Abstract
Current data suggest that the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) epidemic arose by transmission of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) SIVcpz from a subspecies of common chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes troglodytes) to humans. SIVcpz of chimpanzees is itself a molecular chimera of SIVs from two or more different monkey species, suggesting that recombination was made possible by coinfection of one individual animal with different lentiviruses. However, very little is known about SIVcpz transmission and the susceptibility to lentivirus coinfection of its natural host, the chimpanzee. Here, it is revealed that either infected plasma or peripheral blood mononuclear cells readily confer infection when exposure occurs by the intravenous or mucosal route. Importantly, the presence of preexisting HIV-1 infection did not modify the kinetics of SIVcpz infection once it was established by different routes. Although humoral responses appeared as early as 4 weeks postinfection, neutralization to SIVcpz-ANT varied markedly between animals. Analysis of the SIVcpz env sequence over time revealed the emergence of genetic viral variants and persistent SIVcpz RNA levels of between 104 and 105 copies/ml plasma regardless of the presence or absence of concurrent HIV-1 infection. These unique data provide important insight into possible routes of transmission, the kinetics of acute SIVcpz infection, and how readily coinfection with SIVcpz and other lentiviruses may be established as necessary preconditions for potential recombination.
Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes troglodytes and Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) harbor various genetically different strains of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) SIVcpz (20, 30, 34). These variants exhibit molecular similarity to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) isolates belonging to clades M, N, and O, suggesting that at least three multiple cross-species transmission events have occurred in the past (11, 13, 31). Evidence that SIVs can cause AIDS following cross-species transmission has been most clearly illustrated by SIV transmission from asymptomatic African sooty mangabeys (SIVsm) to Asian macaques (6, 18, 22). Furthermore, there is a convincing body of data showing that SIVsm is the nonhuman primate lentivirus ancestor of HIV-2 (16, 21). More than 35 African nonhuman primate species have been reported to carry a variety of different lentiviruses (29). The majority of SIVs infect monkeys, and to date, only SIVcpz of chimpanzees is known among the great apes.
Genetic analysis of diverse SIVcpz isolates from two subspecies of chimpanzees indicates that the ancestor of SIVcpz is most probably a recombinant chimeric virus derived from viruses found in monkey species known to be preyed upon by chimpanzees (1, 35). The SIVcpz gag-pol region shows high sequence similarity with SIVrcm of the red-capped mangabey (Cercocebus torquatus), whereas env is related to the sequence of the SIVs found in the greater spot-nosed monkey (Cercopithecus nictitans) lineage (1). The most plausible explanation for the occurrence of this recombinant virus is that at least one chimpanzee became infected with one of these two viruses and subsequently became superinfected or coinfected with a second monkey lentivirus. It is likely that in the absence of persistent monkey lentiviral infections in chimpanzees, the recombinant ancestors of SIVcpz now circulating in today's populations of chimpanzees acquired the ability to both persist and sustain sufficient plasma virus loads in vivo to be effectively transmitted between individuals of this species. Thus, the sustained dual infection of chimpanzees by one or more distinct monkey SIVs must have been a necessary prerequisite for the recombinatory events which provided the chimeric origin of SIVcpz. In this paper, we present novel data on potential routes of transmission and the acute infection period of SIVcpz, providing fundamental and important insights into the natural history of the ancestor of HIV-1 in the common chimpanzee. Furthermore, we provide direct evidence that secondary lentivirus coinfections can be readily acquired by chimpanzees.
To date, only a limited number of chimpanzees living in captivity have been identified with naturally occurring SIVcpz infections (24). One such chimpanzee was rescued following illegal export from Africa. This animal, ch-No, provided a unique opportunity for virological and immunological follow-up of a natural SIV infection (28, 30, 32). The apparent low prevalence of SIVcpz infection is due to SIVcpz's focal epidemiology, which is relatively high in specific regions and communities of wild chimpanzee populations compared to others (24, 34). The reasons for this are unclear, but it may be due to the dynamics of transmission and social interactions among individual chimpanzees in their communities. Indeed, the modes of SIVcpz transmission in chimpanzees are unknown, and the patterns of transmission may be different than that of HIV-1 in humans.
To address the question of SIVcpz transmission, a series of studies were undertaken in a naïve chimpanzee from the host subspecies, P. t. schweinfurthii, and in a cohort of captive bred chimpanzees previously designated for the study of HIV-1 infection and pathogenesis. These studies revealed that SIVcpz infection could be readily established with either plasma or peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by several different routes independently of the presence of concurrent HIV-1 infection. We show that the early kinetics of SIVcpz infection are similar to those of HIV-1 infection in humans with respect to seroconversion, high levels and persistence of plasma viremia, the development of neutralizing antibody responses, and the evolution of individual sequence variants in plasma. In contrast to humans, the infection in chimpanzees differed in the absence of immune activation, the lack of progressive CD4 T-cell loss, and the development of AIDS despite coinfection with HIV-1.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and longitudinal-study design.
The study group consisted of a total of nine chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), three of which were P. t. schweinfurthii. One (ch-No) of these animals was naturally infected with SIVcpz-ANT; another (ch-Ni) was a seronegative cage mate at risk of infection. ch-No had developed marked thrombocytopenia, which was acquired subsequent to SIVcpz infection. All other hematological and clinical parameters in the two animals were within the normal range. The remaining group consisted of six animals persistently infected with a HIV-1 clade B strain (two HIV-1SF2 [ch-X115 and ch-X123] and four HIV-1IIIB [ch-X062, ch-X310, ch-X176, and ch-X130]), as well as one naïve control (ch-X284) (Table 1). All of the animals were mature and in good health with normal hematological values. The six HIV-1-infected animals had low or undetectable virus loads (below 50 copies/ml plasma), common in HIV-1-infected chimpanzees. Prior to initiating any in vivo procedures, the study protocols were evaluated by independent ethical committees in accordance with national and international regulations (International Animal Care and Use Committee). The study design was developed after prolonged observation of the two P. t. schweinfurthii animals, ch-Ni and ch-No. For social and behavioral reasons, these two animals were housed together despite the fact that ch-No was infected with SIVcpz. The development of a specific quantitative PCR to detect SIVcpz infection confirmed these results (38). During a 5-year observation period, the two male animals became sexually active, and incidents of aggression in which blood was drawn began to increase. It was determined that transmission of SIVcpz infection to the negative cage mate was a question of time, and ethical permission to acquire valuable early SIVcpz infection data in a carefully monitored prospective study was granted. To study the kinetics of SIVcpz infection in P. t. schweinfurthii, the decision was taken to iatrogenically transfer PBMCs intravenously from the naturally infected chronic carrier of SIVcpz-ANT, ch-No. As ch-No had marked thrombocytopenia of suspected autoimmune and idiopathic etiology, treatment with corticosteroids (tapered doses up to 0.2 mg/kg of body weight) was undertaken to confirm the diagnosis and to restore platelets to normal levels prior to donation of infected PBMCs. Two weeks after the intravenous (i.v.) transfer of 200 × 106 PBMCs from donor ch-No, the recipient, ch-Ni, was bled to establish two new ex vivo viral stocks, designated SIVcpz-ANT Ni-2PL (plasma) and Ni-2PB (PBMCs, containing approximately 1,200 infected cells/106 and 5.9 × 106 RNA copies/ml). These ex vivo uncultured stocks were used for subsequent transmission studies of clade B HIV-1-infected or uninfected chimpanzees, as indicated in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Overview of animals used in this study with their virological background, subspecies, sex, and route of exposure
| Animal | Subspecies | Sexa | Preinfection status | Exposure route |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ch-No | schweinfurthii | M | Unknown | |
| ch-Ni | schweinfurthii | M | i.v. | |
| ch-X062 | schweinfurthii | M | HIVIIIB | i.v. |
| ch-X310 | verus | M | HIVIIIB | i.v. |
| ch-X115 | verus | M | HIVIIIB | i.r. |
| ch-X176 | verus | M | HIVsf2 | i.r. |
| ch-X123 | verus | F | HIVsf2 | i.vag. |
| ch-X130 | verus | F | HIVIIIB | i.vag. |
| ch-X284 | verus | F | i.vag. |
M, male; F, female.
Briefly, the subsequent series of studies were undertaken to determine if SIVcpz-ANT infection could be transmitted in the presence of concurrent HIV-1 infection, and if so, if the patterns and kinetics of infection were comparable following i.v., rectal (i.r.), or vaginal mucosal (i.vag.) exposure. The study design included one naive control animal, which would be used to receive SIVcpz by the same dose and route if one of the routes of transmission failed in any of the HIV-1-infected animals. Furthermore, since the infectious dose has been demonstrated not to influence the levels of viremia and kinetics of SIV infection (17) or HIV-1 infection (23), an estimated minimum of a log-fold excess infectious dose was used based on titration studies in macaques and chimpanzees (5, 23, 25). Whenever possible, blood samples from all animals in the study were drawn 1 to 2 months prior to exposure and at 2-week intervals for the first 2 months and then monthly until 6 months postexposure, when sampling was reduced to once every 2 months for the 1-year follow-up period. At each time point, routine clinical biochemistry was performed on fresh plasma, while samples were cryopreserved for retrospective analysis for plasma virology and serology. Similarly, fresh whole blood was analyzed for complete blood cell counts, and separated PBMCs were analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorter for specific lymphocyte subset analysis. Detailed analysis included determination of naïve and memory CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes and determination of changes in B-cell and NK cell levels in peripheral blood (data for ch-Ni only are shown). Evidence of T-cell activation was assessed by examining the levels of expression of HLA DR on CD8 subsets (data not shown).
Differential quantitation of HIV-1 and SIVcpz plasma viral RNA and plasma antigen concentrations.
The quantitation of the combined HIV-1 and SIVcpz viral RNA load in plasma was performed as previously described, using primers that bind to a 175-bp sequence in the pol gene that is conserved in all HIV-1 strains and in SIVcpz-ANT (38, 39). The amount of HIV-1 clade B virus in plasma was determined with the AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR test, version 1.5 (Roche Diagnostics Nederland BV, Almere, The Netherlands). The SIVcpz virus load was determined by subtraction of the HIV-1 load from those determined by the HIV-1/SIVcpz assay as previously performed (38).
The concentration of antigen in the plasma of chronically and acutely infected animals was determined using a commercial HIV-1 antigen capture assay according to the manufacturer's instructions (Murex P24 Elisa; Dartford, United Kingdom). In order to determine if antibody was complexed with SIVcpz antigen, masking true plasma antigenemia, potential complexes were disassociated under conditions of low pH and then measured for free antigen as previously described for HIV-infected individuals (Murex; personal communication).
Serological responses.
Plasma samples from ch-Ni both before and after infection were screened for the presence of antibodies that bound HIV-1 or SIVcpz proteins. The presence of antibodies was determined by Western blotting (Diagnostics HIV blot 2.2; Genelabs, Redwood City, CA).
Buffy coats were obtained from the Antwerp Red Cross Blood Transfusion Centre. PBMCs were separated using Linfosep (Biomedics, Madrid, Spain); adjusted to 1 × 106/ml in RPMI 1640 medium (Cambrex, Verviers, Belgium) supplemented with 0.5 μg/ml phytohemagglutinin (PHA; Abbott Murex, Dartford, United Kingdom), 15% fetal calf serum (FCS; Biochrom AG, Berlin, Germany), and 2 μg/ml hexadimetrine bromide (Sigma-Aldrich, Bornem, Belgium); and incubated for 48 to 72 h. The PHA-transformed PBMCs were then cultured in RPMI 1640 medium, in which the PHA was replaced by 20 U/ml recombinant human interleukin 2 (IL-2) (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland).
Virus stocks were prepared by infecting a 5-ml culture of fresh, PHA-transformed human PBMCs with the plasma from ch-Ni used in the transmission experiments. Twice weekly, the cells were divided, and freshly transformed cells from a different donor were added. This procedure was repeated to eventually generate 30 ml of viral supernatant with high antigen content. The supernatants from these cultures were dispensed into aliquots and stored at −80°C.
For the neutralization assays, an inoculum of 190 μl, containing 80 50% tissue culture infective doses of virus, was mixed with 10 μl of heat-inactivated (30 min at 56°C) plasma (final dilution, 1 in 20) and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. PHA-transformed PBMCs were diluted in RPMI 1640 medium with IL-2 to give 7.5 × 105 cells/ml; 20 μl of each virus-plasma mixture was dispensed into six wells of a 96-well Microtiter cell culture plate (Falcon), and 100 μl of cells was added. The plates were then incubated for 72 h at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Each well was then washed by centrifuging (800 × g) the cultures and aspirating the supernatant. The cells were then resuspended in fresh RPMI 1640 medium containing IL-2 and FCS. This procedure was repeated three times, and the cells were then cultured in 200 μl RPMI 1640 medium with FCS and IL-2 for a further 7 days. After a total of 10 days in culture, 125 μl of medium was removed from each well and diluted immediately in 125 μl of cell culture medium. This 1-in-2 dilution was diluted subsequently to give 1-in-10 and 1-in-50 dilutions. The mean of antigen released from cultures of virus which had been incubated with heat-inactivated plasma from ch-Ni and ch-X284 was used to calculate percent neutralization. The virus was titrated in parallel with the neutralization assay to estimate the actual input under the prevailing experimental conditions. Viral antigen release into culture supernatants was monitored by an in-house enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (4). Optical densities were used to calculate concentrations of released SIVcpz-specific antigen against a standard curve generated with dilutions of SIVcpz-ANT cultured in human PBMCs. The results are given in log10 of arbitrary units of viral antigen (27).
To define statistically significant neutralization, an analysis of variance was performed on the log10-transformed antigen release data from all cultures following incubation of virus with a pretransmission plasma and four posttransmission plasmas. The statistical significance of the F ratio of the variance between the plasma divided by the variance between the individual cultures is reported for each chimpanzee. The individual plasmas that were neutralizing were identified by reference to the minimum significant range calculated from the variance between the cultures and a constant derived from tables for the Studentized range test and depending on numbers of cultures and samples to be compared (7, 9).
Flow cytometric analysis of lymphocyte subsets.
White blood cell and platelet counts were performed with a Technicon H1 (Technicon Instruments, Tarrytown, N.Y.). Absolute and relative CD4 and CD8 T-cell, B-cell, and NK cell counts were determined in EDTA-treated peripheral blood by a direct immunofluorescence method using a combination of directly labeled specific antibodies (Dako Cytomation, Glostrup, Denmark, and Becton Dickinson, Erembodegem, Belgium). In short, cell surface staining was performed by incubating whole blood with the antibody mixture for 15 min at room temperature. The whole-blood sample was treated with lysing solution (Becton Dickinson) for 10 min in the dark to lyse erythrocytes, centrifuged, and washed with PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin. Finally, the cells were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde in PBS overnight and analyzed on a FACSsort (Becton Dickinson).
Analysis of viral quasispecies.
To determine the viral quasispecies, we performed PCR on viral RNA that was isolated from plasma samples or on genomic DNA isolated from PBMCs.
The V1-V3 envelope region was amplified by a nested PCR using the following primers: vcant1, 5′ TAGTTAGGCTCAATACCTCAG (6098 to 6118), and vcant2, 5′ GTGTAGTTGTCATTGAACCAAAG (7050 to 7072), as outer primers and vcant1N, 5′ AACAAAGCCATAAGCCATGTG (6184 to 6204), and vcant2N, 5′ CTCCTTGGGAATTAAACCAATG (7005 to 7026), as the inner primer set. The primer positions are indicated on the basis of their locations on the SIVcpz-ANT genome (40). The vcant2 primer was used for the synthesis of cDNA using the Superscript III First Strand Synthesis system according the manufacturer's recommendations (Invitrogen, Breda, The Netherlands).
One microgram of genomic DNA or 5 μl of cDNA was added to PCR mixtures containing 2 mM MgCl2, 40 nmol of deoxynucleoside triphosphates, 20 pmol of each primer, and 1 U of Taq polymerase (Perkin-Elmer Nederland, Gouda, The Netherlands). PCR amplification was performed for 38 cycles with the following cycle profile: denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 54°C for 30 seconds, and extension at 72°C for 45 seconds. Amplification was completed by a final extension at 72°C for 7 min. Thereafter, 1/20 of the first PCR was used as a template in a second round of amplification for 38 cycles with inner primers using the same cycling conditions. To control for PCR-induced mutations, two independent amplifications were performed with each sample.
PCR products were isolated from gels, cloned into the pGEM-T vector (Promega, Leiden, The Netherlands), and sequenced on an ABI 373, model Stretch, automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Nieuwerkerk a/d IJssel, The Netherlands) using M13 and SP6 primers. From each sample, 8 to 10 PCR fragments were sequenced.
Phylogenetic analysis.
Nucleotide sequences were aligned using ClustalW as incorporated in the MacVector 8.1.1 sequence analysis software package (Accelrys, Cambridge, United Kingdom), and the aligned sequences were manually edited. Phylogenetic analysis was performed with PAUP* version 4.0b10 (37) by using the maximum likelihood (ML) method. To determine the best model of evolution for the alignments, FINDMODEL was used (http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/hiv-db/findmodel/findmodel.html). The optimal models General Time Reversible plus Gamma and Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano plus Gamma were then used to construct the optimal ML trees.
The reliability of the branching orders was tested using the bootstrap approach as implemented by PAUP* for 1,000 replicates.
RESULTS
Transmission and early kinetics of SIVcpz infection.
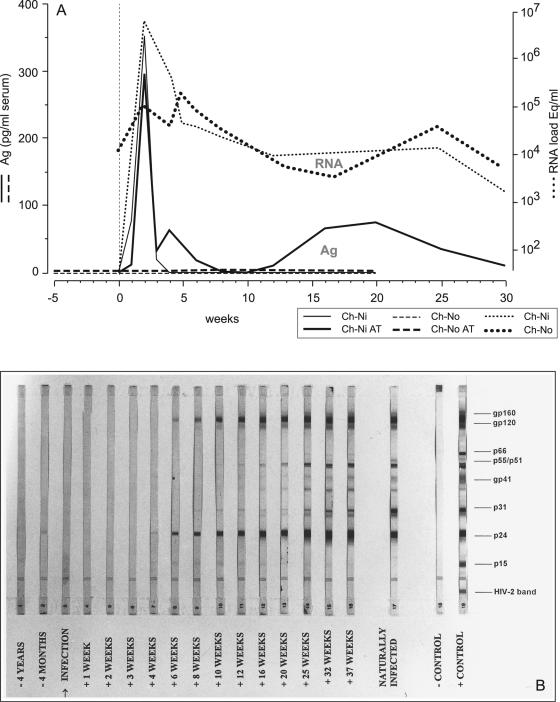
Confirmation that ch-Ni was infected following i.v. exposure to his infected cage mate's (ch-No) PBMCs was provided by a characteristic pattern of seroconversion on a Western blot, where between weeks 4 and 6, antibodies first binding to structural Gag and Env proteins appeared in a pattern common to that observed in HIV-1-infected humans (Fig. 1B). Results were confirmed by ELISA using HIV-1 antigens (data not shown). Plasma viremia was documented by antigen capture in ELISA, as well as with reverse transcription-PCR of plasma as early as 1 week following exposure. While plasma antigen in the chronically infected animal ch-No remained undetectable, Gag antigen was detected at concentrations greater than 350 pg/ml 2 weeks postexposure but rapidly declined following seroconversion in ch-Ni. Indeed, as has been documented in HIV-1-infected humans, immune complexes were detected by acidic dissociation, revealing the evidence of previously undetected antibody-complexed antigen at weeks 4 to 6, which returned between weeks 12 and 30. During that same time period, no antibody complexed to antigen could be detected in the chronically infected animal (Fig. 1A). In contrast, quantitative PCR analysis for plasma viral RNA showed persistently high levels of SIVcpz RNA fluctuating between 104 and 105 RNA copies/ml of plasma in ch-No. Remarkably, 2 weeks following i.v. exposure, the seronegative ch-Ni developed plasma viral-RNA concentrations greater than 5 × 106 copies/ml, which declined rapidly during the seroconversion period and subsequently reached threshold levels similar to those observed in ch-No (Fig. 1A).
FIG. 1.
(A) Plasma p24 antigen (Ag) and virus load kinetics in acute versus chronic SIVcpz-ANT infection. Antigen capture of p24 over time was evaluated in all plasma samples, either directly or following acidic dissociation (AT) (bold lines), of antibody-bound antigen complexes. Plasma viral-RNA levels during the same period are shown plotted on the y axis and are represented by the upper two dotted lines. (B) Seroconversion profile of ch-Ni using HIV-1 Western blot strips (Diagnostics HIV Blot 2.2; Genelabs, Redwood City, CA). Sera of ch-Ni from consecutive time points pre- and postinfection were evaluated for the presence of antibodies to SIVcpz-ANT. As a positive control, serum of the naturally infected ch-No was used.
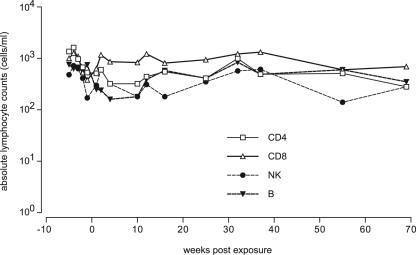
To determine the effect of acute SIVcpz infection on CD4+ T cells and other subsets, a detailed longitudinal analysis was undertaken. Interestingly, in the immediate postinfection period, a minor decline in both CD4 T cells and NK subsets was observed, but fluctuations remained within normal limits (Fig. 2). Similarly, a transient decline in the B-cell subset was apparent within 5 weeks of infection. All lymphocyte subsets remained in the normal range up to 70 weeks postinfection. No evidence of thrombocytopenia or anemia has been observed in this animal to date.
FIG. 2.
Absolute lymphocyte counts. Whole blood of ch-Ni was analyzed for specific lymphocyte subsets. □, CD4 T-cells; ▵, CD8 T-cells; •, NK cells; ▾, B cells.
SIVcpz superinfection in the presence of HIV-1.
In contrast to the chimpanzee subspecies P. t. schweinfurthii and P. t. troglodytes, from which several variants of SIVcpz have been isolated, no evidence for natural SIVcpz infection has been found in the subspecies Pan troglodytes verus (33). The vast majority of chimpanzees that were used to establish captive chimpanzee breeding colonies in North America and in Europe have been of the P. t. verus subspecies. Of the seven animals available for the transmission study, six were of the subspecies P. t. verus and one was retrospectively identified as a P. t. schweinfurthii animal. Five P. t. verus and one P. t. schweinfurthii chimpanzees were persistently infected with clade B strains of HIV-1 (Table 1).
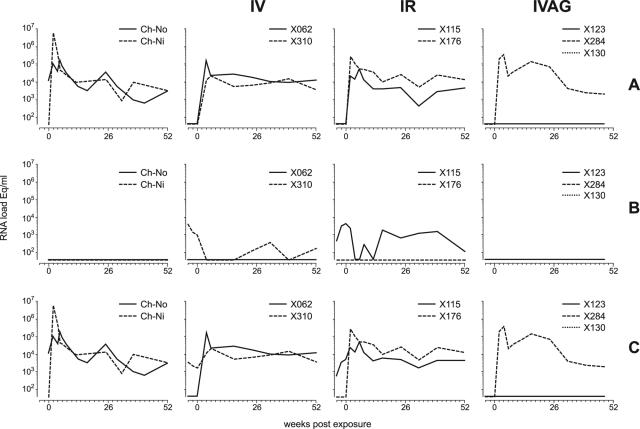
To determine if SIVcpz was capable of establishing infection despite the presence of preexisting HIV-1 infection, two HIV+ animals were exposed i.v. to an excess number of freshly cryopreserved PBMCs, established as a stock from ch-Ni in the acute infection phase. The two HIV-1IIIB-infected chimpanzees, ch-X062 and ch-X310, were readily infected by SIVcpz as determined by quantity-controlled PCR (Fig. 3). Intravenous exposure resulted in the rapid appearance of SIVcpz RNA in plasma. Interestingly, despite the rapid establishment of SIVcpz infection and the development of steady-state plasma RNA levels comparable to those of ch-No and ch-Ni (Fig. 3), the peak viral load was at least 1 log unit less than in the natural P. t. schweinfurthii host. One animal (ch-X310) had detectable HIV-1 viral loads in plasma prior to SIVcpz superinfection (approximately 103 RNA eq/ml), which declined below detection levels (40 copies/ml) during the acute phase of SIVcpz infection (Fig. 3).
FIG. 3.
Viral RNA in plasma. (A) SIVcpz-specific, (B) HIV-1-specific, and (C) cumulative lentiviral loads per ml of plasma. Column 1 (from left), i.v. exposure of naive P. t. schweinfurthii (ch-Ni); column 2, i.v. exposure of two HIV-1 carriers; column 3, i.r. exposure of two HIV-1 carriers; column 4, i.vag. exposure of two HIV-1 carriers and one naive animal (X284).
Having demonstrated that SIVcpz superinfection could occur by i.v. exposure with PBMCs, we set out to determine if mucosal infection could occur as easily by using plasma separated from the same PBMCs from ch-Ni used to infect ch-X062 and ch-X310. Approximately 0.25 ml of cell-free plasma was diluted in 1.75 ml of PBS and was administered i.r. to ch-X115 (HIV-1SF2 preinfected) and ch-X176 (persistently HIV-1IIIB infected). Despite detectable HIV-1 RNA in the plasma of animal ch-X115, both that animal and ch-X176 (in which no HIV-1 viremia was detected) became infected (Fig. 4) with kinetics similar to those of the i.v.-exposed animals. Notably, in animal ch-X115, which had detectable HIV-1 viremia prior to SIVcpz exposure, the preexisting HIV-1 RNA loads dropped during the acute phase of SIVcpz infection, as was seen in the i.v.-exposed ch-X310.
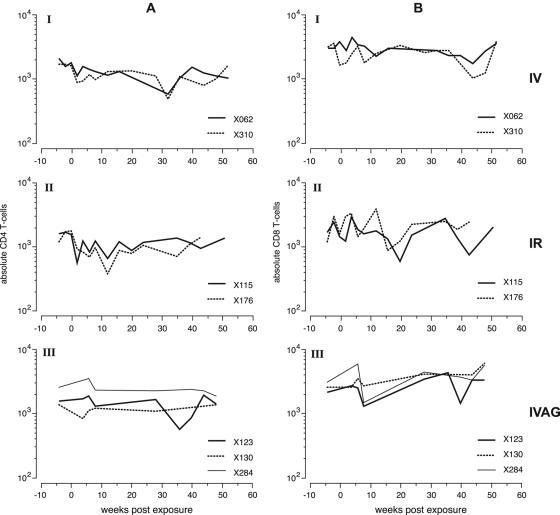
FIG. 4.
Absolute CD4 T-cell counts (A) and absolute CD8 T-cell counts (B) in the three different groups of animals used in the SIVcpz transmission/superinfection study. I, intravenous exposure; II, intrarectal exposure; III, intravaginal exposure.
The effects of vaginal exposure of SIVcpz were studied in two chronically HIV-1-infected animals, one with HIV-1SF2 (ch-X123) and one with HIVIIIB (ch-X130). Neither animal became infected when the same dose of plasma that resulted in i.r. infection was used. The animals were monitored for approximately 8 months to confirm their negative status. To determine if the addition of infected cells would facilitate vaginal infection, the animals were reexposed to SIVcpz using the same dose of plasma mixed together with the same dose of PBMCs used to establish i.v. superinfection. In addition, a naïve control animal was added to the group and exposed at the same time to rule out possible effects of preexisting HIV infection. None of the animals were in estrus at the time of administration and were estimated by the attending veterinarian to be at similar stages of their cycles. However, as seen in Fig. 3, only the HIV-1-naïve animal, ch-X284, became infected, while the two HIV-1-infected animals resisted vaginal exposure to the same combination of infected plasma and PBMCs.
Lack of evidence for progression to AIDS after primary or secondary SIVcpz infection.
Detailed longitudinal fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis failed to reveal any evidence of progression to AIDS in the study animals. Interestingly, while absolute CD4+ T-cell levels appeared to subtly and transiently decline following i.v. and i.r. infection (Fig. 4A), the effect was not observed in the i.vag.-infected previously HIV-1-naïve animal, ch-X284 (Fig. 4A). CD8 T-cell levels were not influenced by HIV/SIVcpz coinfection (Fig. 4B). These results were in agreement with normal uninfected chimpanzee values and did not differ from previous follow-up studies (15, 32).
Kinetics of neutralizing-antibody development.
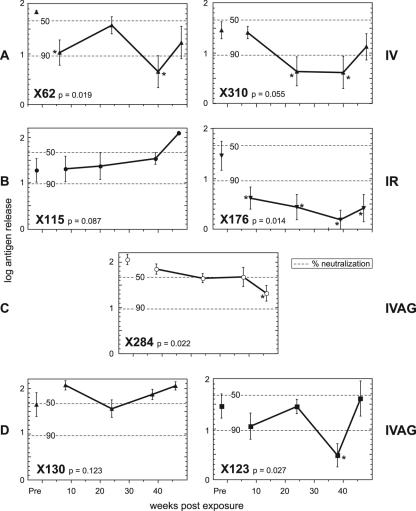
Plasma taken from five of the HIV-1-infected chimpanzees before their exposure to SIVcpz produced a 50 to 90% reduction in antigen release. The exception was ch-X062, where no reduction was observed. However, none of the reductions reached statistical significance.
Both the chimpanzees challenged by the intravenous route developed statistically significant neutralization: X62 by week 6 and X310 by week 24 (Fig. 5). The intrarectally challenged chimpanzee, X176, also developed statistically significant neutralization by week 6. In contrast, X115 did not show a neutralizing-antibody response at any time (final observation was at week 46). Of the female chimpanzees, X123 showed neutralization of the challenge virus at week 37 despite showing no viremia with the virus at any stage. Chimpanzee X130 never developed neutralizing antibodies. The control intravaginally challenged chimpanzee first showed a low level of neutralization, which was nonetheless statistically significant, at week 46.
FIG. 5.
Neutralization of SIVcpz by plasma from HIV-1-infected chimpanzees (closed symbols) and a control chimpanzee (open symbols) prior to (Pre) and following infection with SIVcpz. Means with standard-error bars of antigen concentrations released into culture supernatants expressed in log10 arbitrary units are displayed. P, statistical significance of the F ratio derived from analysis of variance; asterisks indicate statistically significant reduction in antigen release relative to the mean from plasmas of two control chimpanzees. The dotted lines indicate 50% and 90% reductions in antigen release.
Analysis of viral variation following transmission of SIVcpz.
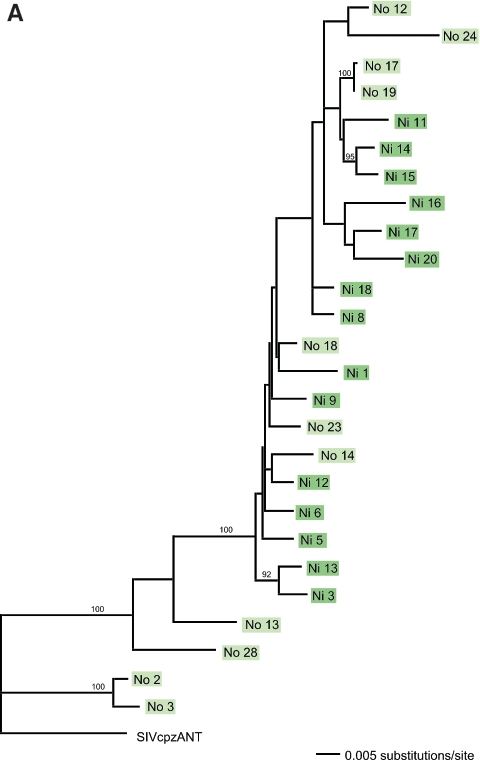
To determine which viral variants were transferred to ch-Ni after experimental infection with PBMCs from ch-No, we determined the quasispecies in the viral inoculum from ch-No and in the blood sample taken from ch-Ni 2 weeks posttransmission (Fig. 6A). From ch-No and ch-Ni, we analyzed 11 and 15 clones, respectively, each spanning the V1-V5 region.
FIG.6.
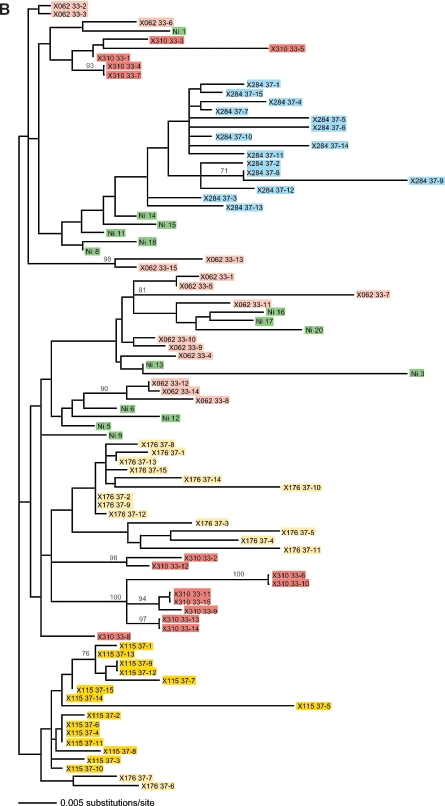
Quasispecies analysis of challenge inocula and virus populations in SIVcpz-ANT-infected chimpanzees. (A) Maximum likelihood analysis using the General Time Reversible plus Gamma model of nucleotide sequences obtained from the ch-No inoculum (light-green boxes) and from the 2-week postexposure ch-Ni sample (dark-green boxes), encompassing the gp120 V1-V5 regions (nucleotides 5813 to 7161 relative to the SIVcpz-ANT published sequence). Bootstrap values (as percentages of 1,000 resamplings) are indicated. The tree was rooted with the published SIVcpz-ANT sequence derived from ch-No 5 years earlier (GenBank accession no. U42720). (B) Phylogenetic analysis of the SIVcpz quasispecies after superinfection of HIV-1-infected chimpanzees. The ML tree was estimated using the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano plus Gamma model as suggested by FINDMODEL. The analysis was based on the alignment of the gp120 V1-V5 regions (nucleotides 5987 to 6828). Viral variants found after infection via different routes are indicated by color coding. Pink boxes, intravenous; yellow boxes, intrarectal; blue boxes, intravaginal. Sequences derived from the ch-Ni inoculum are indicated in green. Different individuals receiving SIV via the same route are indicated by different shades of the same color.
The blood sample taken from ch-Ni at this time point was used to establish the plasma-derived and PBMC-derived SIVcpz stock used to infect the seven other chimpanzees (six HIV-infected and one transmission control animal) in the second part of this study. Quasispecies analysis was done to see if the route of transmission had an effect on the viral variants that were transmitted. We applied the same genetic analysis to SIVcpz V1-V3 env sequences obtained from each of the animals that had received SIVcpz via different infection routes (i.v., i.r., and i.vag.) from the ch-Ni inocula. Interestingly, no evidence was found for a clustering of viral variants related to the route of infection, but viruses from individual animals clustered together irrespective of the transmission route (Fig. 6B).
DISCUSSION
The transmission of SIVcpz from chimpanzees to humans is the leading hypothesis for the origin of the AIDS pandemic. However, many crucial questions remain to be answered concerning the natural history of this apparently apathogenic infection in its natural host, the chimpanzee. Detailed information on transmission and follow-up of SIVcpz infection in free-ranging chimpanzee populations is unlikely because of ethical and sociobehavioral constraints on studying endangered species in the wild. In controlled settings in specialized primate research centers, a number of critical observations are possible, providing data on the possible routes of transmission and the early and longitudinal effects of acute and chronic SIVcpz infection. Furthermore differences between retroviral infections in human and chimpanzee hosts may be anticipated.
A case in point is human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1, which in human populations in southern Japan is primarily transmitted during breastfeeding. Until recently, STLVcpz of chimpanzees, the counterpart of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 of humans, was assumed to be transmitted in this way. However, a retrospective study of a large closed breeding group of chimpanzees studied for more than 20 years revealed that breastfeeding was not the primary cause of transmission of this retrovirus in this species (26). In addition to species-specific social and behavioral factors, possible explanations for differences in the modes transmission may include subtle differences in cell and tissue tropism and patterns of viremia. Alternatively, the lower vaginal transmission rates may differ in captivity and in the wild or have a much lower efficiency than in HIV-1-infected humans (33, 36).
The transmission of uncultured SIVcpz from cell-free plasma and/or plasma-free PBMCs from a viremic donor was established by intravenous transmission or by the intrarectal mucosal route. Most remarkably, the prior presence of chronic HIV-1 infection did not prevent or even slightly modify infection with the related SIVcpz. However, this observation was different with respect to vaginal transmission. Both animals that were chronically infected with HIV-1 resisted SIVcpz infection even when separate infectious stocks of plasma and PBMCs were combined, while the naïve animal became readily infected by the same route and with the same dose. Although limited in number of animals studied, further consideration should be given to local immunity induced by prior HIV infection preventing infection via the vaginal mucosa. However, mucosal washes before exposure failed to detect specific mucosal antibody titers to HIV-1/SIVcpz (unpublished data), which would imply that other adaptive cellular or innate mechanisms might have played a role (33, 36).
SIVcpz has been identified from only two subspecies of chimpanzees to date. The two subspecies from which SIVcpz has not been isolated (P. t. verus and Pan troglodytes vellerosus) are geographically located west and north, respectively, of P. t. troglodytes and further west of the eastern P. t. schweinfurthii chimpanzees, the last two being documented carriers of SIVcpz (10, 11). From the data presented in this study, transmission from one subspecies (P. t. schweinfurthii) to another, geographically distant subspecies (P. t. verus) is clearly possible. Natural geographic barriers separating wild, free-ranging populations may have played a role in limiting the spread of SIVcpz to this subpopulation in the past.
The early kinetics of SIVcpz infection in many ways were similar to HIV-1 infection in humans. Peak plasma concentrations of SIVcpz RNA were mirrored by plasma antigen peaks at 2 weeks, which then declined to low or undetectable levels as animals began to seroconvert. Furthermore, evidence of immune complex formation between SIVcpz and antibodies was documented by acid dissociation, and using this technique, plasma antigen could be detected for a longer period in ch-Ni. Interestingly, similar to HIV-1 in humans, animals infected with SIVcpz seroconvert early to the Gag antigen. However, this observation differs from the other relatively well-studied natural SIV infections of African green monkeys (SIVagm) and sooty mangabeys (SIVsm), which frequently fail to seroconvert to Gag and are proposed to be tolerant of that antigen (19). The development of neutralizing antibodies was protracted and differed from animal to animal, independently of prior HIV infection.
Only a minor subset of the variants found in the inoculum of ch-No were found in the serum of ch-Ni 2 weeks after transfer of SIVcpz. As in HIV-infected humans, sequence divergence was greater in the healthy asymptomatic chronic carrier (ch-No stock) than in the acutely infected animal (ch-Ni; week 2 postexposure). These observations suggest that intact adaptive immune responses had matured and were more effective in eliciting observable adaptive viral envelope changes as a result of chronic versus acute infection.
We were interested to see if preexisting infection with HIV-1, in combination with different routes of infection, would influence the compositions of the quasispecies. No inoculation route-specific selection of variants was evident following superinfection of HIV-1-infected animals (Fig. 6B). Regardless of the preexisting HIV infection or infection route, the individual quasispecies were derived from one or a few variants that were found in the inoculum.
Detailed analyses of the cellular immune responses which chimpanzees mount to SIVcpz infection have recently been initiated and will be correlated with sequence variants in other regions of the SIVcpz genome. Sequence analysis of animals that became infected by different routes failed to reveal a distinct pattern of variants that became established as a consequence of the route by which infection was acquired; however, more detailed longitudinal analysis is planned.
The hallmark changes of CD4+ T-cell depletion and activation of CD8+ T cells, as seen in humans, were not observed in these animals infected with SIVcpz or with coinfections of SIVcpz and HIV-1. A minor and transient decline in CD4+ lymphocytes, and also B cells and NK cells, was observed in a few animals, but levels remained within the normal range, and shortly after infection, the subsets returned to preinfection levels. The critical difference between SIVcpz infection of chimpanzees and HIV-1 infection of humans appears to be related to mechanisms which allow chimpanzees to maintain numerical and functional T-cell helper activity in the face of persistent viremia. Indeed our hypothesis, which was proposed a decade ago (15), is gaining support. Our data continue to support the hypothesis that chimpanzees are able to preserve the network important for sustained CD4+ T-cell ontogeny and the antigen-presenting cell microenvironment necessary for the replacement of mature antigen-specific memory CD4+ T cells continually lost during infection (14). Part of this may be explained by this species' very effective cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) and NK responses to lentiviruses. We have previously demonstrated that HIV-1-infected chimpanzees have CTL responses that recognize highly conserved epitopes, which map across all clades (2, 3). Interestingly, long-term human survivors recognize the same or similar epitopes but are restricted by different major histocompatibility complex class I alleles (3). As further support for this hypothesis, we determined that chimpanzees have undergone a marked reduction of many major histocompatibility complex loci and that by evolutionary selection, class I loci capable of binding critical lentiviral CTL epitopes may have been selected (8). Importantly, this disease resistance is relative, and certain individuals or subspecies may prove susceptible to SIVcpz-related disease if greater numbers of naïve populations become exposed or live long enough to develop immunosuppressive disease.
This study has revealed a number of important findings. It demonstrated the potential routes of SIVcpz transmission (with the exception of mother to child) (36) and documented the early posttransmission history of SIVcpz infection in chimpanzees. Furthermore, it was revealed that SIVcpz can be readily transmitted to other subspecies of chimpanzees not known to carry SIVcpz and it was demonstrated that they too remain asymptomatic. The relative resistance of chimpanzees to the development of AIDS was again observed in the absence of immune activation and overt CD4+ T-cell loss in the face of high levels of persistent plasma lentiviremia (12). Finally, these findings demonstrate how easily HIV-1-related lentivirus super- or coinfections are established without any apparent impact of adaptive responses on plasma virus loads. Although evidence of recombination has not yet been found, these findings provide evidence for the necessary preconditions upon which they may arise.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Luiz Barbosa of NHLBI for his encouragement and for partial funding support provided under NHLBI contract NO1HB27091.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bailes, E., F. Gao, F. Bibollet-Ruche, V. Courgnaud, M. Peeters, P. A. Marx, B. H. Hahn, and P. M. Sharp. 2003. Hybrid origin of SIV in chimpanzees. Science 300:1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Balla-Jhagjhoorsingh, S., P. Mooij, G. Koopman, T. Haaksma, V. Teeuwsen, J. Heeney, and R. Bontrop. 1999. Differential cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses in HIV-1 immunised sibling chimpanzees with shared MHC haplotypes. Immunol. Lett. 66:61-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Balla-Jhagjhoorsingh, S. S., G. Koopman, P. Mooij, T. G. Haaksma, V. J. Teeuwsen, R. E. Bontrop, and J. L. Heeney. 1999. Conserved CTL epitopes shared between HIV-infected human long-term survivors and chimpanzees. J. Immunol. 162:2308-2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Beirnaert, E., B. Willems, M. Peeters, A. Bouckaert, L. Heyndrickx, P. Zhong, K. Vereecken, S. Coppens, D. Davis, P. Ndumbe, W. Janssens, and G. van der Groen. 1998. Design and evaluation of an in-house HIV-1 (group M and O), SIVmnd and SIVcpz antigen capture assay. J. Virol. Methods 73:65-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bogers, W. M., W. H. Koornstra, R. H. Dubbes, P. J. ten Haaft, B. E. Verstrepen, S. S. Jhagjhoorsingh, A. G. Haaksma, H. Niphuis, J. D. Laman, S. Norley, H. Schuitemaker, J. Goudsmit, G. Hunsmann, J. L. Heeney, and H. Wigzell. 1998. Characteristics of primary infection of a European human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade B isolate in chimpanzees. J. Gen. Virol. 79:2895-2903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Daniel, M. D., N. L. Letvin, N. W. King, M. Kannagi, P. K. Sehgal, R. D. Hunt, P. J. Kanki, M. Essex, and R. C. Desrosiers. 1985. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science 228:1201-1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Davis, D., H. Donners, B. Willems, K. Lovgren-Bengtsson, L. Akerblom, G. Vanham, S. Barnett, B. Morein, J. L. Heeney, and G. van der Groen. 2004. Neutralization of primary HIV-1 SF13 can be detected in extended incubation phase assays with sera from monkeys immunized with recombinant HIV-1 SF2 gp120. Vaccine 22:747-754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Groot, N. G., N. Otting, G. G. Doxiadis, S. S. Balla-Jhagjhoorsingh, J. L. Heeney, J. J. van Rood, P. Gagneux, and R. E. Bontrop. 2002. Evidence for an ancient selective sweep in the MHC class I gene repertoire of chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:11748-11753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Donners, H., T. Vermoesen, B. Willems, D. Davis, and G. van der Groen. 2003. The first generation of candidate HIV-1 vaccines can induce antibodies able to neutralize primary isolates in assays with extended incubation phases. Vaccine 22:104-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gagneux, P., M. K. Gonder, T. L. Goldberg, and P. A. Morin. 2001. Gene flow in wild chimpanzee populations: what genetic data tell us about chimpanzee movement over space and time. Phil. Trans R. Soc. Lond B 356:889-897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gao, F., E. Bailes, D. L. Robertson, Y. Chen, C. M. Rodenburg, S. F. Michael, L. B. Cummins, L. O. Arthur, M. Peeters, G. M. Shaw, P. M. Sharp, and B. H. Hahn. 1999. Origin of HIV-1 in the chimpanzee Pan troglodytes troglodytes. Nature 397:436-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gougeon, M. L., H. Lecoeur, F. Boudet, E. Ledru, S. Marzabal, S. Boullier, R. Roue, S. Nagata, and J. Heeney. 1997. Lack of chronic immune activation in HIV-infected chimpanzees correlates with the resistance of T cells to Fas/Apo-1 (CD95)-induced apoptosis and preservation of a T helper 1 phenotype. J. Immunol. 158:2964-2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hahn, B. H., G. M. Shaw, K. M. De Cock, and P. M. Sharp. 2000. AIDS as a zoonosis: scientific and public health implications. Science 287:607-614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Heeney, J., W. Bogers, L. Buijs, R. Dubbes, P. ten Haaft, W. Koornstra, H. Niphuis, P. Nara, and V. Teeuwsen. 1996. Immune strategies utilized by lentivirus infected chimpanzees to resist progression to AIDS. Immunol. Lett. 51:45-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Heeney, J. L. 1995. AIDS: a disease of impaired Th-cell renewal? Immunol. Today 16:515-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hirsch, V. M., R. A. Olmsted, M. Murphey-Corb, R. H. Purcell, and P. R. Johnson. 1989. An African primate lentivirus (SIVsm) closely related to HIV-2. Nature 339:389-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Holterman, L., H. Niphuis, W. Koornstra, R. Dubbes, P. ten Haaft, and J. L. Heeney. 2000. The rate of progression to AIDS is independent of virus dose in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques. J. Gen. Virol. 81:1719-1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Holterman, L., E. J. Verschoor, B. Rosenwirth, and J. L. Heeney. 2000. Primate lentiviruses and AIDS research. AIDS Rev. 2:155-167. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Holzammer, S., E. Holznagel, A. Kaul, R. Kurth, and S. Norley. 2001. High virus loads in naturally and experimentally SIVagm-infected African green monkeys. Virology 283:324-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huet, T., R. Cheynier, A. Meyerhans, G. Roelants, and S. Wain-Hobson. 1990. Genetic organization of a chimpanzee lentivirus related to HIV-1. Nature 345:356-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marx, P. A., Y. Li, N. W. Lerche, S. Sutjipto, A. Gettie, J. A. Yee, B. H. Brotman, A. M. Prince, A. Hanson, R. G. Webster, et al. 1991. Isolation of a simian immunodeficiency virus related to human immunodeficiency virus type 2 from a West African pet sooty mangabey. J. Virol. 65:4480-4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Murphey-Corb, M., L. N. Martin, S. R. Rangan, G. B. Baskin, B. J. Gormus, R. H. Wolf, W. A. Andes, M. West, and R. C. Montelaro. 1986. Isolation of an HTLV-III-related retrovirus from macaques with simian AIDS and its possible origin in asymptomatic mangabeys. Nature 321:435-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Murthy, K. K., E. K. Cobb, Z. el-Amad, H. Ortega, F. C. Hsueh, W. Satterfield, D. R. Lee, M. L. Kalish, N. L. Haigwood, R. C. Kennedy, K. S. Steimer, A. Schultz, and J. A. Levy. 1996. Titration of a vaccine stock preparation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1SF2 in cultured lymphocytes and in chimpanzees. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 12:1341-1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nerrienet, E., M. L. Santiago, Y. Foupouapouognigni, E. Bailes, N. I. Mundy, B. Njinku, A. Kfutwah, M. C. Muller-Trutwin, F. Barre-Sinoussi, G. M. Shaw, P. M. Sharp, B. H. Hahn, and A. Ayouba. 2005. Simian immunodeficiency virus infection in wild-caught chimpanzees from Cameroon. J. Virol. 79:1312-1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Niphuis, H., R. H. Dubbes, P. J. ten Haaft, W. H. Koornstra, R. E. Bontrop, M. P. Cranage, and J. L. Heeney. 1994. Infectivity and virulence of cell-associated SIVmac after single passage in vivo. AIDS 8:1730-1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Niphuis, H., E. J. Verschoor, I. Bontjer, M. Peeters, and J. L. Heeney. 2003. Reduced transmission and prevalence of simian T-cell lymphotropic virus in a closed breeding colony of chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus). J. Gen. Virol. 84:615-620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ondoa, P., D. Davis, B. Willems, L. Heyndrickx, L. Kestens, I. van der Berg, S. Coppens, W. Janssens, J. Heeney, and G. van der Groen. 2001. Genetic variability of the V1 and V2 env domains of SIVcpz-ant and neutralization pattern of plasma viruses in a chimpanzee infected naturally. J. Med. Virol. 65:765-776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ondoa, P., L. Kestens, D. Davis, C. Vereecken, B. Willems, K. Fransen, J. Vingerhoets, G. Zissis, P. ten Haaft, J. Heeney, and G. van der Groen. 2001. Longitudinal comparison of virus load parameters and CD8 T-cell suppressive capacity in two SIVcpz-infected chimpanzees. J. Med. Primatol. 30:243-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Peeters, M., V. Courgnaud, B. Abela, P. Auzel, X. Pourrut, F. Bibollet-Ruche, S. Loul, F. Liegeois, C. Butel, D. Koulagna, E. Mpoudi-Ngole, G. M. Shaw, B. H. Hahn, and E. Delaporte. 2002. Risk to human health from a plethora of simian immunodeficiency viruses in primate bushmeat. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 8:451-457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Peeters, M., K. Fransen, E. Delaporte, M. Van den Haesevelde, G. M. Gershy-Damet, L. Kestens, G. van der Groen, and P. Piot. 1992. Isolation and characterization of a new chimpanzee lentivirus (simian immunodeficiency virus isolate cpz-ant) from a wild-captured chimpanzee. AIDS 6:447-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Peeters, M., and P. M. Sharp. 2000. Genetic diversity of HIV-1: the moving target. AIDS 14(Suppl. 3):S129-S140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rutjens, E., S. Balla-Jhagjhoorsingh, E. Verschoor, W. Bogers, G. Koopman, and J. Heeney. 2003. Lentivirus infections and mechanisms of disease resistance in chimpanzees. Front Biosci. 8:d1134-d1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Santiago, M. L., M. Lukasik, S. Kamenya, Y. Li, F. Bibollet-Ruche, E. Bailes, M. N. Muller, M. Emery, D. A. Goldenberg, J. S. Lwanga, A. Ayouba, E. Nerrienet, H. M. McClure, J. L. Heeney, D. P. Watts, A. E. Pusey, D. A. Collins, R. W. Wrangham, J. Goodall, J. F. Brookfield, P. M. Sharp, G. M. Shaw, and B. H. Hahn. 2003. Foci of endemic simian immunodeficiency virus infection in wild-living eastern chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii). J. Virol. 77:7545-7562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Santiago, M. L., C. M. Rodenburg, S. Kamenya, F. Bibollet-Ruche, F. Gao, E. Bailes, S. Meleth, S. J. Soong, J. M. Kilby, Z. Moldoveanu, B. Fahey, M. N. Muller, A. Ayouba, E. Nerrienet, H. M. McClure, J. L. Heeney, A. E. Pusey, D. A. Collins, C. Boesch, R. W. Wrangham, J. Goodall, P. M. Sharp, G. M. Shaw, and B. H. Hahn. 2002. SIVcpz in wild chimpanzees. Science 295:465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sharp, P. M., G. M. Shaw, and B. H. Hahn. 2005. Simian immunodeficiency virus infection of chimpanzees. J. Virol. 79:3891-3902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Switzer, W. M., B. Parekh, V. Shanmugam, V. Bhullar, S. Phillips, J. J. Ely, and W. Heneine. 2005. The epidemiology of simian immunodeficiency virus infection in a large number of wild- and captive-born chimpanzees: evidence for a recent introduction following chimpanzee divergence. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 21:335-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Swofford, D. L. 2002. PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods), v. 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass.
- 38.ten Haaft, P., K. Murthy, M. Salas, H. McClure, R. Dubbes, W. Koornstra, H. Niphuis, D. Davis, G. van der Groen, and J. Heeney. 2001. Differences in early virus loads with different phenotypic variants of HIV-1 and SIV(cpz) in chimpanzees. AIDS 15:2085-2092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.ten Haaft, P., B. Verstrepen, K. Uberla, B. Rosenwirth, and J. Heeney. 1998. A pathogenic threshold of virus load defined in simian immunodeficiency virus- or simian-human immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques. J. Virol. 72:10281-10285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vanden Haesevelde, M. M., M. Peeters, G. Jannes, W. Janssens, G. van der Groen, P. M. Sharp, and E. Saman. 1996. Sequence analysis of a highly divergent HIV-1-related lentivirus isolated from a wild captured chimpanzee. Virology 221:346-350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]