Abstract
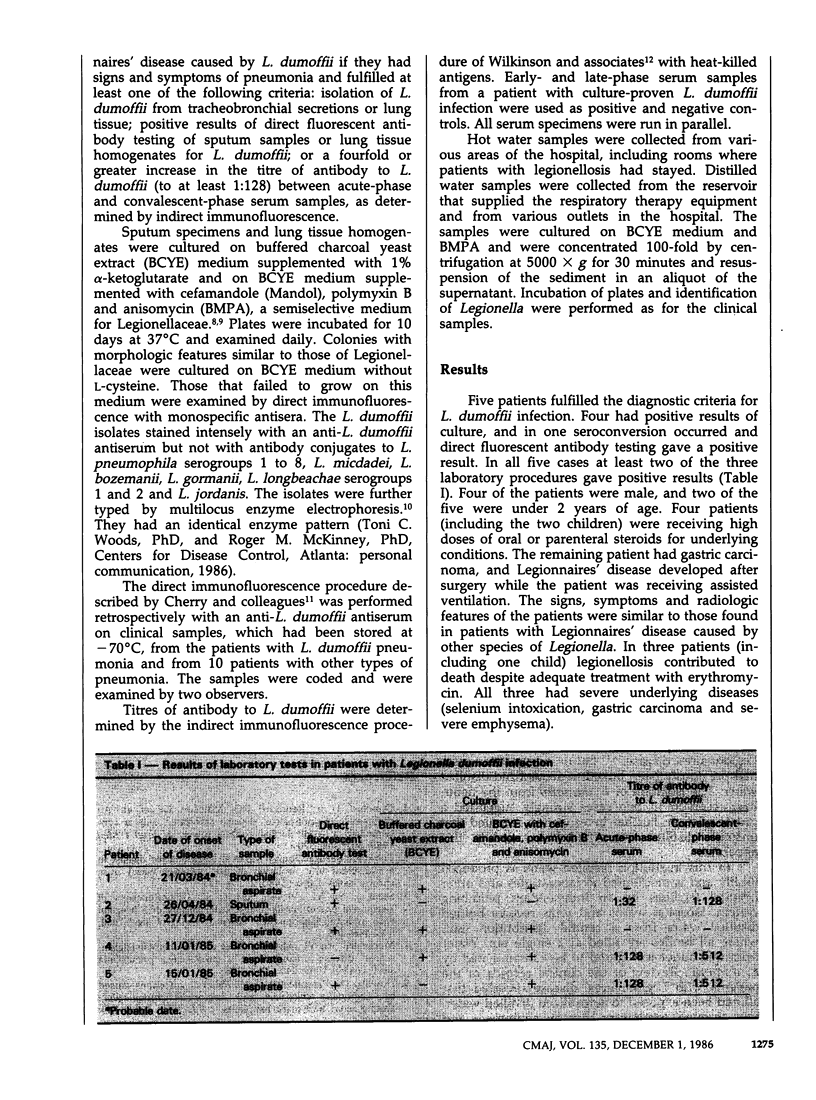
Five cases of Legionnaires' disease caused by Legionella dumoffii were identified within an 11-month period in a hospital in the Quebec City area. In four cases bacterial isolates were obtained from clinical specimens, and in one case seroconversion was demonstrated. All the patients had been admitted to hospital within 10 days before diagnosis. Two of the patients were immunosuppressed children. Only 1 of the 40 hot water samples from the hospital yielded L. dumoffii; however, 6 of 11 distilled water samples contained the bacterium. All the patients had been exposed to distilled water, four through respiratory therapy equipment and one through a room humidifier. Following the use of sterile distilled water in the apparatus, no further cases were identified. This is the first reported outbreak of Legionnaires' disease caused by L. dumoffii, and it is the first time that nosocomial legionellosis has been linked to contaminated distilled water in Canada.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnow P. M., Chou T., Weil D., Shapiro E. N., Kretzschmar C. Nosocomial Legionnaires' disease caused by aerosolized tap water from respiratory devices. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):460–467. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best M., Yu V. L., Stout J., Goetz A., Muder R. R., Taylor F. Legionellaceae in the hospital water-supply. Epidemiological link with disease and evaluation of a method for control of nosocomial legionnaires' disease and Pittsburgh pneumonia. Lancet. 1983 Aug 6;2(8345):307–310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero T. J., Jr, Rendtorff R. C., Mallison G. F., Weeks R. M., Levy J. S., Wong E. W., Schaffner W. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):365–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. N., Pasculle A. W., Frola F. N., Zaphyr M. K., Yee R. B. Infections caused by Legionella micdadei and Legionella pneumophila among renal transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):703–713. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaan J. A., Simoons-Smit A. M., MacLaren D. M. Another source of aerosol causing nosocomial Legionnaires' disease. J Infect. 1985 Sep;11(2):145–148. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(85)92051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D. Symposium on infectious complications of neoplastic disease (Part II). Legionnaires' disease. Aspects of nosocomial infection. Am J Med. 1984 Apr;76(4):657–663. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90291-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muder R. R., Yu V. L., McClure J. K., Kroboth F. J., Kominos S. D., Lumish R. M. Nosocomial Legionnaires' disease uncovered in a prospective pneumonia study. JAMA. 1983 Jun 17;249(23):3184–3188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Thomason B. M., Brake B. J., Thacker L., Wilkinson H. W., Kuritsky J. N. Legionella pneumonia in the United States: the distribution of serogroups and species causing human illness. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):819–819. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J., Yu V. L., Vickers R. M., Zuravleff J., Best M., Brown A., Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. Ubiquitousness of Legionella pneumophila in the water supply of a hospital with endemic Legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 25;306(8):466–468. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202253060807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. O., Beare J., Dunnill M. S., Fisher-Hoch S., French M., Mitchell R. G., Morris P. J., Muers M. F. Legionnaires' disease in a transplant unit: isolation of the causative agent from shower baths. Lancet. 1980 Jul 19;2(8186):118–121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D. Indirect immunofluorescence test for serodiagnosis of Legionnaires disease: evidence for serogroup diversity of Legionnaires disease bacterial antigens and for multiple specificity of human antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):379–383. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.379-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


