DNA polymerase reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 11;39(3):538–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90611-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton E. W., Billen D. X-ray-induced degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid in a polyauxotrophic bacterium. Radiat Res. 1966 May;28(1):109–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes R. H. The interpretation of microbial inactivation and recovery phenomena. Radiat Res. 1966;(Suppl):1–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey R. M., Steward D. L., Sedita B. A. DNA-strand breaks and rejoining following exposure of synchronized Chinese hamster cells to ionizing radiations. Mutat Res. 1968 Nov-Dec;6(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. DNA-strand scission and loss of viability after x irradiation of normal and sensitized bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp D. S., Smith K. C. Chemical nature of chain breaks produced in DNA by x-irradiation in vitro. Radiat Res. 1970 Apr;42(1):34–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp D. S., Smith K. C. Lack of in vitro repair of x-ray-induced chain breaks in DNA by the polynucleotide-joining enzyme. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1969 Jan 17;14(6):567–571. doi: 10.1080/09553006914551741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Cozzarelli N. R., Deutscher M. P., Lehman I. R., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXXII. Replication of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid by polymerase at a single strand break. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett J. T., Caldwell I., Dean C. J., Alexander P. Rejoining of x-ray induced breaks in the DNA of leukaemia cells. Nature. 1967 May 20;214(5090):790–792. doi: 10.1038/214790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Edelman G. M. Polynucleotide ligase from myeloid and lymphoid tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):680–687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. B. Radiation-induced DNA degradation in human cells: lack of evidence following moderate doses of x-rays. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1968;13(6):591–595. doi: 10.1080/09553006814550671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman P. H. Induction and rejoining of breaks in the deoxyribonucleic acid of human cells irradiated at various phases of the cell cycle. Mutat Res. 1968 Nov-Dec;6(3):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(68)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath R. A., Williams R. W. Reconstruction in vivo of irradiated Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid; the rejoining of broken pieces. Nature. 1966 Oct 29;212(5061):534–535. doi: 10.1038/212534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath R. A., Williams R. W., Swartzendruber D. C. Breakdown of DNA in x-irradiated Escherichia coli. Biophys J. 1966 Jan;6(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86643-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll H. Characterization of macromolecules by constant velocity sedimentation. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):360–363. doi: 10.1038/215360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi M. An ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease from Escherichia coli with a possible role in genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1292–1299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Lehman I. R. Linkage of polynucleotides through phosphodiester bonds by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1426–1433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. C. Phosphorylation of nucleic acid by an enzyme from T4 bacteriophage-infected Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):158–165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. C. The 5'-terminal nucleotides of T7 bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Okada S. Rejoining of single-strand breaks of DNA in cultured mammalian cells. Radiat Res. 1970 Jan;41(1):145–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski W. Molecular events resulting in radiation injury, repair and sensitization of DNA. Radiat Res Suppl. 1967;7:147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid, I. Repair of single-strand breaks in DNA by an enzyme system from Escherichia coli infected with T4 bacteriophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Thompson A., Richardson C. C. Ezymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. VII. Properties of the enzyme-adenylate intermediate in the polynucleotide ligase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4556–4563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


