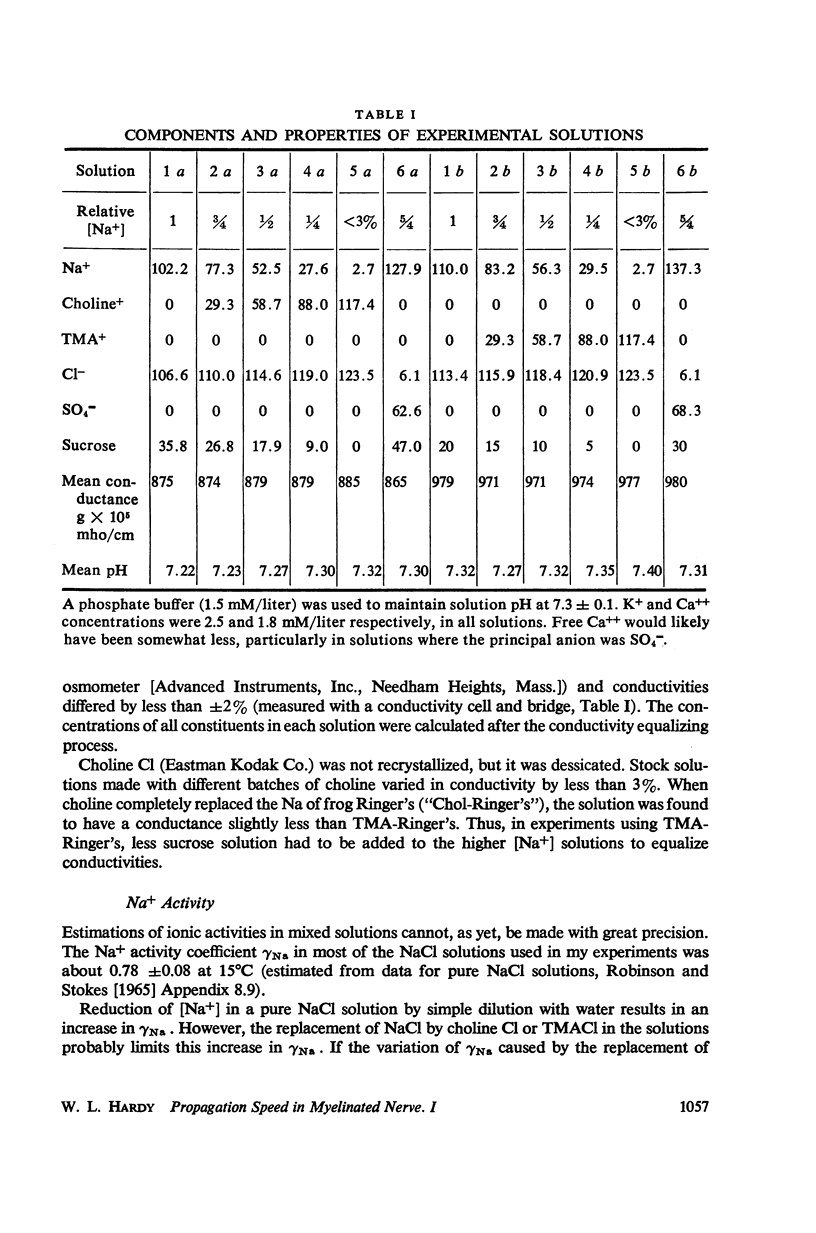
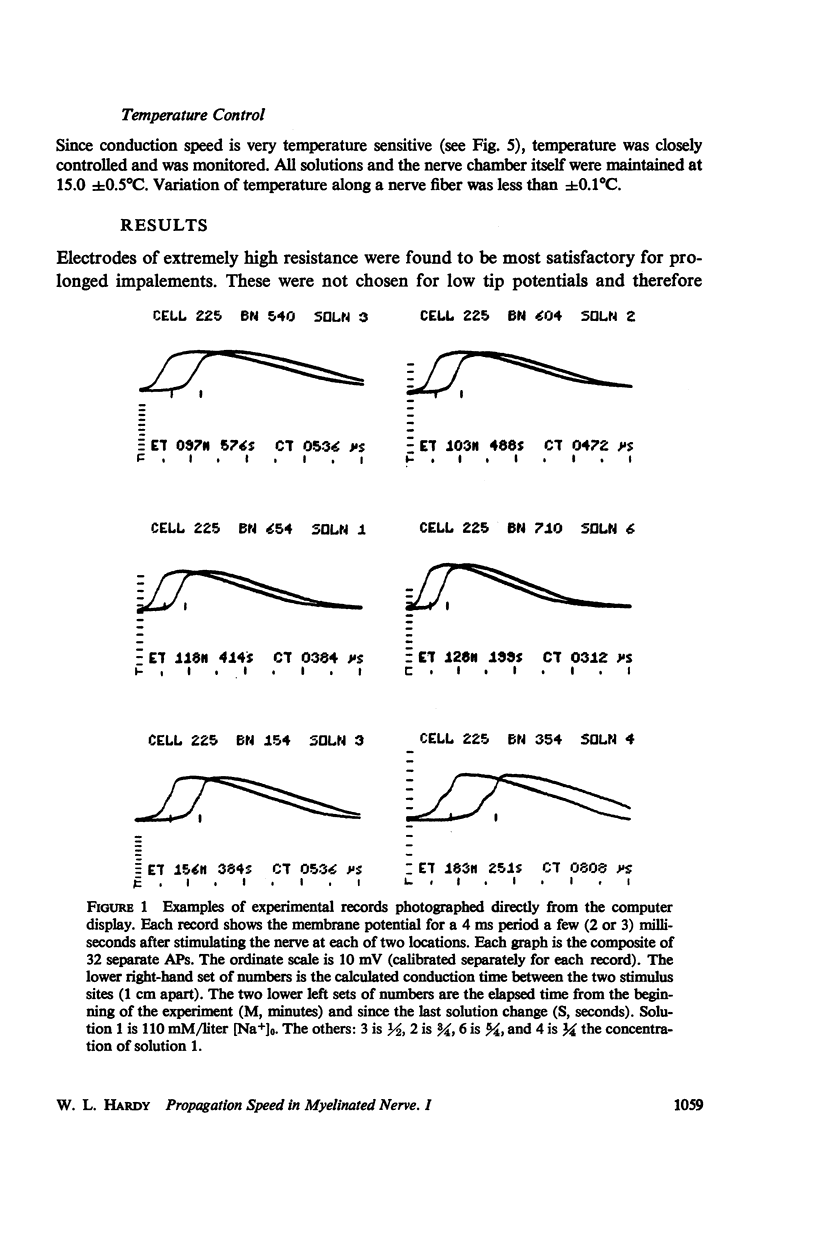
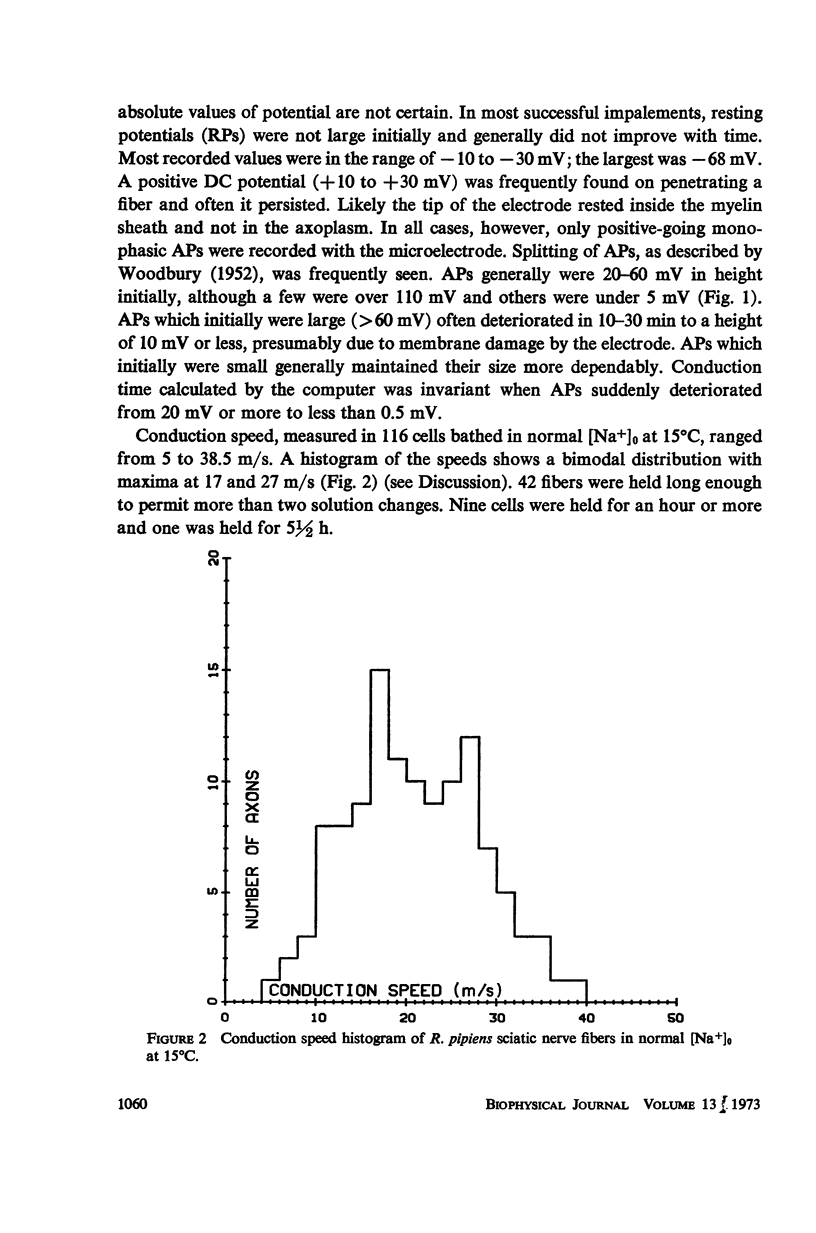
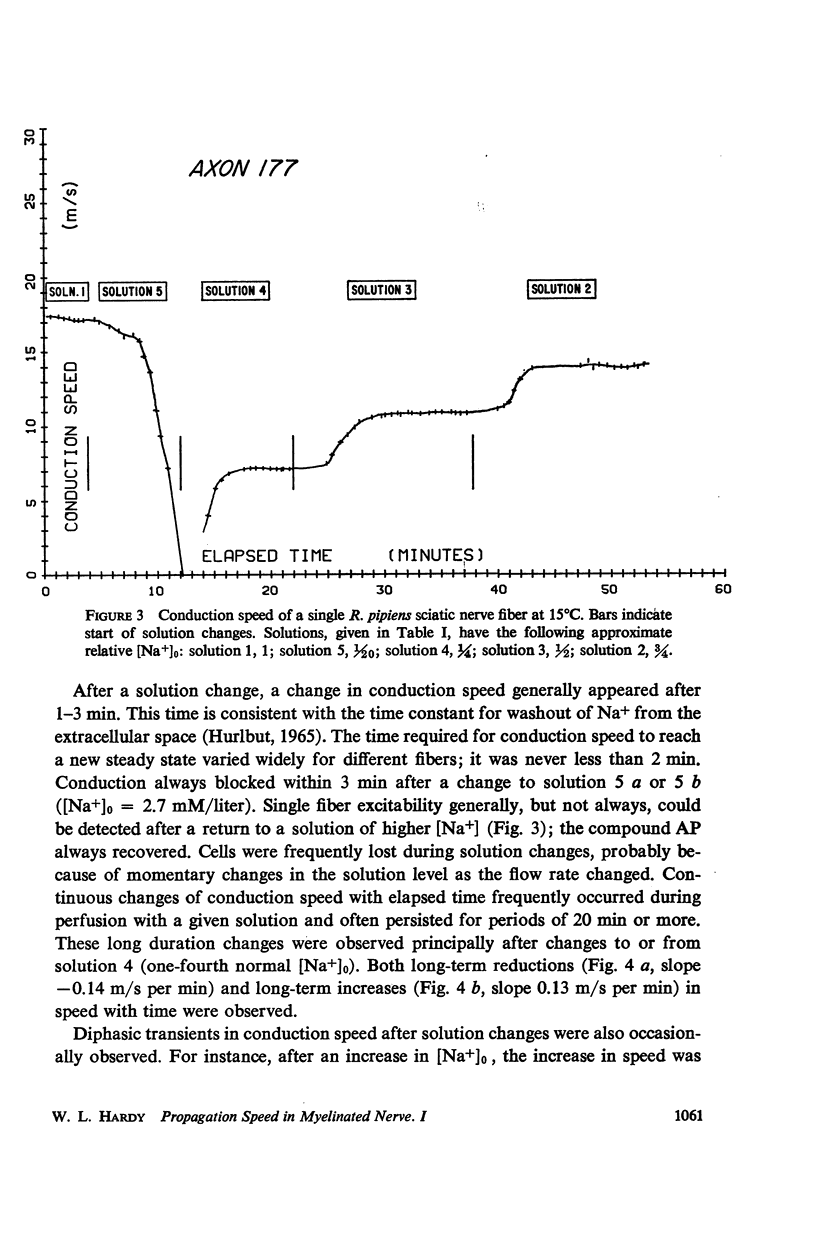
Abstract
Conduction speed (θ) in single myelinated Rana pipiens sciatic nerve fibers has been precisely measured using intracellular recording and on-line digital computer techniques. The dependence of relative speed on external Na concentration at 15°C has been found to be ln(θ1/θ2) = 0.524 (±0.018) ln ([Na+]1/[Na+]2) + 0.003. Thus θ has very close to a square root dependence on [Na+]0 for these fibers. This experimental finding is not in complete agreement with a theoretical prediction based on a solution of the Hodgkin-Huxley (H.H.) equations. The effect of small temperature variations around 15°C on θ has also been measured for Rana fibers in Ringer's solution. θ has close to an exponential dependence on T and a Q10 of 2.95 has been estimated.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ritchie J. M. The interaction at equilibrium between tetrodotoxin and mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):533–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., WALTMAN B. Membrane resistance and conduction velocity of large myelinated nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:677–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBUT W. P. SODIUM FLUXES IN DESHEATHED FROG SCIATIC NERVE. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Jul;46:1191–1222. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.6.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., STAMPFLI R. Direct determination of membrane resting potential and action potential in single myelinated nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):476–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. L. Propagation speed in myelinated nerve. II. Theoretical dependence on external Na and on temperature. Biophys J. 1973 Oct;13(10):1071–1089. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86046-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbut W. P. Salicylate: effects on ion transport and afterpotentials in frog sciatic nerve. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1295–1303. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson N. A., Koles Z. J., Smith R. S. Conduction velocity in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):279–289. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E. Effect of temperature and calcium ions on rate constants of myelinated nerve. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):131–137. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal J. R. Metabolic dependence of resting and action potentials of frog nerve. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1216–1225. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODBURY J. W. Direct membrane resting and action potentials from single myelinated nerve fibers. J Cell Physiol. 1952 Apr;39(2):323–339. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030390210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


