Abstract
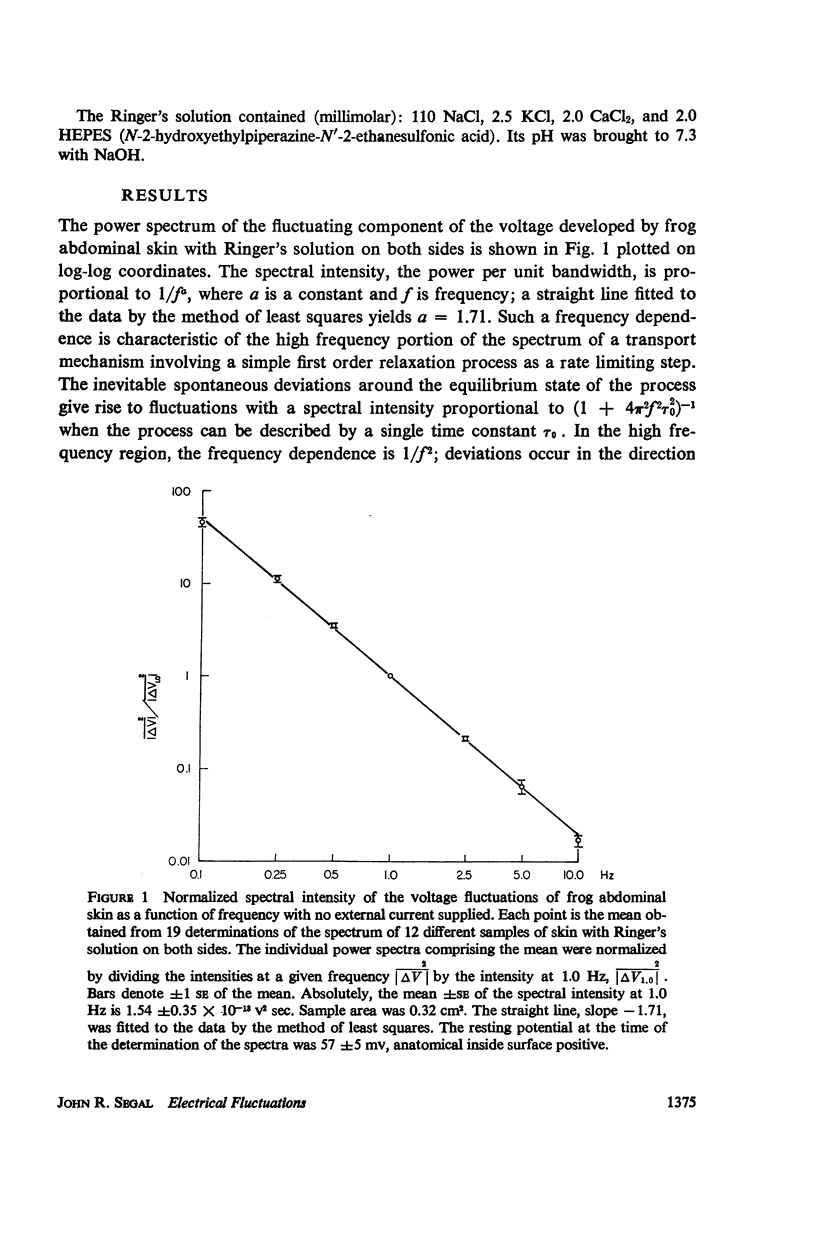
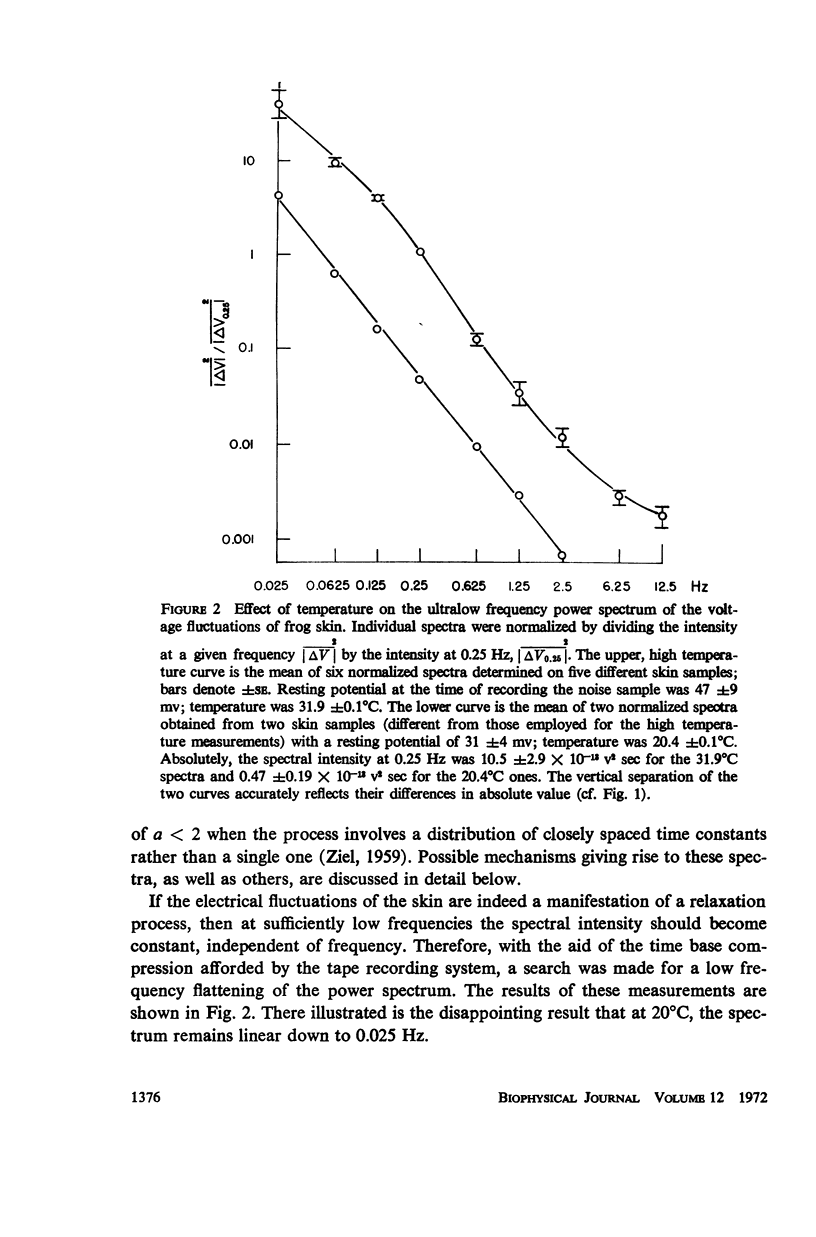
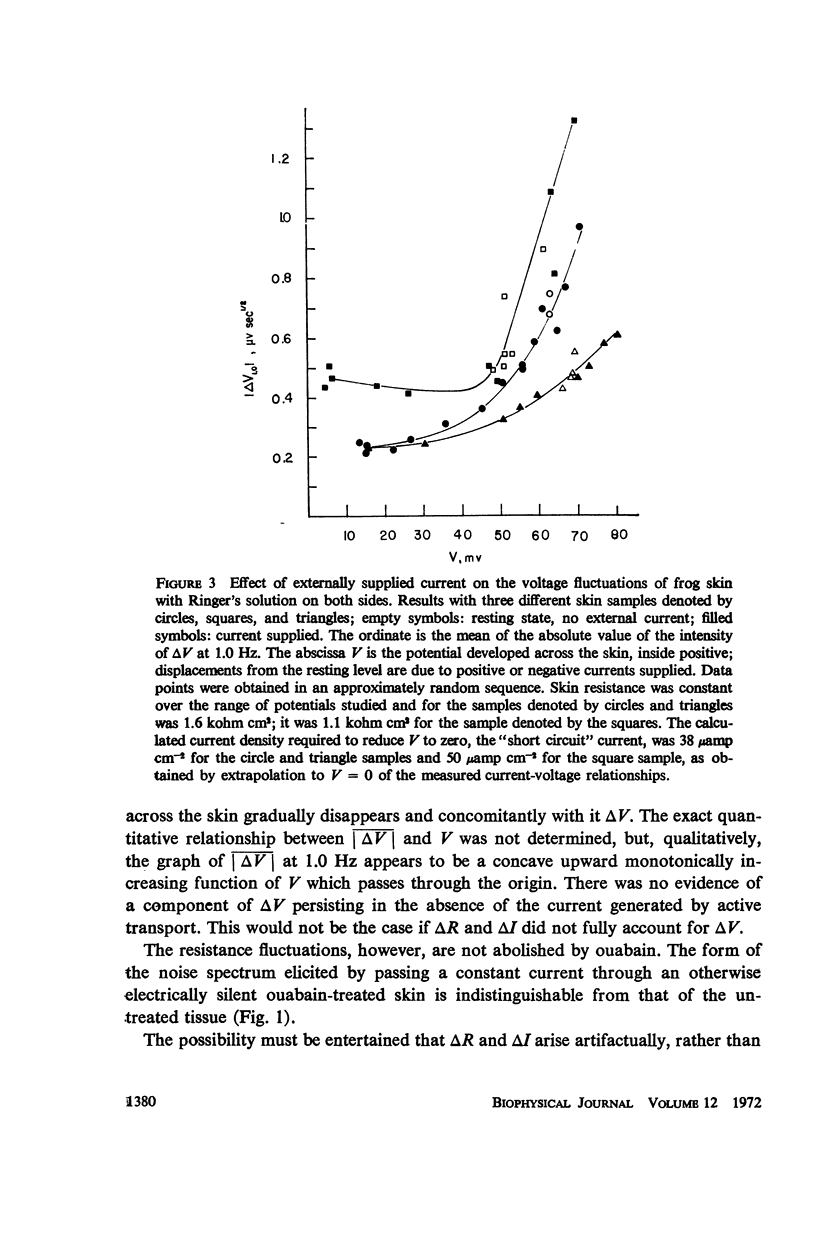
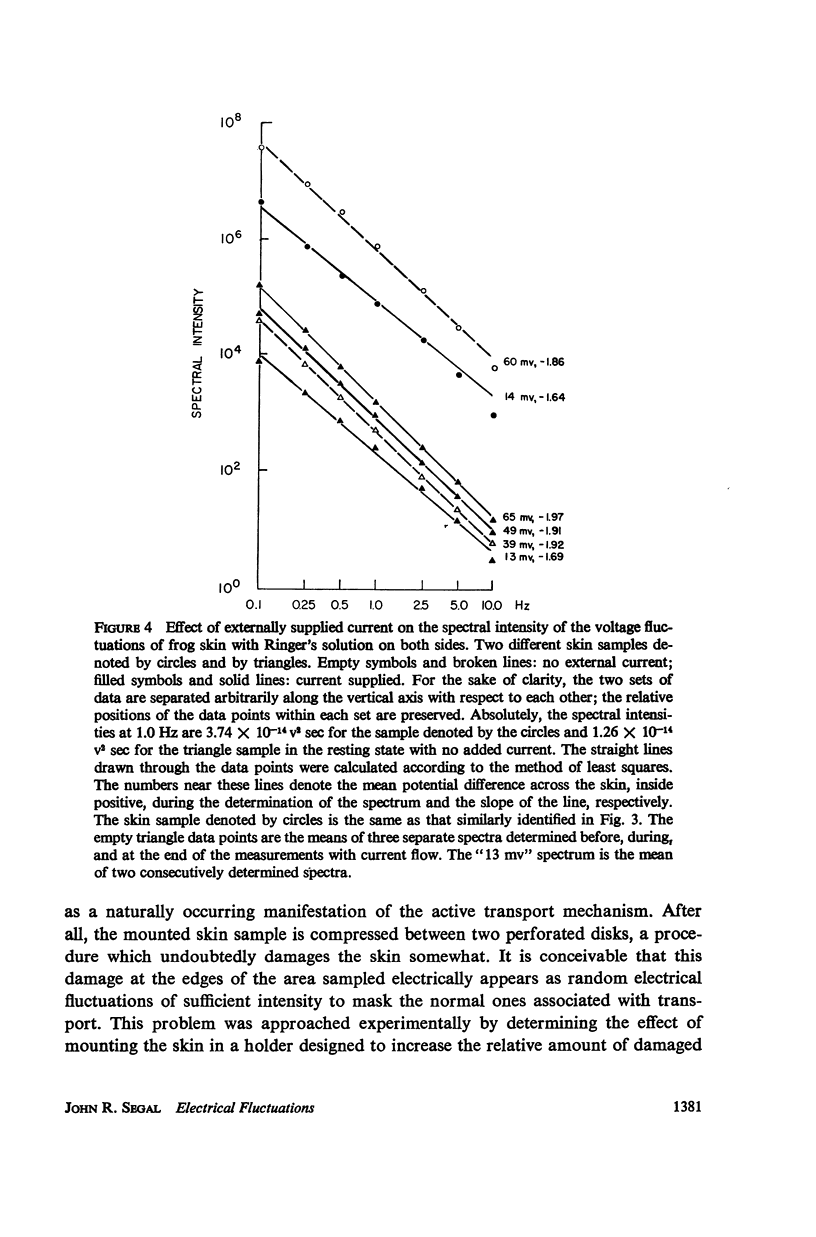
Measurements were made of the spectrum of the voltage fluctuations developed in the 0.025-10 Hz band during active transport by frog abdominal skin with Ringer's solution on both sides. Decreasing the potential across the skin by an external supply of current diminishes the voltage fluctuations, but they do not disappear, reaching a minimum finite value. Thus, fluctuations in both the resistance of the skin and the electric current attendant to the active transport of sodium contribute to the voltage fluctuations. Ouabain eliminates the current fluctuations but not those of the resistance. At 20°C, the spectral intensities of the resistance and current fluctuations are nearly identical, varying as 1/fa, where f is frequency and a = 1.6-2.0. At 32°C, the spectrum of the voltage fluctuations is sigmoid shaped, evidencing a relaxation process with a time constant of 0.6 sec. The fluctuations can be accounted for by stochastic variations in the concentration of a complex formed between a carrier molecule, fixed or mobile, and the actively transported species, sodium.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CURRAN P. F., HERRERA F. C., FLANIGAN W. J. The effect of Ca and antidiuretic hormone on Na transport across frog skin. II. Sites and mechanisms of action. J Gen Physiol. 1963 May;46:1011–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.5.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen H. E., Verveen A. A. Fluctuations of resting neural membrane potential. Science. 1966 Mar 18;151(3716):1388–1389. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3716.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHRMAN F. A. Inhibition of active sodium transport in the isolated frog skin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Nov;171(2):266–278. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.171.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., RENSHAW A. Ion transport and respiration of isolated frog skin. Biochem J. 1957 Jan;65(1):82–90. doi: 10.1042/bj0650082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poussart D. J. Membrane current noise in lobster axon under voltage clamp. Biophys J. 1971 Feb;11(2):211–234. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86209-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poussart D. J. Nerve membrane current noise: direct measurements under voltage clamp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


