Abstract
l-Cysteine is an important amino acid in terms of its industrial applications. We previously found a marked production of l-cysteine from glucose in recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing an altered cysE gene encoding feedback inhibition-insensitive serine acetyltransferase. Also, a lower level of cysteine desulfhydrase (CD) activity, which is involved in l-cysteine degradation, increased l-cysteine productivity in E. coli. The use of an l-cysteine efflux system could be promising for breeding l-cysteine overproducers. In addition to YdeD and YfiK, which have been reported previously as l-cysteine exporter proteins in E. coli, we analyzed the effects of 33 putative drug transporter genes in E. coli on l-cysteine export and overproduction. Overexpression of the acrD, acrEF, bcr, cusA, emrAB, emrKY, ybjYZ, and yojIH genes reversed the growth inhibition of tnaA (the major CD gene)-disrupted E. coli cells by l-cysteine. We also found that overexpression of these eight genes reduces intracellular l-cysteine levels after cultivation in the presence of l-cysteine. Amino acid transport assays showed that Bcr overexpression conferring bicyclomycin and tetracycline resistance specifically promotes l-cysteine export driven by energy derived from the proton gradient. When a tnaA-disrupted E. coli strain expressing the altered cysE gene was transformed with a plasmid carrying the bcr gene, the transformant exhibited more l-cysteine production than cells carrying the vector only. A reporter gene assay suggested that the bcr gene is constitutively expressed at a substantial level. These results indicate that the multidrug transporter Bcr in the major facilitator family is involved in l-cysteine export and overproduction in genetically engineered E. coli cells.
l-Cysteine is an important amino acid in terms of its applications in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries. However, due to feedback inhibition by l-cysteine of serine acetyltransferase (SAT), which catalyzes the formation of O-acetyl-l-serine (OAS) from acetyl-coenzyme A and l-serine (19, 32), microorganisms do not excrete l-cysteine. To obtain l-cysteine producers, we previously constructed Escherichia coli cysE genes that encode altered SATs. These genes were made genetically less sensitive to feedback inhibition by l-cysteine through site-directed or random mutagenesis (22, 34). We found a marked production of l-cysteine plus l-cystine from glucose in recombinant E. coli cells expressing the altered cysE genes (22, 34). Furthermore, the expression of two cDNAs encoding feedback inhibition-insensitive SATs of Arabidopsis thaliana significantly increased productivity (35).
In the same investigation (22), we discovered that proteins with cysteine desulfhydrase (CD) activity were crucial for l-cysteine degradation in E. coli and also that CD activity was closely related to the l-cysteine productivity of E. coli. CD is known to catalyze the degradation of l-cysteine to pyruvate, ammonia, and sulfide. In E. coli, cystathionine-β-lyase, which mainly catalyzes the conversion of cystathionine to homocysteine, pyruvate, and ammonia (10), and tryptophanase, which primarily degrades l-tryptophan to indole, pyruvate, and ammonia (23), have been shown to exhibit CD activity in vitro and in vivo (10, 24). In addition to the above two enzymes, we recently identified three additional proteins with CD activity as OAS sulfhydrylase A, OAS sulfhydrylase B, and the MalY protein (2). Gene disruption of each protein was significantly effective for overproduction of l-cysteine and l-cystine.
Because high levels of intracellular l-cysteine have been reported to be inhibitory or even toxic (8, 15-17, 26, 33), further improvements in l-cysteine production are expected to use the amino acid efflux system. Recently, export systems for l-cysteine in E. coli were identified. The ydeD and yfiK genes were discovered to augment l-cysteine production when overexpressed (6, 12). E. coli cells overexpressing YdeD, which belongs to the PecM family of transporters, excreted considerable amounts of OAS and l-cysteine (6). Overexpression of YfiK, an RthB family member, led to the drastic and parallel secretion of OAS and l-cysteine into the medium (12). l-Cysteine is also exported from the E. coli cytoplasm to the periplasm by CydDC, which is an ATP-binding cassette-type transporter required for cytochrome assembly (5, 27). CydDC overexpression conferred resistance to high extracellular l-cysteine concentrations. In E. coli, there are 37 open reading frames (ORFs) assumed to be drug transporter genes on the basis of sequence similarities, although the transport abilities of most of them have not yet been established. Five families of drug extrusion translocases have currently been identified based on sequence similarity (4, 28). These are the MF (major facilitator) family, SMR (small multidrug resistance) family, RND (resistance nodulation cell division) family, ABC (ATP-binding cassette) family, and MATE (multidrug and toxic compound extrusion) family. Nishino and Yamaguchi (25) cloned all 37 putative drug transporter genes in E. coli and investigated their drug resistance phenotypes.
Our objectives in this study were (i) to identify an l-cysteine exporter from 33 putative drug transporter genes in E. coli, (ii) to analyze the function of the transporter in l-cysteine export in vivo and in vitro, and (iii) to test l-cysteine production by E. coli cells overexpressing the transporter gene. As a result, we report here that the MF-type transporter Bcr is involved in the export and overproduction of l-cysteine in E. coli cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and plasmids.
The E. coli strains used in this study were JM39 (F+ cysE51 tfr-8) (9) and JM39ΔtnaA, which is a tnaA disruptant derived from JM39 (1). Strain DH5α [F−λ− φ80dlacZΔM15 Δ(lacZYA-argF)U169 deoR recA1 endA1 hsdR17(rK− mK+) supE44 thi-1 gyrA96] was used to subclone the E. coli gene.
The 33 multicopy plasmids carrying putative drug transporter ORFs were constructed as reported previously (25). The ORFs were amplified with native promoters and peripheral genes by PCR using primers containing the restriction enzyme site that exists in the multicloning sites of the pUC118 and pUC119 vectors containing the bacterial ampicillin resistance gene (Takara Bio, Ohtsu, Japan). All drug transporter ORFs were arranged to be in the same orientation as the lac promoter of pUC vectors, while some of the ORFs were in the reverse orientation. Plasmid pACYC184 (supplied by S. Yasuda), containing the bacterial chloramphenicol resistance gene, was used to clone the altered cysE gene that encodes the Met256Ile mutant SAT. Plasmid pNN387 (supplied by R. W. Davis), containing the bacterial chloramphenicol resistance gene, was used for reporter gene assay of the bcr gene.
Media and cultivation.
Luria-Bertani (LB) complete medium (30) and M9 minimal medium (30) were used for general cultivations. The E. coli recombinant strains were grown in LB or M9 medium containing 0.4% glucose (wt/vol). If necessary, ampicillin (50 μg/ml) and/or chloramphenicol (100 μg/ml) was added. For solid media, 2% agar was added. Growth was monitored by measurement of the optical density at 610 nm (OD610).
C1 medium with sodium thiosulfate (C1+TS) was used for the production of l-cysteine and l-cystine (35). The pH was adjusted to 7.0 using KOH. For the production of amino acids, a loopful of cells cultured for 24 h on LB solid medium containing ampicillin and chloramphenicol at 30°C was inoculated into 20 ml of C1+TS in a 500-ml flask and cultured at 30°C for 72 h on a reciprocal shaker maintained at 120 strokes per min (35). Growth was measured by the absorbance (OD562) of the culture broth after appropriate dilution with 0.1 N HCl.
Construction of plasmids.
The enzymes used for DNA manipulations were obtained from Takara Bio. The yde gene involved in efflux of l-cysteine and OAS (6) was cloned into pUC118. A DNA fragment of the yde gene containing the putative promoter and terminator regions was prepared by PCR from genomic DNA from strain JM39, using oligonucleotide primers 5′-TTT GGG AAG CTT CTT ATC CGC CAG GAT ACC AAA ACC-3′ and 5′-GTT TGG GGA TCC CCA GTT GTT ACT TCT TGT GCC AAT G-3′ (underlining indicates the positions of HindIII and BamHI sites, respectively). The unique amplified band of 1.3 kb was digested with HindIII and BamHI and then ligated to the large fragment of pUC118 digested with HindIII and BamHI to construct pUCydeD. The nucleotide sequence of the ydeD gene was confirmed by DNA sequencing.
To coexpress the Met256Ile mutant SAT with the l-cysteine exporter, the 1.2-kb BamHI-SalI fragment from plasmid pCEM256I (22) was ligated to the large fragment of pACYC184 digested with BamHI and SalI to construct pACYC-M256I.
We also constructed a plasmid carrying only the bcr gene as follows. The plasmid pUCbcr was digested with Eco81I and BstPI to recover the 5.1-kb fragment. This fragment carried the incomplete rsuA gene, with a truncation of the sequence encoding the carboxyl terminus from amino acid residues 70 to 232, and the entire bcr gene with its native promoter. Both ends of the fragment were blunted by T4 DNA polymerase and self-ligated to construct plasmid pUCbcr-rsuA.
Intracellular and extracellular contents of l-cysteine.
After cultivation in 2 ml of LB medium containing ampicillin at 37°C for 12 h to stationary phase, culture samples were diluted with LB medium to an OD610 of 2.0. The cells from 1 ml of diluted suspension were harvested, washed twice with distilled water, and suspended in 0.1 ml of distilled water. The cells were incubated in a water bath, and intracellular amino acids were extracted by boiling for 10 min. After centrifugation (1 min at 15,000 × g), the supernatant was used as intracellular samples. The amount of l-cysteine was determined by the method of Gaitonde, as described previously (13). One hundred microliters of sample which had been treated with Gaitonde reagent (250 mg ninhydrin dissolved in a mixture of 4 ml of HCl and 16 ml of acetic acid) was heated in a boiling water bath for 5 min and then cooled rapidly on ice before dilution to 400 μl using 100% ethanol. After 30 min at room temperature, the reaction products were measured at 560 nm.
Culture supernatants were used as extracellular samples. The concentrations of l-cysteine and l-cystine were determined by a microbioassay with Pediococcus acidilactici IFO 3076, as described by Tsunoda et al. (36). Since l-cysteine in the culture fluid was easily oxidized to l-cystine, which was slightly soluble in water, the culture fluids were assayed after l-cystine was dissolved with 0.5 N HCl.
Amino acid transport assays.
E. coli cells were cultured in 2 ml of LB medium containing ampicillin to the stationary growth phase. Culture samples were diluted with LB to an OD610 of 1.0. The cells from 1 ml of diluted suspension were harvested, washed with 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.3) containing 100 mM NaCl and 0.5 mM MgCl2, and suspended in 1 ml of M9 medium containing 0.4% glucose. Amino acid uptake assays were performed by incorporation of l-[35S]cysteine (1,075 Ci/mmol; 1 Ci = 37 GBq), l-[14C]leucine (20 mCi/mmol), l-[14C]valine (55 mCi/mmol), l-[14C]proline (246 mCi/mmol), l-[14C]serine (50 mCi/mmol), l-[14C]arginine (20 mCi/mmol), l-[14C]glutamic acid (55 mCi/mmol), and l-[14C]methionine (55 mCi/mmol) (New England Nuclear, Wilmington, Del.). One milliliter of cell suspension was preincubated for 5 min at 30°C, and the reactions were initiated at 30°C by the addition of nonlabeled and labeled amino acids to final concentrations of 200 μM and 1.0 μCi/ml, respectively. At intervals, 100-μl aliquots of the cell suspension were rapidly removed, collected on nitrocellulose filters (0.45-μm pore size) (Advantec, Tokyo, Japan), and washed twice with 10 ml of 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.3) containing 100 mM NaCl and 0.5 mM MgCl2 under vacuum within 1 min to avoid significant losses of amino acids from the cells. Amino acid export assays were performed as follows. The above reaction mixtures containing nonlabeled and labeled amino acids were incubated for 60 min at 30°C, washed with 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.3) containing 100 mM NaCl and 0.5 mM MgCl2, and suspended in 1 ml of M9 medium containing 0.4% glucose. After incubation at 30°C, 100-μl aliquots of the cell suspension were removed, collected on nitrocellulose filters, and washed twice with 10 mM morpholineethanesulfonic acid-Tris (pH 7.0). The filters were dried, and intracellular labeled amino acids were determined by liquid scintillation counting. Amino acid uptake activities were calculated in nmol per min per mg dry weight. The export rate was also determined based on the remaining labeled amino acid content in the cells. E. coli cells were de-energized with carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) (200 μM [final concentration]) to collapse the proton gradient.
Reporter gene assay.
A 400-bp fragment containing the 5′ upstream region of the bcr gene was amplified by PCR with plasmid pUCbcr (25) and oligonucleotide primers 5′-CGC GCG GCC GCG GTG CTG ATG ACT GAT GAT-3′ and 5′-CGC AAG CTT AAC GGG CTC CTG AAA GTC ATT-3′ (underlining indicates the positions of NotI and HindIII sites, respectively). The PCR products were digested with NotI and HindIII and inserted into the NotI-HindIII site proximal to the coding region of lacZ in pNN387 to generate pNNbcr-P. Plasmid pNNbcr-P was used to transform strain JM39ΔtnaA. After incubation of the resultant transformant in LB medium containing chloramphenicol at 37°C to the exponential growth phase, tetracycline (1 μg/ml) or 10 mM l-cysteine was added. At intervals (0 min to 180 min), the cells were harvested and lysed. β-Galactosidase activity was then measured at 30°C by means of the hydrolysis of o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside to produce o-nitrophenol and galactose. β-Galactosidase activity (in Miller units) was calculated using the following formula: (OD420 of o-nitrophenol × 1,000/min/ml)/OD600 of the culture (21).
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The GenBank accession numbers for the bcr and ydeD genes are X63703 and D90796, respectively.
RESULTS
Overexpression of eight drug transporter genes reverses growth inhibition of tnaA-disrupted E. coli cells by l-cysteine.
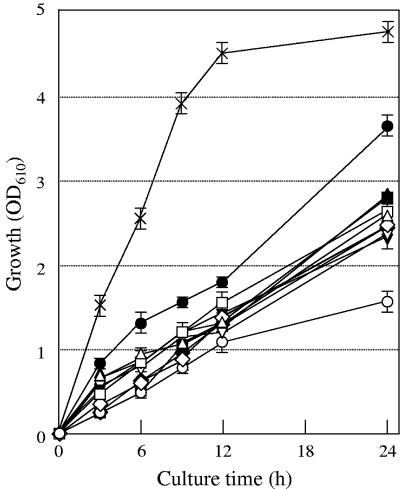
Although the mechanisms are not yet understood, it has previously been observed that the growth of E. coli cells is inhibited by excess l-cysteine (15). It was demonstrated that proteins with CD activity are involved in l-cysteine degradation in E. coli cells (1, 2, 22). Therefore, E. coli cells with a lower level of CD activity would be much more sensitive to l-cysteine than wild-type cells. Among the five CD proteins identified in E. coli, tryptophanase, encoded by the tnaA gene, contributes primarily to l-cysteine degradation (2). As shown in Fig. 1, the growth of tnaA-disrupted JM39ΔtnaA was significantly inhibited relative to that of wild-type JM39 when the cells were cultured in LB medium plus 30 mM l-cysteine at 37°C. Both strains showed the same level of growth when cultured in LB medium (data not shown).
FIG. 1.
Growth (OD610) of E. coli strains in LB medium plus 30 mM l-cysteine at 37°C. Cells of strain JM39 with pUC118 (×) and of JM39ΔtnaA with pUC118 (○), pUCydeD carrying ydeD (▵), pUCbcr carrying bcr (□), pUCemrAB carrying emrAB (▿), pUCemrKY carrying emrKY (⋄), pUCcusA carrying cusA (•), pUCacrD carrying acrD (▴), pUCacrEF carrying acrEF (▪), pUCybjYZ carrying ybjYZ (▾), or pUCyojIH carrying yojIH (⧫) were grown in LB medium at 37°C. At stationary phase, cells were diluted 1:100 in 5 ml of LB medium plus 30 mM l-cysteine. Values indicate means and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments.
Because high levels of l-cysteine are toxic to the cell, one might expect that the active efflux of a toxic metabolite such as l-cysteine is mediated by a family of transmembrane proteins referred to as drug transporters. We therefore transformed JM39ΔtnaA cells with plasmids carrying one of 33 ORFs assumed to be drug transporter genes in E. coli and examined the effects of their overexpression on the growth of E. coli cells in the presence of l-cysteine (Fig. 1). Of these 33 genes, the acrD, acrEF, bcr, cusA, emrAB, emrKY, ybjYZ, and yojIH genes significantly reversed the growth inhibition of JM39ΔtnaA cells by l-cysteine after cultivation for 24 h. We also found that the overexpression of YdeD, which is involved in the efflux of l-cysteine and OAS (6), improves the growth of JM39ΔtnaA cells in the presence of l-cysteine.
In contrast, overexpression of either the acrAB, emrD, emrE, fsr, mdfA, mdlAB, sugE, yajR, yceE, yceL, yddA, ydeA, ydeF, ydgFE, ydhC, ydhE, ydiM, yebQ, yegMNOB, yhiH, yhiUV, yidY, yieO, yjiO, or ynfM gene had no influence on the growth of JM39ΔtnaA cells in the presence of l-cysteine (data not shown). Accordingly, the eight putative drug transporter genes (the acrD, acrEF, bcr, cusA, emrAB, emrKY, ybjYZ, and yojIH genes) were chosen as likely candidates for an l-cysteine exporter.
Overexpression of eight drug transporter genes reduces intracellular l-cysteine levels in tnaA-disrupted E. coli cells.
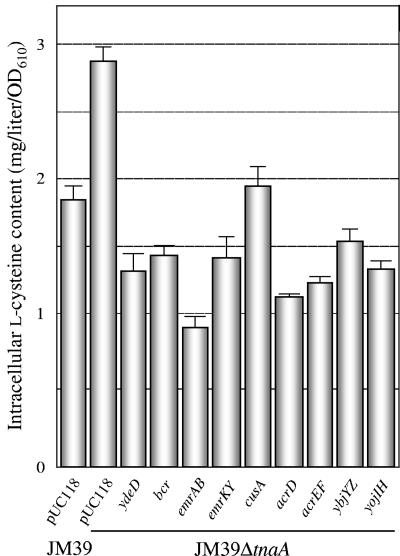
We assumed that transformants overexpressing l-cysteine exporter candidates excreted considerable amounts of l-cysteine into the medium and had decreased intracellular l-cysteine levels. E. coli cells were cultivated in LB medium plus 30 mM l-cysteine at 37°C for 12 h, and the intracellular l-cysteine levels were examined (Fig. 2). No l-cysteine was detected in any of the strains when they were cultivated in LB medium (data not shown). The intracellular l-cysteine level in JM39ΔtnaA carrying vector only was approximately 1.5-fold higher than that in JM39, probably due to lower CD activity. After cultivation in the presence of l-cysteine for 12 h, the intracellular l-cysteine contents of eight transformants were significantly reduced, to 30 to 70% of that of JM39ΔtnaA harboring the vector. We also observed that YdeD overexpression resulted in a 50% decrease in the l-cysteine level. These results suggest that these eight genes might be involved in l-cysteine export into the medium. Table 1 lists the eight drug transporter genes being considered as l-cysteine exporter candidates.
FIG. 2.
Intracellular l-cysteine contents of E. coli strains with plasmids carrying drug transporter genes. Cells were grown in LB medium plus 30 mM l-cysteine at 37°C for 12 h, and the intracellular l-cysteine content was measured. Values indicate means and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments.
TABLE 1.
Drug transporter genes in E. coli being considered as l-cysteine exporter candidates
| Drug transporter family | Gene | Known function (reference) |
|---|---|---|
| MF | bcr | Resistance to bicyclomycin, tetracycline, fosfomycin, sulfathiazole, etc. (3, 25, 37) |
| emrAB | Resistance to deoxycholate, CCCP, etc. (20, 25) | |
| emrKY | Resistance to deoxycholate (25) | |
| RND | cusA | Efflux of copper ion (14) |
| acrD | Resistance to deoxycholate, SDS, novobiocin, etc. (25, 29) | |
| acrEF | Resistance to acriflavine, ethidium bromide, rhodamine 6G, deoxycholate, etc. (18, 25) | |
| ABC | ybjYZ | Resistance to erythromycin (25) |
| yojIH | Putative transporter |
Bcr overexpression promotes l-cysteine export in tnaA-disrupted E. coli cells.
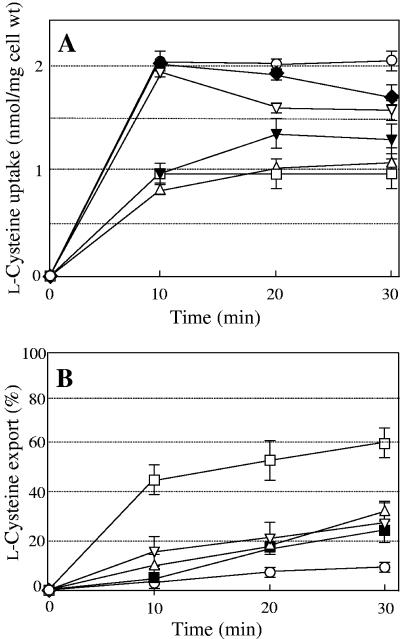
To determine whether any genes were involved in l-cysteine export, we tested JM39ΔtnaA cells overexpressing eight genes and YdeD for the uptake and export of radiolabeled l-cysteine. As shown in Fig. 3, the cells overexpressing YdeD showed a prominent decrease in the uptake and an increase in the export of l-cysteine relative to the cells carrying the vector only. Among the eight drug transporter genes tested, five genes had somewhat negative effects on uptake and positive effects on export, with those effects being greater in the case of the bcr gene. Bcr, from the MF family, and YbjYZ, from the ABC family, significantly blocked l-cysteine uptake, with levels ranging from 40% to 50% of that observed in the cells carrying the vector only (Fig. 3A). EmrAB and YojIH also reduced l-cysteine uptake after 10 min and 20 min, respectively. Bcr and EmrAB, from the MF family, and AcrEF, from the RND family, significantly accelerated l-cysteine export compared with the cells carrying the vector only (Fig. 3B). In particular, the Bcr protein highly exported l-cysteine, removing up to about 60% of the initial amount in the cells. However, the transport activities of other ORFs (AcrD, CusA, and EmrKY) were virtually unchanged from that in the cells harboring the vector only (data not shown). These results indicated that the Bcr protein would be an effective exporter of l-cysteine in E. coli, in addition to YdeD.
FIG. 3.
Time courses of l-cysteine uptake (A) and export (B) by cells of strain JM39ΔtnaA with pUC118 (○), pUCydeD carrying ydeD (▵), pUCbcr carrying bcr (□), pUCemrAB carrying emrAB (▿), pUCacrEF carrying acrEF (▪), pUCybjYZ carrying ybjYZ (▾), or pUCyojIH carrying yojIH (⧫). Values indicate means and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments.
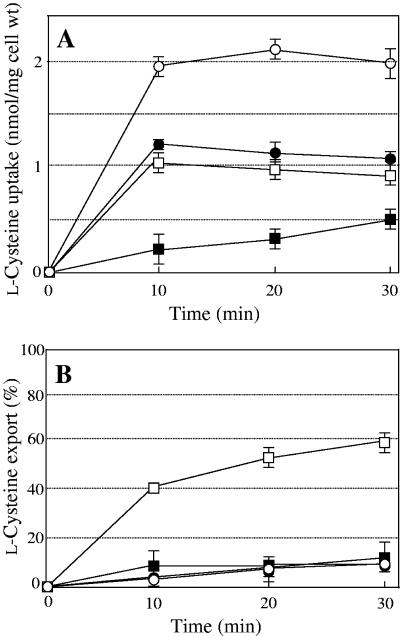
The Bcr sequence showed that it belongs to the MF family, a large family of integral membrane proteins with 12 transmembrane domains (11). Most members of the MF family are dependent on the proton motive force for substrate transport. To determine whether Bcr requires the proton motive force to transport l-cysteine, we tested whether the effect of Bcr could be prevented by the protonophore CCCP (Fig. 4). The incubation of JM39ΔtnaA cells overexpressing Bcr with CCCP significantly diminished the uptake (Fig. 4A) and export of l-cysteine, such that the rate was indistinguishable from that observed with JM39ΔtnaA cells carrying pUC118 (Fig. 4B). Interestingly, the addition of CCCP also resulted in a 50% decrease in l-cysteine uptake in the cells carrying the vector only, suggesting that there is another protein(s) involved in l-cysteine uptake. These results confirm that the Bcr transporter derives energy for l-cysteine export from the proton gradient.
FIG. 4.
Time courses of l-cysteine uptake (A) and export (B) in the absence (open symbols) or presence (filled symbols) of CCCP by cells of strain JM39ΔtnaA with pUC118 (circles) or pUCbcr carrying bcr (squares). Values indicate means and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments.
To further examine the substrate specificity of Bcr for amino acids, we performed various amino acid transport assays, including assays with hydrophilic residues (l-proline and l-serine), hydrophobic residues (l-leucine and l-valine), a basic residue (l-arginine), an acidic residue (l-glutamic acid), and a sulfur-containing residue (l-methionine). However, Bcr overexpression had no discernible effect on the uptake and export of these amino acids (data not shown). These results suggest that l-cysteine may be the only amino acid exported by Bcr.
Bcr overexpression contributes to l-cysteine production in tnaA-disrupted E. coli cells that express an altered cysE gene.
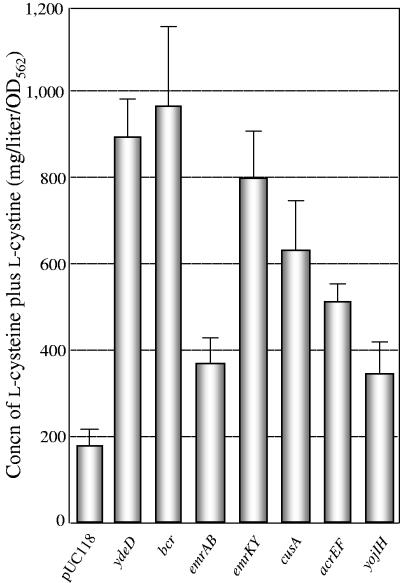
In order to confirm whether the overexpression of drug transporter genes was involved in l-cysteine production in E. coli cells, each plasmid or the vector pUC119 was introduced into JM39ΔtnaA harboring pACYC-M256I, which carries an altered cysE gene encoding feedback-insensitive Met256Ile mutant SAT. The transformed cells were grown in C1+TS medium, and the medium was analyzed for its l-cysteine and l-cystine contents. As shown in Fig. 5, the cells overexpressing Bcr, EmrAB, EmrKY, CusA, AcrEF, and YojIH after 48 h of cultivation showed approximately two- to five-fold increases in l-cysteine production. It is noteworthy that when the bcr gene was overexpressed, the l-cysteine level was approximately fivefold higher than that of the cells harboring the vector only. This finding is in agreement with the results of the in vitro transport assay (Fig. 3). A significant effect on l-cysteine production was also observed in ydeD-overexpressing cells. However, AcrD and YbjYZ did not cause increases in l-cysteine production (data not shown).
FIG. 5.
Production of l-cysteine plus l-cystine by E. coli strain JM39ΔtnaA with pACYC-M256I carrying the altered cysE gene and plasmids carrying drug transporter genes after 48 h of cultivation. Detailed procedures for culture are described in the text. The concentration of l-cysteine plus l-cystine was determined by a microbioassay. Values indicate means and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments.
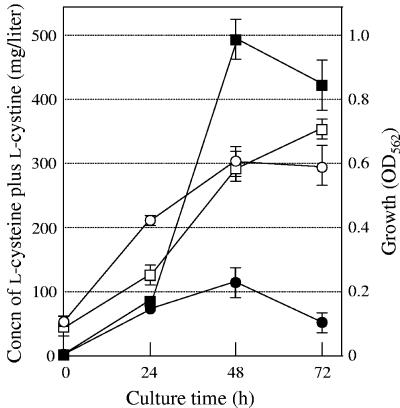
Figure 6 shows the time courses of growth and l-cysteine production by cells of strain JM39ΔtnaA harboring pACYC-M256I and pUC118 or pUCbcr (carrying bcr). Both types of transformed cells showed the same level of growth after 72 h of cultivation, although the growth of cells overexpressing Bcr was inhibited after 24 h of cultivation. The amounts of increasing l-cysteine produced by the cells overexpressing Bcr were approximately five- to sixfold higher than those observed in the cells carrying the vector only after 48 h and 72 h of cultivation. These results clearly indicate that Bcr plays important roles in l-cysteine export in E. coli cells and that Bcr overexpression is effective in l-cysteine production by E. coli cells. However, the decrease in l-cysteine production commenced after 48 h of cultivation, probably because of the remaining CD enzymes.
FIG. 6.
Time courses of growth (OD562) (open symbols) and l-cysteine plus l-cystine production (filled symbols) by cells of strain JM39ΔtnaA with pACYC-M256I carrying the altered cysE gene and pUC118 (circles) or pUCbcr carrying bcr (squares). Detailed procedures for culture are described in the text. Values indicate means and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments.
Functional analysis of the bcr gene.
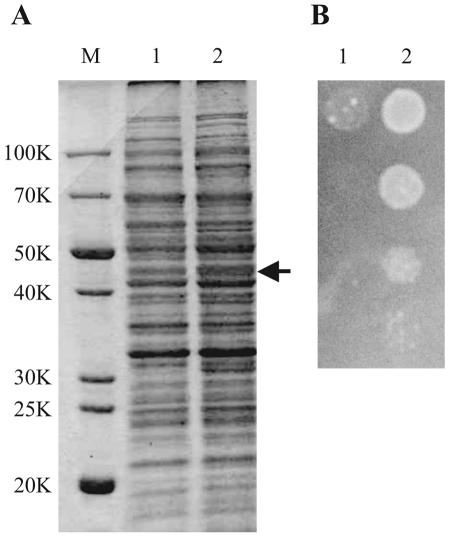
The plasmid pUCbcr used to overexpress the bcr gene also contains another gene, rsuA (formerly designated yejD), encoding 16S rRNA pseudouridine synthase (25, 31, 38). As shown in Fig. 7A, actual expression of the Bcr protein was confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of crude cell extracts. Moreover, as reported previously (25), pUCbcr conferred resistance to tetracycline (Fig. 7B). However, one cannot exclude the possibility that the positive effects of Bcr on l-cysteine export and production were due to overexpression of the rsuA gene. We therefore constructed plasmid pUCbcr-rsuA, carrying only the bcr gene, and analyzed the function of the Bcr protein. Strain JM39ΔtnaA with pACYC-M256I and pUCbcr-rsuA produced l-cysteine plus l-cystine (410 ± 55 mg/liter) after 48 h of cultivation at the same rate as strain JM39ΔtnaA with pACYC-M256I and pUCbcr (422 ± 125 mg/liter). It was also found that strain JM39ΔtnaA harboring pUCbcr-rsuA was resistant to tetracycline (data not shown). These results verify that the Bcr protein alone functions properly and is sufficient to increase l-cysteine production in a CD-disrupted E. coli strain that expresses an altered SAT.
FIG. 7.
Overexpression of bcr gene in E. coli. (A) SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of strain JM39ΔtnaA with pUC118 (lane 1) or pUCbcr carrying bcr (lane 2). After cultivation in LB medium at 37°C for 12 h, crude extracts were isolated and separated in a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Each lane was loaded with a sample containing 30 μg of protein. The gel was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. Molecular mass standards are shown at the left (lane M). The arrow indicates the position of the Bcr protein (43K). (B) Growth phenotypes on tetracycline-containing medium of strain JM39ΔtnaA with pUC118 (lane 1) and pUCbcr carrying bcr (lane 2). After cultivation in LB medium at 37°C for 12 h, serial dilutions (10−2 to 10−5) of approximately 108 cells (from top to bottom) were spotted onto an LB plate containing 2 μg of tetracycline/ml. The plate was incubated at 37°C for 12 h.
The bcr gene has been reported to code for resistance to tetracycline (4-fold) and fosfomycin (4-fold), in addition to bicyclomycin (16-fold), in E. coli cells (25). We suspected that bcr gene expression might be under the control of these drugs or l-cysteine. To test this, we examined the effects of tetracycline and l-cysteine on bcr gene expression by a reporter gene assay. We transformed strain JM39ΔtnaA with plasmid pNNbcr-P and the vector (pNN387), and the obtained transformants were cultivated in LB medium for 3 h in the presence or absence of tetracycline or l-cysteine. When cultured in LB medium only, the cells harboring pNNbcr-P yielded substantial levels of β-galactosidase activity (33 to 39 units). However, the β-galactosidase activities in the cells harboring pNNbcr-P were virtually unchanged after the addition of tetracycline (34 to 39 units) or l-cysteine (31 to 38 units). These results showed that exogenous l-cysteine or tetracycline does not induce the expression of the bcr gene.
DISCUSSION
Although there are 37 ORFs in the chromosomal DNA of E. coli that can be assumed to be genes encoding drug transporters, none of these had yet been reported to have l-cysteine transport activity. This is the first report of an l-cysteine exporter identified by the overexpression of putative drug transporters. We found that Bcr in the MF family is apparently involved in l-cysteine export and overproduction in E. coli cells.
In addition to the bcr gene, seven other drug transporter genes, acrD, acrEF, cusA, emrAB, emrKY, ybjYZ, and yojIH, were picked up as candidates for the l-cysteine exporter. In the MF-type drug transporter family, EmrAB was identified as a transporter involved in multidrug resistance (20). EmrAB overexpression from a plasmid conferred resistance to a broad range of compounds, including deoxycholate and CCCP (25). EmrKY overexpression also conferred resistance to various drugs, such as doxorubicin, rhodamine 6G, and benzalkonium (25). Based on the intracellular l-cysteine levels in CD-disrupted E. coli cells (Fig. 2), EmrAB, AcrD, AcrEF, and YojIH also appeared to be promising l-cysteine exporters. As shown in Fig. 5, however, there is a poor correlation between the intracellular l-cysteine level and l-cysteine production. A transport assay using radiolabeled amino acids also showed that the l-cysteine export capability of the cells overexpressing Bcr was much higher than those observed in the case of other transporters and even of a previously characterized exporter, YdeD.
From the RND-type family, three genes, acrEF, acrD, and cusA, were listed as candidates. AcrEF (18) and AcrD (29) have been identified as drug exporters. AcrEF overexpression from a plasmid conferred resistance to acriflavine, ethidium bromide, rhodamine 6G, and deoxycholate (25). Although the acrD gene was reported to mediate aminoglycoside resistance (29), this gene conferred resistance to some other compounds (deoxycholate, SDS, novobiocin, etc.) in addition to aminoglycosides (29). CusA overexpression did not show any resistance to the 26 representative antimicrobial agents (25), despite a report that the gene product was involved in the efflux of copper (14). In the amino acid transport assay, however, only AcrEF overexpression seemed to somewhat increase l-cysteine export.
Among putative ABC-type drug exporters, only YbjYZ overexpression conferred erythromycin-specific resistance on E. coli cells (25). Thus, it appears that the ybjYZ gene is a novel macrolide resistance determinant. Judging from the growth phenotype results and intracellular l-cysteine levels in CD-disrupted E. coli cells, the overexpression of YbjYZ and YojIH might be involved in l-cysteine efflux. However, an amino acid transport assay showed that only YbjYZ overexpression resulted in a slight decrease in l-cysteine uptake. In conclusion, our results using 33 putative drug transporter genes indicate that the Bcr protein is involved in l-cysteine export and overproduction in E. coli cells.
It was previously reported that the bcr gene, when present on a high-copy-number plasmid, confers resistance to the diketopiperazine antibiotic bicyclomycin (3). E. coli cells overexpressing Bcr were also resistant to some other drugs, such as tetracycline, fosfomycin (25), and sulfathiazole (37). However, disruption of the bcr gene did not increase the susceptibility to l-cysteine and tetracycline (our unpublished results), although the E. coli strain lacking this gene resulted in the loss of bicyclomycin resistance (3). This is probably because there are several export systems in E. coli for l-cysteine (YdeD and YfiK) (6, 12) and tetracycline (MdfA, AcrAB, etc.) (26). Analysis using radioactive amino acids showed that the Bcr protein has specificity for l-cysteine and does not significantly export any amino acids tested, including l-serine, which has a large side chain volume, and l-valine, which inhibits the growth of E. coli cells (7).
It is presumed that Bcr is energized by a proton gradient. When CCCP was added to dissipate the proton motive force, the transport activity for l-cysteine significantly decreased (Fig. 4). This is the first experimental indication that the Bcr protein utilizes the proton motive force for l-cysteine transport. Among 19 putative transporters of the MF family, most possess 12 hydrophobic regions, which may be transmembrane segments, and a conserved GXXXX(R/K)XGR(R/K) motif in the putative cytoplasmic loop between the hydrophobic regions (39). An altered Bcr protein with a high transport activity or substrate specificity for l-cysteine might be useful for further improvements in l-cysteine production. Such engineering of the bcr gene is currently under way.
It is not clear which form of l-cysteine is transported across the membrane. It is possible that l-cysteine is exported as free l-cysteine, as l-cystine, or as 2-methyl-2,4-thiazolidinedicarboxylic acid (CP), which is the product of a nonenzymatic condensation reaction of l-cysteine with pyruvate in the cytoplasm or the medium (6). Therefore, one cannot rule out the possibility that YdeD and YfiK do not export free l-cysteine, but l-cysteine bound in CP. We found that both the Bcr and YdeD proteins significantly export free l-cysteine (Fig. 3). To examine the substrate of these l-cysteine exporters in further detail, we will analyze the intracellular and extracellular metabolite profiles of l-cysteine-producing E. coli cells overexpressing these genes.
Both ydeD and yfiK are expressed at very low levels (6, 13). No regulation could be detected for the expression of these two genes, but the phenotype of a ydeD insertion mutant and the chromosomal organization of the yfiK gene support the possibility that these genes are regulated (6, 13). On the other hand, nothing is yet known about the regulation of expression of the bcr gene. The plasmid pUCbcr used here possesses two genes, bcr and yejD (putative regulator) (25). When the bcr gene alone was cloned into the expression vector under the control of the trc promoter, the drug resistance pattern of the recombinant plasmid was comparable to that of pUCbcr (25). This and the results of the reporter gene assay suggest that the bcr gene is constitutively expressed at a substantial level. Although it is unknown whether YejD belongs to the family of known regulators, it is unlikely that YejD regulates the expression of the bcr gene.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate M. Takahashi and Y. Hamano (Fukui Prefectural University, Fukui, Japan) for their helpful discussions of this work. We thank S. Yasuda (National Institute of Genetics, Shizuoka, Japan) and R. W. Davis (Stanford University School of Medicine, Calif.) for providing the plasmids. The technical assistance of C. Maruyama in our laboratory is greatly appreciated.
This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for Young Scientists (no. 01978 to N.A.) and by a grant from Ajinomoto Co., Inc., to H.T.
REFERENCES
- 1.Awano, N., M. Wada, A. Kohdoh, T. Oikawa, H. Takagi, and S. Nakamori. 2003. Effect of cysteine desulfhydrase gene disruption on l-cysteine overproduction in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 62:239-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Awano, N., M. Wada, H. Mori, S. Nakamori, and H. Takagi. 2005. Identification and functional analysis of cysteine desulfhydrases in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71:4149-4152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bentley, J., L. S. Hyatt, K. Ainley, J. H. Parish, R. B. Herbert, and G. R. White. 1993. Cloning and sequence analysis of an Escherichia coli gene conferring bicyclomycin resistance. Gene 127:117-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bolhuis, H., H. W. van Veen, B. Poolman, A. J. Driessen, and W. N. Konings. 1997. Mechanisms of multidrug transporters. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 21:55-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cook, G. M., and R. K. Poole. 2000. Oxidase and periplasmic cytochrome assembly in Escherichia coli K-12: CydDC and CcmAB are not required for haem-membrane association. Microbiology 146:527-536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Daßler, T., T. Maier, C. Winterhalter, and A. Böck. 2000. Identification of a major facilitator protein from Escherichia coli involved in efflux of metabolites of the cysteine pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 36:1101-1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Felice, M., C. Squires, M. Levinthal, J. Guardiola, A. Lamberti, and M. Iaccarino. 1977. Growth inhibition of Escherichia coli K-12 by l-valine: a consequence of a regulatory pattern. Mol. Gen. Genet. 156:1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Delaney, J. M., D. Ang, and C. Georgopoulos. 1992. Isolation and characterization of the Escherichia coli htrD gene, whose product is required for growth at high temperatures. J. Bacteriol. 174:1240-1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Denk, D., and A. Böck. 1987. l-Cysteine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence and expression of the serine acetyltransferase (cysE) gene from the wild-type and cysteine excreting mutant. J. Gen. Microbiol. 133:515-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dwivedi, C. M., R. C. Ragin, and J. R. Uren. 1982. Cloning, purification, and characterization of β-cystathionase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 21:3064-3069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Eisenberg, D., E. Schwarz, M. Komaromy, and R. Wall. 1984. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J. Mol. Biol. 179:125-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Franke, I., A. Resch, T. Daßler, T. Maier, and A. Böck. 2003. YfiK from Escherichia coli promotes export of O-acetylserine and cysteine. J. Bacteriol. 185:1161-1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gaitonde, M. K. 1967. A spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of cysteine in the presence of other naturally occurring amino acids. Biochem. J. 104:627-633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Grass, G., and C. Rensing. 2001. Genes involved in copper homeostasis in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 183:2145-2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Harris, C. L. 1981. Cysteine and growth inhibition of Escherichia coli: threonine deaminase as the target enzyme. J. Bacteriol. 145:1031-1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Harris, C. L., and L. Lui. 1981. Cysteine and growth inhibition of Escherichia coli: depression of the ilvGEDA operon. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 101:1145-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kari, C., Z. Nagy, P. Kovacs, and F. Hernadi. 1971. Mechanism of the growth inhibitory effect of cysteine on Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 68:349-356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kawamura-Sato, K., K. Shibayama, T. Horii, Y. Iimuma, Y. Arakawa, and M. Ohta. 1999. Role of multiple efflux pumps in Escherichia coli in indole expulsion. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 179:345-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kredich, N. M. 1983. Regulation of cysteine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, p. 115-132. In K. M. Herrmann and R. L. Sommerville (ed.), Amino acids: biosynthesis and genetic regulation. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, London, United Kingdom.
- 20.Lomovskaya, O., and K. Lewis. 1992. Emr, an Escherichia coli locus for multidrug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8938-8942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miller, J. 1972. Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 22.Nakamori, S., S. Kobayashi, C. Kobayashi, and H. Takagi. 1998. Overproduction of l-cysteine and l-cystine by Escherichia coli strains with a genetically altered serine acetyltransferase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:1607-1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Newton, W. A., and E. F. Snell. 1964. Catalytic properties of tryptophanase, a multifunctional pyridoxal phosphate enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 51:382-389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Newton, W. A., Y. Morino, and E. F. Snell. 1965. Properties of crystalline tryptophanase. J. Biol. Chem. 240:1211-1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nishino, K., and A. Yamaguchi. 2001. Analysis of a complete library of putative drug transporter genes in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 183:5803-5812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Park, S., and J. A. Imlay. 2003. High levels of intracellular cysteine promote oxidative DNA damage by driving the Fenton reaction. J. Bacteriol. 185:1942-1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pittman, M. S., H. Corker, G. Wu, M. B. Binet, A. J. G. Moir, and R. K. Poole. 2002. Cysteine is exported from the Escherichia coli cytoplasm by CydDC, an ATP-binding cassette-type transporter required for cytochrome assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 277:49841-49849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Putman, M., H. W. van Veen, and W. N. Konings. 2000. Molecular properties of bacterial multidrug transporters. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64:672-693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rosenberg, E. Y., D. Ma, and H. Nikaido. 2000. AcrD of Escherichia coli is an aminoglycoside efflux pump. J. Bacteriol. 182:1754-1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sambrook, J., and D. W. Russell. 2001. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 31.Sivaraman, J., V. Sauvé, R. Larocque, E. A. Stura, J. D. Schrag, M. Cygler, and A. Matte. 2002. Structure of the 16S rRNA pseudouridine synthase RsuA bound to uracil and UMP. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9:353-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Soda, K. 1987. Microbial sulfur amino acids: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 143:453-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sorensen, M. A., and S. Pedersen. 1991. Cysteine, even in low concentrations, induces transient amino acid starvation in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 173:5244-5246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Takagi, H., C. Kobayashi, S. Kobayashi, and S. Nakamori. 1999. PCR random mutagenesis into Escherichia coli serine acetyltransferase: isolation of the mutant enzymes that cause overproduction of l-cysteine and l-cystine due to the desensitization to feedback inhibition. FEBS Lett. 452:323-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Takagi, H., N. Awano, S. Kobayashi, C. Kobayashi, M. Noji, K. Saito, and S. Nakamori. 1999. Overproduction of l-cysteine and l-cystine by expression of genes for feedback inhibition-insensitive serine acetyltransferase from Arabidopsis thaliana in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 179:453-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsunoda, T., S. Eguchi, and K. Narumi. 1961. On the bioassay of amino acids. II. Determination of arginine, aspartic acid and cysteine. Amino Acids 3:7-13. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vedantam, G., G. G. Guay, N. E. Austria, S. Z. Doktor, and B. P. Nichols. 1998. Characterization of mutations contributing to sulfathiazole resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42:88-93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wrzesinski, J., A. Bakin, K. Nurse, B. G. Lane, and J. Ofengand. 1995. Purification, cloning, and properties of the 16S RNA pseudouridine 516 synthase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 34:8904-8913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yamaguchi, A., T. Kimura, Y. Someya, and T. Sawai. 1993. Metal-tetracycline/H+ antiporter of Escherichia coli encoded by transposon Tn10. The structural resemblance and functional difference in the role of the duplicated sequence motif between hydrophobic segments 2 and 3 and segments 8 and 9. J. Biol. Chem. 268:6496-6504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]