Abstract
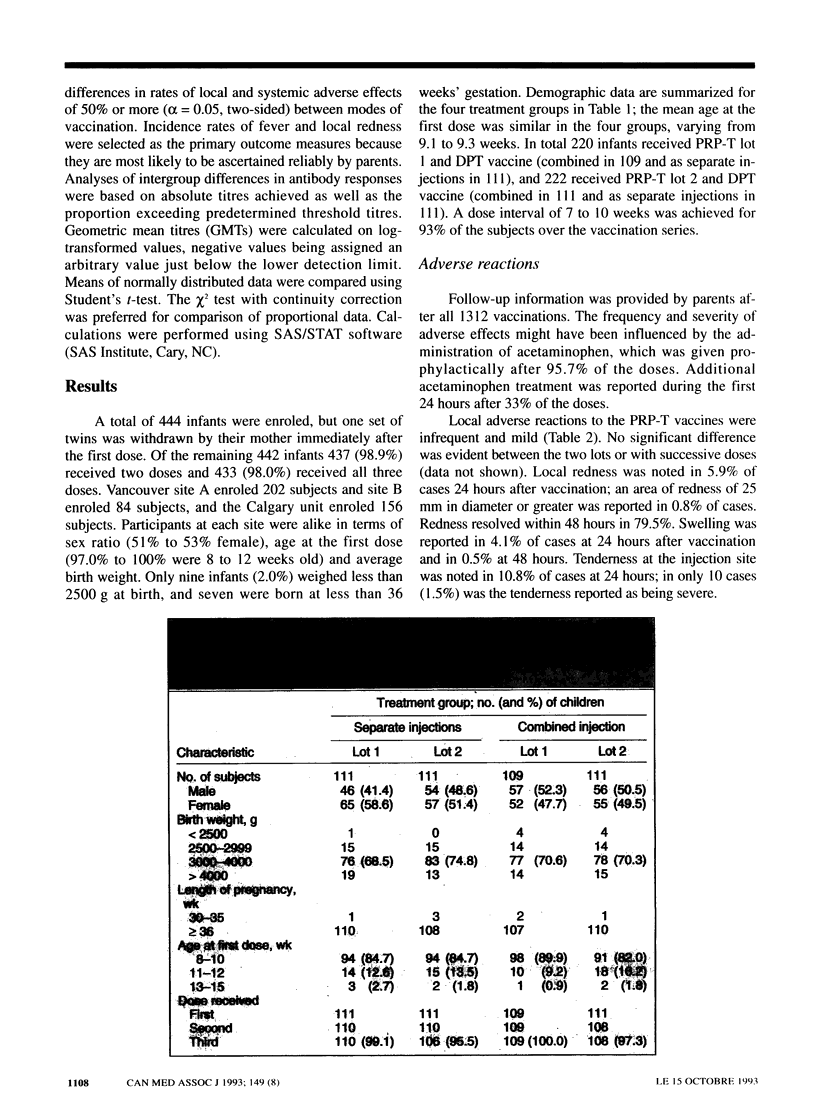
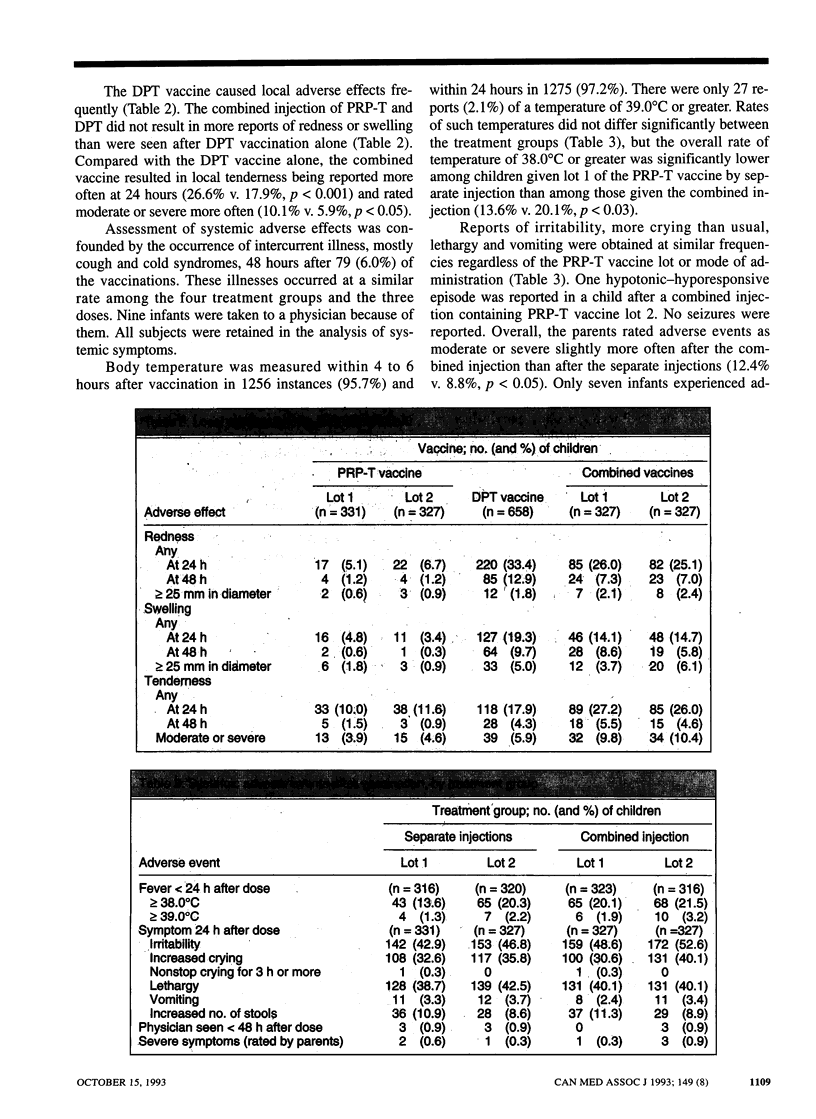
OBJECTIVE: To assess the side effects and immune responses after three serial doses of PRP-T vaccine (a Haemophilus influenzae type b [Hib]-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine) given concurrently or mixed with adsorbed DPT vaccine (diphtheria toxoid-pertussis vaccine-tetanus toxoid). DESIGN: Multicentre randomized controlled trial. SETTING: Four public health units in western Canada. PARTICIPANTS: Healthy infants 8 to 15 weeks old at entry who were able to receive routine primary vaccinations. Of 444 infants enrolled, 433 (98%) completed the study. INTERVENTIONS: All infants received PRP-T and DPT vaccines at 2, 4 and 6 months of age: half received them mixed in one injection and the others as separate, bilateral injections. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES: Side-effects 24 and 48 hours after each dose and serologic responses to each vaccine component. RESULTS: Follow-up was obtained after all 1312 vaccinations. Fever was infrequent in the two treatment groups. Local adverse effects of the PRP-T vaccine were infrequent and mild (e.g., redness was noted in 5.9% of cases and the area of redness was more than 2.5 cm in diameter in 0.8%). The incidence rate of local effects of the DPT-containing vaccines was the same in the two groups except for tenderness, which was more frequent in the group given the mixed vaccine (26.6% v. 17.9%, p < 0.001). Serologic data were available for 97% of the subjects. After the three doses 98.1% of the subjects had a PRP antibody level of 0.15 micrograms/mL or more, and 87.9% had a level of 1.0 micrograms/mL or more, both levels compatible with protection against Hib. Responses to PRP-T were comparable between the treatment groups as were responses to the diphtheria and tetanus toxoids. Pertussis agglutinin titres were reduced after administration of one of two PRP-T lots mixed with DPT vaccine, but responses to four other pertussis antigens were not impaired. CONCLUSION: PRP-T vaccine is well tolerated and immunogenic. Combined PRP-T and DPT vaccines performed satisfactorily and may be the preferred method of administration.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraff L. J., Manclark C. R., Cherry J. D., Christenson P., Marcy S. M. Analyses of adverse reactions to diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and pertussis vaccine by vaccine lot, endotoxin content, pertussis vaccine potency and percentage of mouse weight gain. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Aug;8(8):502–507. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198908000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. B., Shinefield H. R., Fireman B., Hiatt R., Polen M., Vittinghoff E. Efficacy in infancy of oligosaccharide conjugate Haemophilus influenzae type b (HbOC) vaccine in a United States population of 61,080 children. The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center Pediatrics Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Feb;10(2):97–104. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199102000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. B., Shinefield H. R., Lampert D., Fireman B., Hiatt R. A., Polen M., Vittinghoff E. Safety and immunogenicity of oligosaccharide conjugate Haemophilus influenzae type b (HbOC) vaccine in infancy. The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center Pediatrics Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Feb;10(2):92–96. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199102000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens J. D., Ferreccio C., Levine M. M., Horwitz I., Rao M. R., Edwards K. M., Fritzell B. Impact of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-tetanus protein conjugate vaccine on responses to concurrently administered diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis vaccine. JAMA. 1992 Feb 5;267(5):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody C. L., Baraff L. J., Cherry J. D., Marcy S. M., Manclark C. R. Nature and rates of adverse reactions associated with DTP and DT immunizations in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1981 Nov;68(5):650–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Asmar B. I., Thirumoorthi M. C. Systemic Haemophilus influenzae disease: an overview. J Pediatr. 1979 Mar;94(3):355–364. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker M. D., Edwards K. M., Bradley R., Palmer P. Comparative trial in infants of four conjugate Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines. J Pediatr. 1992 Feb;120(2 Pt 1):184–189. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine P. E., Clarkson J. A. Reflections on the efficacy of pertussis vaccines. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9(5):866–883. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.5.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzell B., Plotkin S. Efficacy and safety of a Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide-tetanus protein conjugate vaccine. J Pediatr. 1992 Sep;121(3):355–362. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)81786-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Holmes S. J. Comparative immunogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines. Vaccine. 1991 Jun;9 (Suppl):S30–S43. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipp M. M., Gold R., Greenberg S., Goldbach M., Kupfert B. B., Lloyd D. D., Maresky D. C., Saunders N., Wise S. A. Acetaminophen prophylaxis of adverse reactions following vaccination of infants with diphtheria-pertussis-tetanus toxoids-polio vaccine. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Aug;6(8):721–725. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198708000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Reimer C., Black C., Welfare S., Bryla D., Levi L., Pavliakova D., Cramton T., Schulz D. Clinical and immunologic responses to Haemophilus influenzae type b-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine in infants injected at 3, 5, 7, and 18 months of age. J Pediatr. 1991 Feb;118(2):184–190. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80480-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santosham M., Wolff M., Reid R., Hohenboken M., Bateman M., Goepp J., Cortese M., Sack D., Hill J., Newcomer W. The efficacy in Navajo infants of a conjugate vaccine consisting of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide and Neisseria meningitidis outer-membrane protein complex. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 20;324(25):1767–1772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106203242503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro E. D. New vaccines against Haemophilus influenzae type b. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1990 Jun;37(3):567–583. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)36905-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watemberg N., Dagan R., Arbelli Y., Belmaker I., Morag A., Hessel L., Fritzell B., Bajard A., Peyron L. Safety and immunogenicity of Haemophilus type b-tetanus protein conjugate vaccine, mixed in the same syringe with diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis vaccine in young infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Oct;10(10):758–763. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199110000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Granoff D. M. Polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines for the prevention of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease. J Pediatr. 1988 Oct;113(4):621–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


