Abstract
Over a wide range of water contents, aqueous lecithin-water mixtures are mesophases in which lecithin bilayers alternate with water layers. This paper reports on low-angle X-ray diffraction measurements of the effects of electrolytes, at 1.0 N concentration, on the thicknesses of the bilayers in mesophases formed by the synthetic lecithin: 1-octadec-9-enyl-2-hexadecylglycerophosphocholine. With solutions of LiCl, NaCl, Na2SO4, KCl, and CsCl, the bilayer thicknesses are less than with pure water. The maximum reduction in bilayer thickness with these electrolytes is about 10% and occurs with mesophases of high content of KCl and CsCl solutions. With HCl solutions the bilayer thicknesses are about 5% greater than with pure water, and with CaCl2 solutions the bilayer thicknesses are about the same as with pure water. The maximum amount of solution which can be mixed with lecithin before a second, purely aqueous phase is formed is also affected by electrolytes, the order for the various 1.0 N solutions being CsCl = KCl > NaCl > Na2SO4 > (pure water) = LiCl > CaCl2.
Full text
PDF





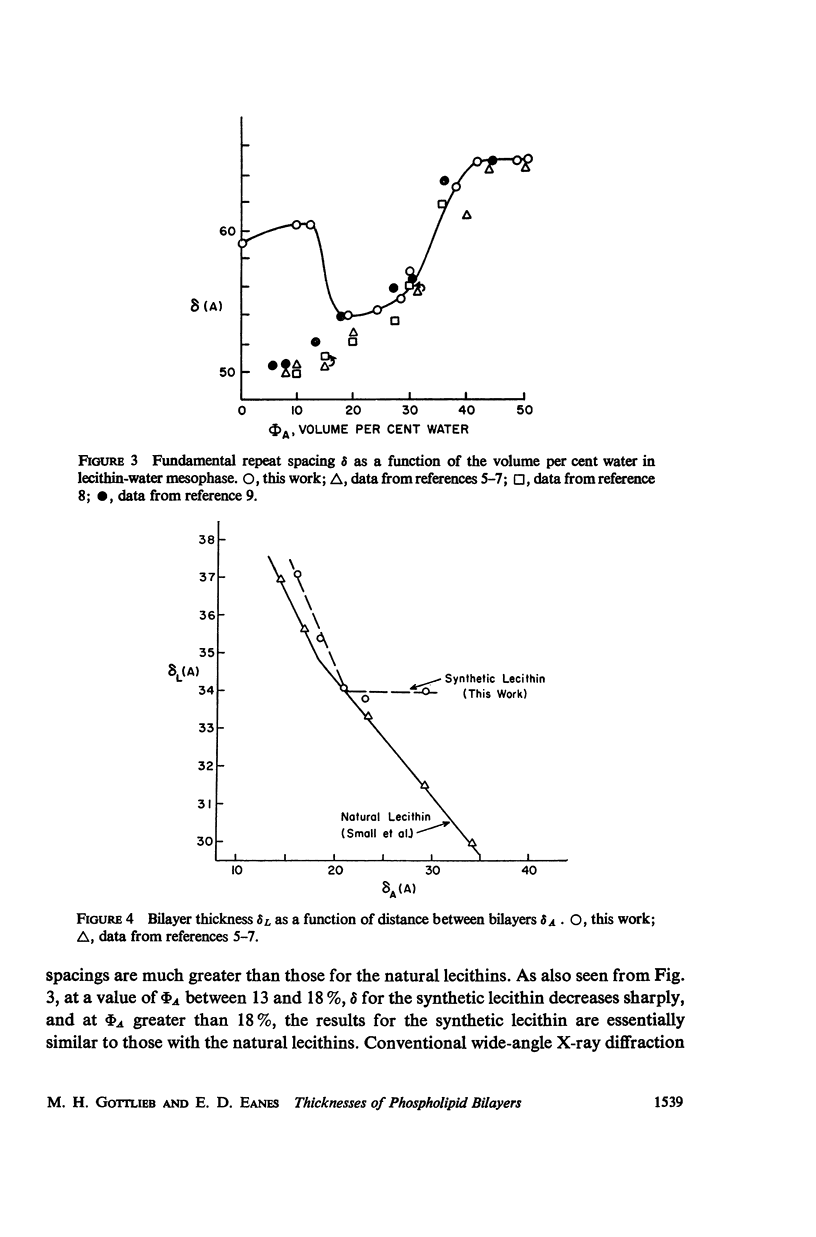
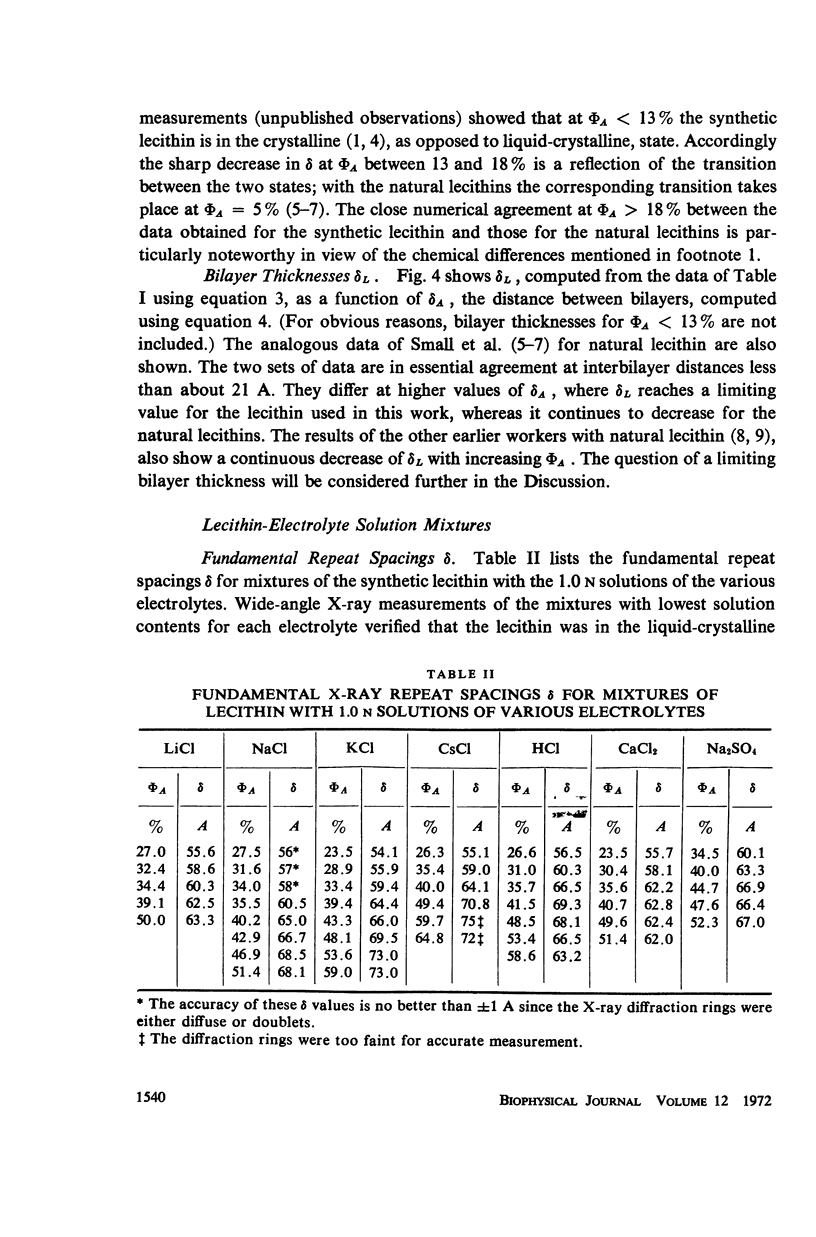
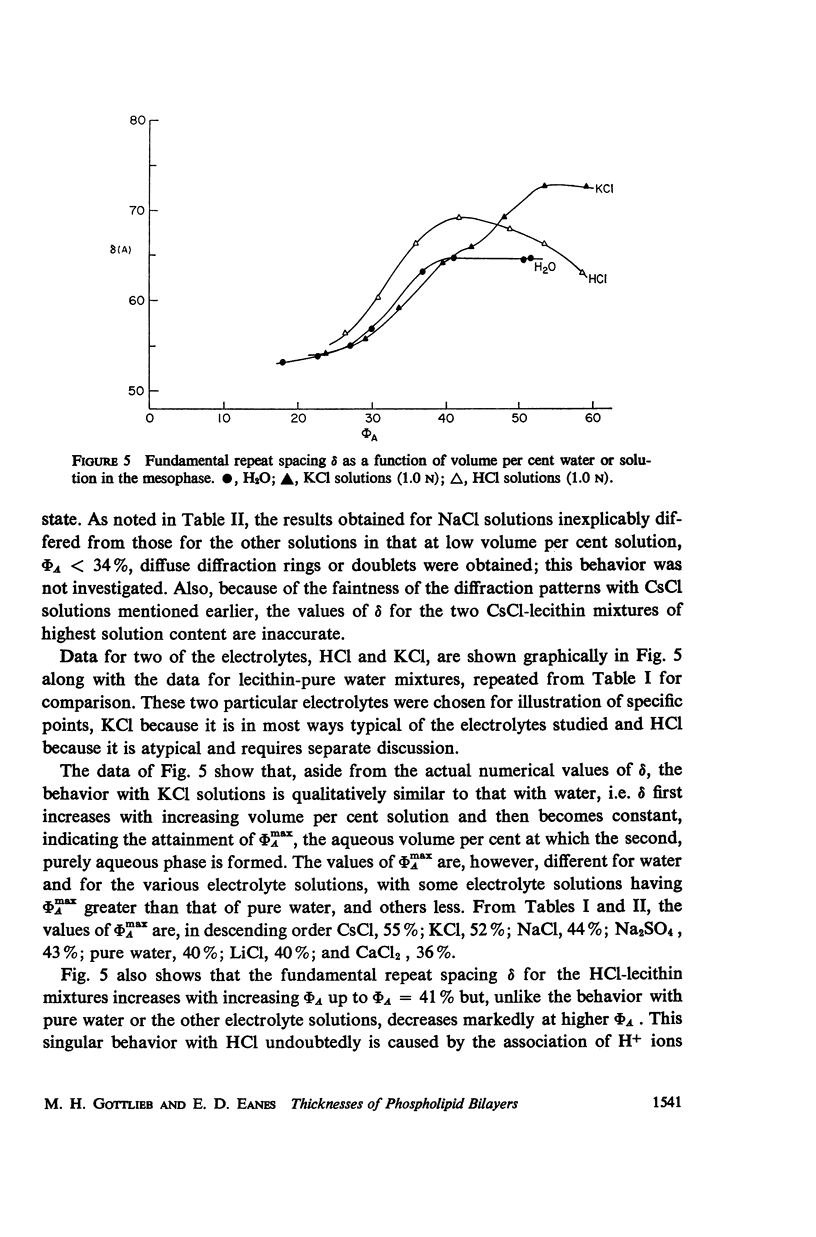
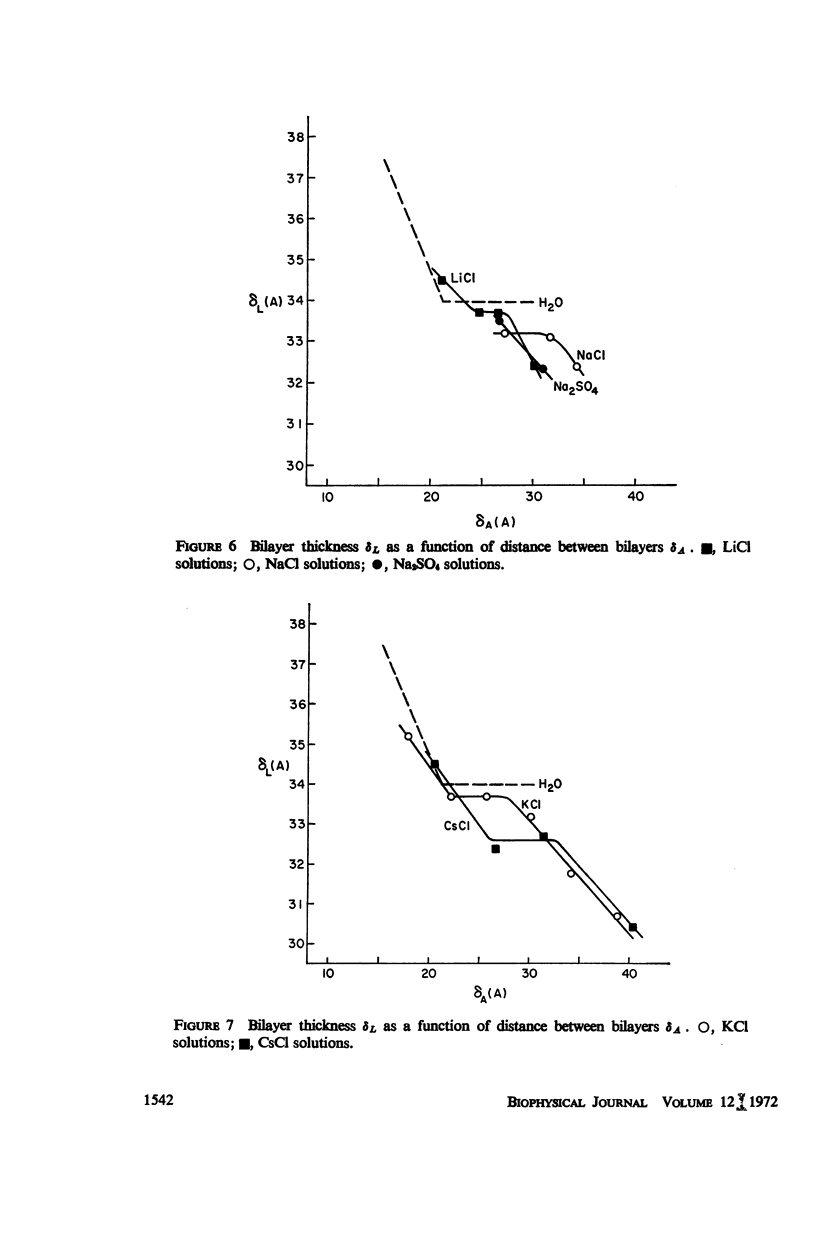





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Giannoni G., Padden F. J., Jr, Roe R. J. A lamellar complex of lecithin and poly-L-tyrosine. Biophys J. 1971 Dec;11(12):1018–1029. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86275-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulik-Krzywicki T., Shechter E., Vittorio Luzzati, Faure M. Interactions of proteins and lipids: structure and polymorphism of protein-lipid-water phases. Nature. 1969 Sep 13;223(5211):1116–1121. doi: 10.1038/2231116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRT R., BERCHTOLD R. Zur Synthese der Phosphatide. 2. Eine neue Synthese der Lecithine. Pharm Acta Helv. 1958 Aug-Oct;33(8-10):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUZZATI V., HUSSON F. The structure of the liquid-crystalline phasis of lipid-water systems. J Cell Biol. 1962 Feb;12:207–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecuyer H., Dervichian D. G. Structure of aqueous mixtures of lecithin and cholesterol. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 14;45(1):39–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of cell membranes and their derivatives. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:3–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Luzzati V. X-ray diffraction study in water of lipids extracted from human erythrocytes: the position of cholesterol in the lipid lamellae. Biophys J. 1968 Jan;8(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86479-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P. Structural studies by X-ray diffraction of model lipid-protein membranes of serum albumin-lecithin-cardiolipin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 14;241(3):823–834. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss-Husson F. Structure des phases liquide-cristallines de différents phospholipides, monoglycérides, sphingolipides, anhydres ou en présence d'eau. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):363–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. O., SCHULMAN J. H. BINDING OF METAL IONS TO MONOLAYERS OF LECITHINS, PLASMALOGEN, CARDIOLIPIN, AND DICETYL PHOSPHATE. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. G., Leslie R. B., Chapman D. X-ray diffraction study of the interaction of phospholipids with cytochrome c in the aqueous phase. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):561–562. doi: 10.1038/222561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Bourgès M. C., Dervichian D. G. The biophysics of lipidic associations. I. The ternary systems: lecithin-bile salt-water. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):563–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. Phase equilibria and structure of dry and hydrated egg lecithin. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):551–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


