Abstract
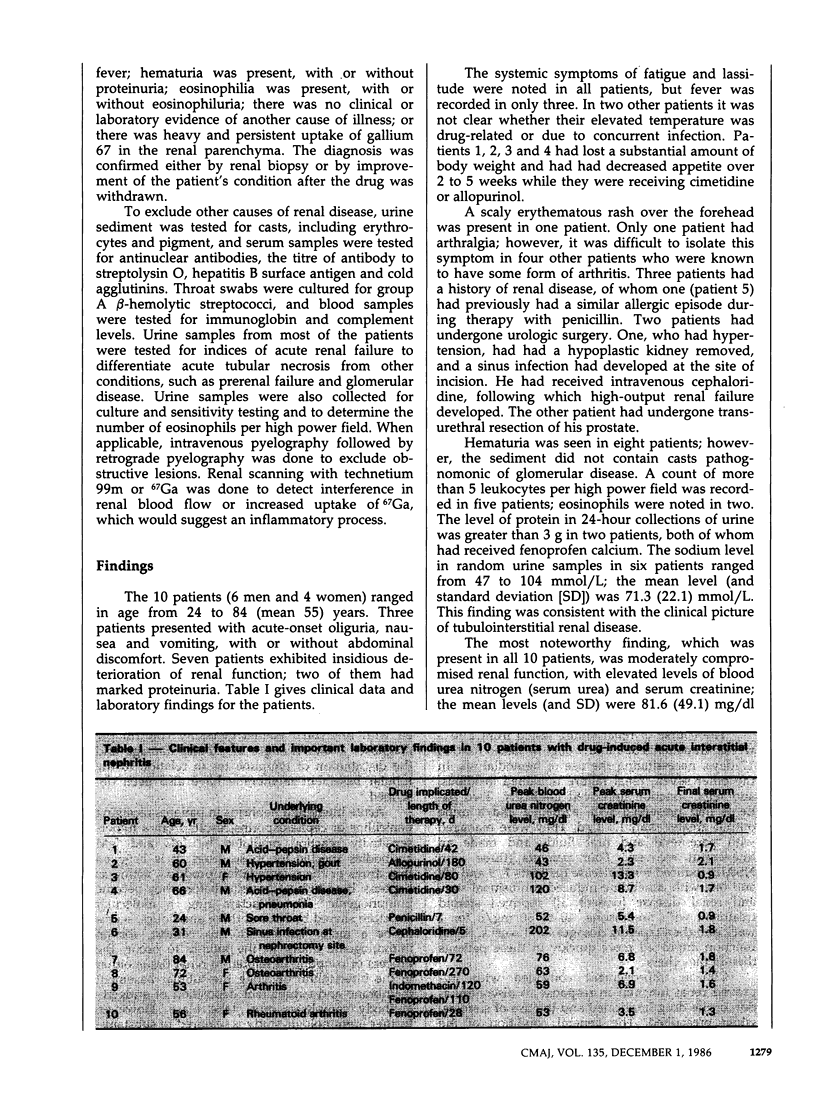
Between January 1979 and June 1985, 10 patients with acute allergic interstitial nephritis were seen in a clinical nephrology service at a large regional hospital. The onset of renal failure was temporally related to the use of a drug: a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) (in four patients), cimetidine (in three), antibiotics (in two) or allopurinol (in one). The onset of renal failure was acute in three patients and insidious in seven. Two patients also exhibited marked proteinuria. Clinical features such as fever, rash, hematuria, pyuria with or without eosinophiluria, and mild to marked proteinuria had led to suspicion of the disease. The diagnosis was confirmed by renal biopsy findings of inflammatory cells, predominantly lymphocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils. Three patients required hemodialysis; two of them received steroids as well. Steroid therapy was also used in two patients with NSAID-induced proteinuria. Renal function improved in nine patients by 35 days, but one patient continued to have slow but progressive deterioration of renal function. Acute interstitial nephritis can be distinguished from other forms of acute renal failure by heavy renal uptake of gallium 67, maximal 48 hours or more after injection. The improvement in renal function after discontinuation of the implicated drug, the characteristic histopathological findings of allergic interstitial nephritis, and the presence of eosinophils and sometimes IgE in the blood suggest a hypersensitivity reaction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averbuch S. D., Austin H. A., 3rd, Sherwin S. A., Antonovych T., Bunn P. A., Jr, Longo D. L. Acute interstitial nephritis with the nephrotic syndrome following recombinant leukocyte a interferon therapy for mycosis fungoides. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 5;310(1):32–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401053100107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Lehman D. H., Egan J. D., Sass H. J., Glode J. E., Wilson C. B. Antitubular basement-membrane antibodies in methicillin-associated interstitial nephritis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 22;291(8):381–384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408222910803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezin J. H., Katz S. M., Schwartz A. B., Chinitz J. L. Reversible renal failure and nephrotic syndrome associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med. 1979 Dec 6;301(23):1271–1273. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197912063012306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clive D. M., Stoff J. S. Renal syndromes associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 1;310(9):563–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403013100905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Fraley D. S., Stachura I., Feldman H. A., Gandy D. R., Bourke E. Fenoprofen nephropathy: lipoid nephrosis and interstitial nephritis. A possible T-lymphocyte disorder. Am J Med. 1982 Jan;72(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galpin J. E., Shinaberger J. H., Stanley T. M., Blumenkrantz M. J., Bayer A. S., Friedman G. S., Montgomerie J. Z., Guze L. B., Coburn J. W., Glassock R. J. Acute interstitial nephritis due to methicillin. Am J Med. 1978 Nov;65(5):756–765. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90793-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbart D. R., Weinstein A. B., Fajardo L. F. Allopurinol-induced interstitial nephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Feb;86(2):196–198. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-2-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen H. A., Halveg A. B., Saunamäki K. I. Permanent impairment of renal function after methicillin nephropathy. Br Med J. 1971 Nov 13;4(5784):406–406. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5784.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovnat P., Labovitz E., Levison S. P. Antibiotics and the kidney. Med Clin North Am. 1973 Jul;57(4):1045–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. L., Clark W. F., Driedger A. A., Turnbull D. I., Lindsay R. M. Acute interstitial nephritis due to drugs: Review of the literature with a report of nine cases. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Nov;93(5):735–741. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-5-735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons H., Pinn V. W., Cortell S., Cohen J. J., Harrington J. T. Allergic interstitial nephritis causing reversible renal failure in four patients with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 18;288(3):124–128. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301182880304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan W. R., Vermillion S. E. Acute interstitial nephritis related to cimetidine therapy. Gastroenterology. 1980 Oct;79(4):746–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. S., Jao W., First M. R., Mancilla R., Pollak V. E. Acute interstitial nephritis. A clinical and pathologic study based on renal biopsies. Am J Med. 1975 Nov;59(5):614–628. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennke H. G., Roos P. C., Wall S. G. Drug-induced interstitial nephritis with heavy glomerular proteinuria. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 20;302(12):691–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachura I., Jayakumar S., Bourke E. T and B lymphocyte subsets in fenoprofen nephropathy. Am J Med. 1983 Jul;75(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres V. E. Present and future of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in nephrology. Mayo Clin Proc. 1982 Jun;57(6):389–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood B. C., Sharma J. N., Germann D. R., Wood W. G., Crouch T. T. Gallium citrate Ga 67 imaging in noninfectious interstitial nephritis. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Nov;138(11):1665–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


