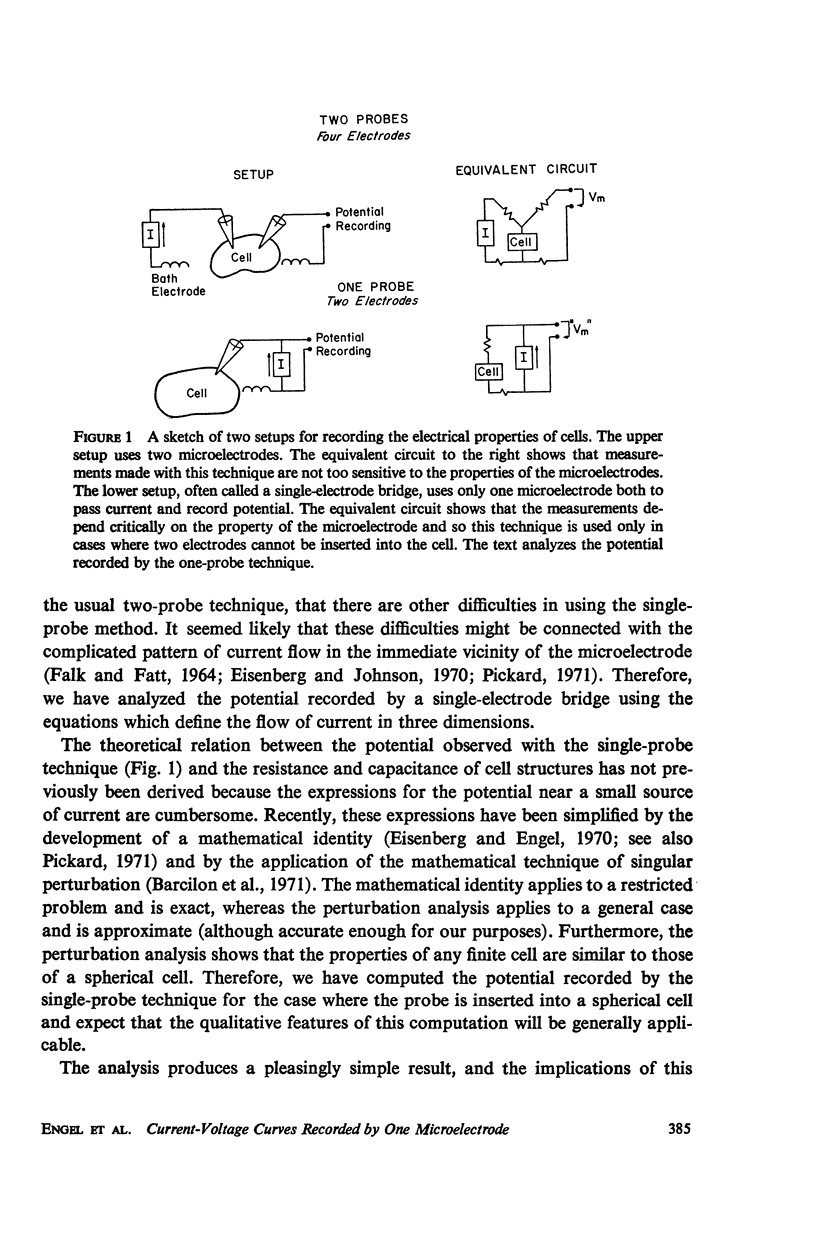
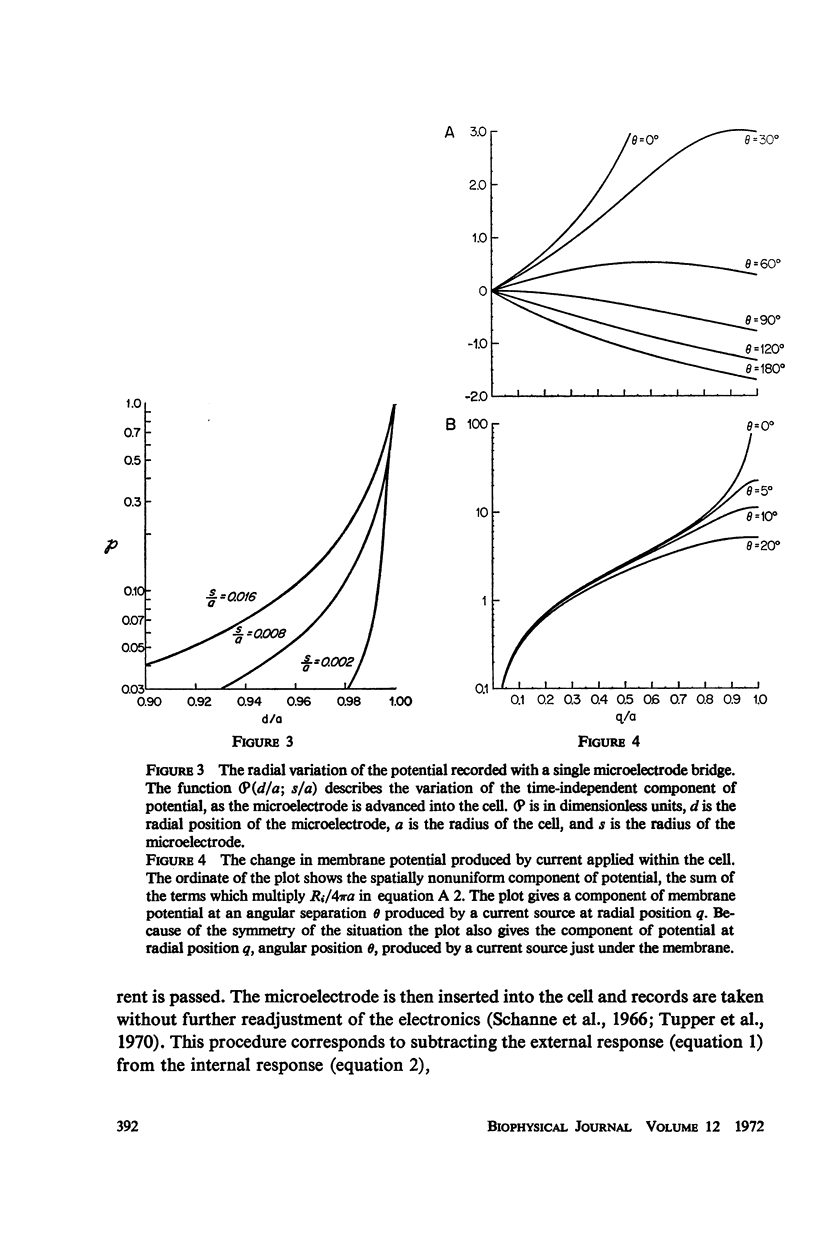
Abstract
An analysis is presented of the displacement of potential recorded when one microelectrode is used both to apply current to and record potential from a spherical cell. There are three significant components of the displacement in potential: a component produced inside the microelectrode, a time-independent component representing the spatially nonuniform flow of current in the immediate vicinity of the microelectrode, and a time-dependent spatially uniform component representing the average potential across the cell membrane. The second component describes changes in the potential across the cell membrane as well as potential drops in the interior of the cell, the importance of each factor being dependent on the location of the electrode. Simple expressions, derived by a theoretical treatment, are given for each component of potential. The implications for the interpretation of experimental results determined with the “single-electrode bridge” technique are discussed and an optimal balancing procedure is suggested.
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., OTANI T. Response of single motoneurons to direct stimulation in toad's spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1955 Sep;18(5):472–485. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Costantin L. L., Peachey L. D. Radial spread of contraction in frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):231–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Engel E. The spatial variation of membrane potential near a small source of current in a spherical cell. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):736–757. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK G., FATT P. LINEAR ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF STRIATED MUSCLE FIBRES OBSERVED WITH INTRACELLULAR ELECTRODES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Apr 14;160:69–123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. A., TILLE J. Changes in polarisation resistance during the repolarisation phase of the rabbit ventricular action potential. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Dec;38:509–513. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. A., TILLE J. Investigations of the electrical properties of cardiac muscle fibres with the aid of intracellular double-barrelled electrodes. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Jan;44:443–467. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., PILAR G. DUAL MODE OF SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION IN THE AVIAN CILIARY GANGLION. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:443–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Distributions of potential in cylindrical coordinates and time constants for a membrane cylinder. Biophys J. 1969 Dec;9(12):1509–1541. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86468-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanne O., Kawata H., Schäfer B., Lavallée M. A study on the electrical resistance of the frog sartorius muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):897–912. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper J., Saunders J. W., Jr, Edwards C. The onset of electrical communication between cells in the developing starfish embryo. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):187–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


