Abstract
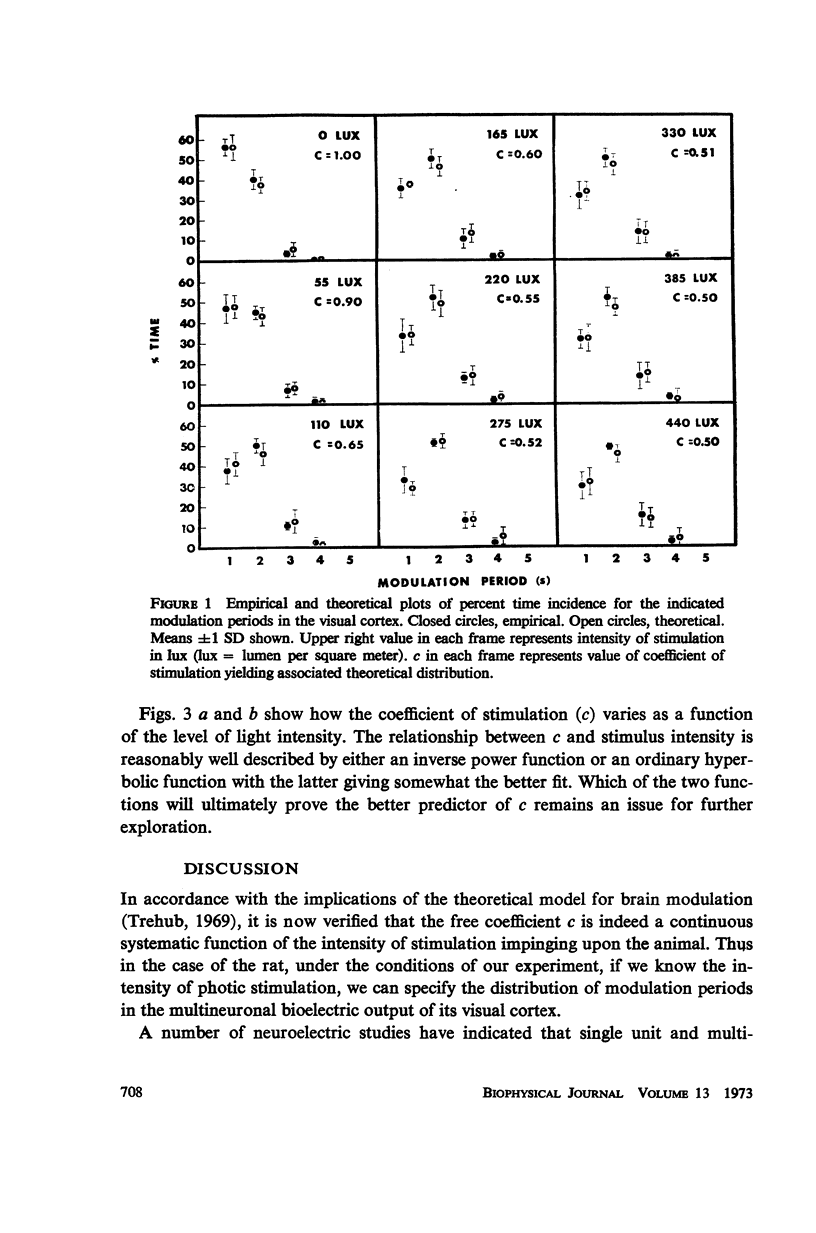
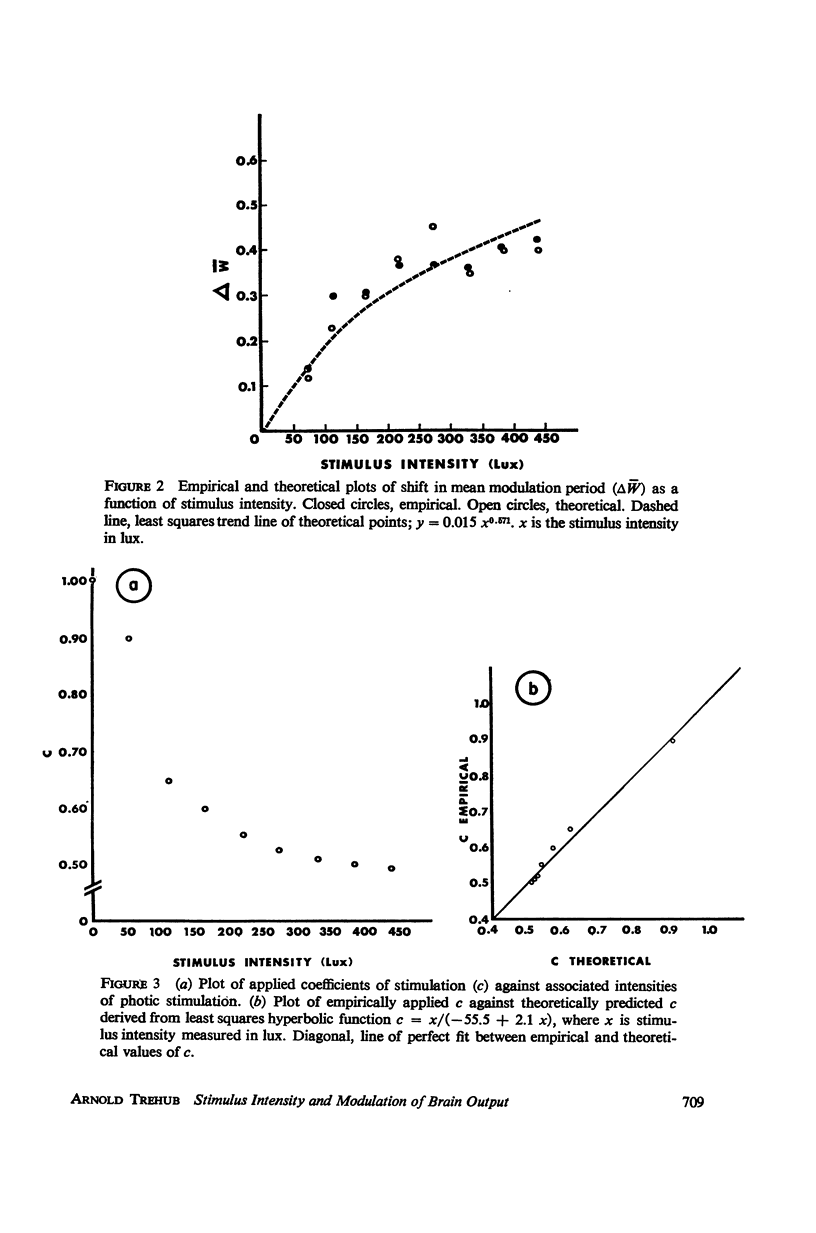
In accordance with the implications of a previously proposed mathematical model of modulation of bioelectric response in the brain, it is found that a single free coefficient predicts the observed modulation periods over a range of stimulus intensities. This coefficient is shown to be a computable function of stimulus intensity. Change in the mean modulation period of evoked bioelectric output at the visual cortex of the rat can be described as a power function of the intensity of photic stimulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mountcastle V. B., Talbot W. H., Sakata H., Hyvärinen J. Cortical neuronal mechanisms in flutter-vibration studied in unanesthetized monkeys. Neuronal periodicity and frequency discrimination. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):452–484. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trehub A. A Markov model for modulation periods in brain output. Biophys J. 1969 Jul;9(7):965–969. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86430-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trehub A. Signal characteristics of visual cortex and lateral geniculate during contralateral and ipsilateral photic stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1971 Feb;30(2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(71)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


