Abstract
The several widely different values of the elastic modulus of the human red blood cell membrane which have been reported in the literature are incorporated into a single strain energy function consisting of two terms. One term gives the small stresses and low elastic modulus which is observed when the red cell membrane is deformed at constant area. The second term contributes a large isotropic stress dependent on the change of area. The strain energy function is applied to the process of sphering of red blood cells in a hypotonic solution. It is shown that a nearly perfect sphere can result even though the red blood cell membrane is homogeneous in all areas of the cell. Results pertinent to sieving and micropipette experiments are also explored.
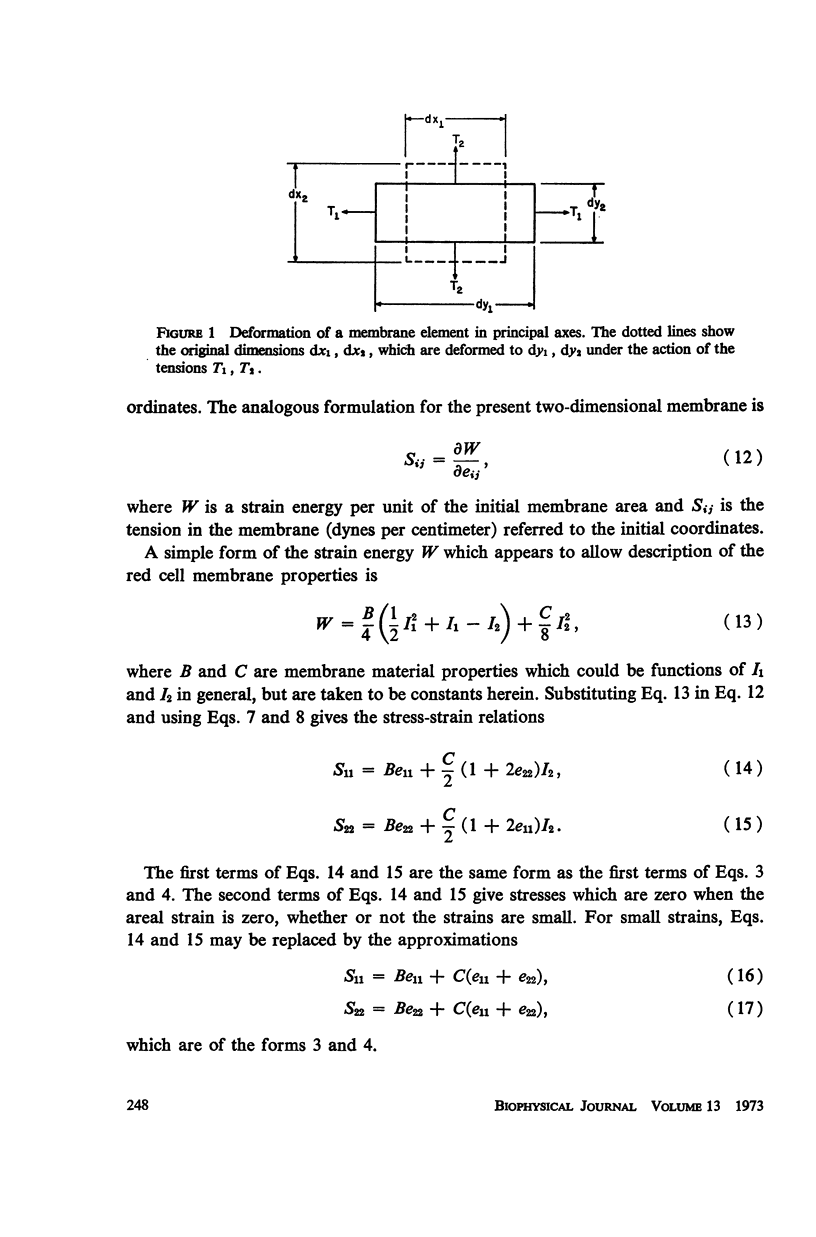
Full text
PDF


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOS T., DOURMASHKIN R. R., HUMPHREY J. H. LESIONS IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES CAUSED BY IMMUNE HAEMOLYSIS. Nature. 1964 Apr 18;202:251–252. doi: 10.1038/202251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D. Fracture faces of frozen membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1048–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canham P. B., Parkinson D. R. The area and volume of single human erythrocytes during gradual osmotic swelling to hemolysis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;48(6):369–376. doi: 10.1139/y70-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Luse S. A., Bryant C. A. Hemolysis during filtration through micropores: a scanning electron microscopic and hemorheologic correlation. Microvasc Res. 1971 Apr;3(2):183–203. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(71)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. C. Theoretical considerations of the elasticity of red cells and small blood vessels. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1761–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. C., Tong P. Theory of the sphering of red blood cells. Biophys J. 1968 Feb;8(2):175–198. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86484-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen M. I., Bryant C. A., Hammerle W. E., Usami S., Chien S. Flow Characteristics of Human Erythrocytes through Polycarbonate Sieves. Science. 1967 Aug 18;157(3790):825–827. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3790.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLIER J., HOFFMAN J. F. On the ultrastructure of the plasma membrane as determined by the electron microscope. J Cell Physiol. 1953 Oct;42(2):203–247. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030420205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm M., Ostling S. G., Persson A. E. The loss of certain cellular components from human erythrocytes during hypotonic hemolysis in the presence of dextran. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 May;67(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Mohandas N. Uniaxial loading of the red-cell membrane. J Biomech. 1972 Sep;5(5):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(72)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND R. P., BURTON A. C. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE RED CELL MEMBRANE. I. MEMBRANE STIFFNESS AND INTRACELLULAR PRESSURE. Biophys J. 1964 Mar;4:115–135. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86773-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND R. P. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE RED CELL MEMBRANE. II. VISCOELASTIC BREAKDOWN OF THE MEMBRANE. Biophys J. 1964 Jul;4:303–316. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86784-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutera S. P., Seshadri V., Croce P. A., Hochmuth R. M. Capillary blood flow. II. Deformable model cells in tube flow. Microvasc Res. 1970 Oct;2(4):420–433. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(70)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


