Abstract
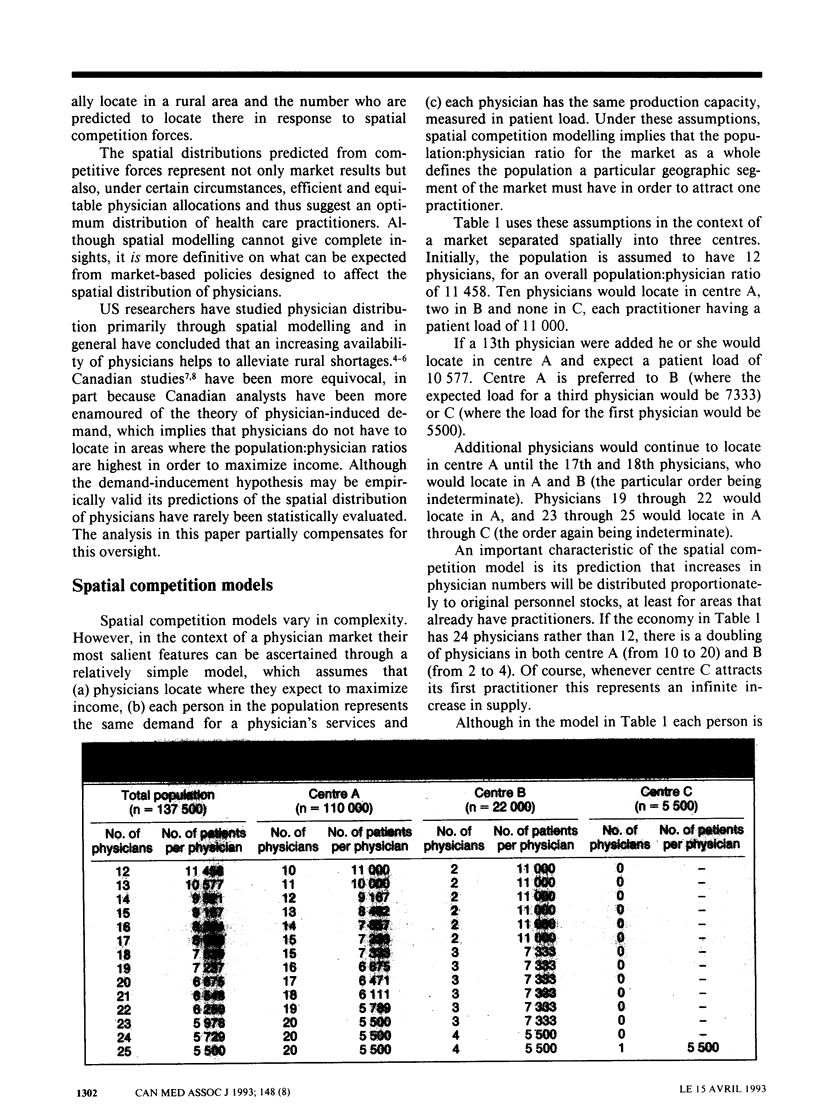
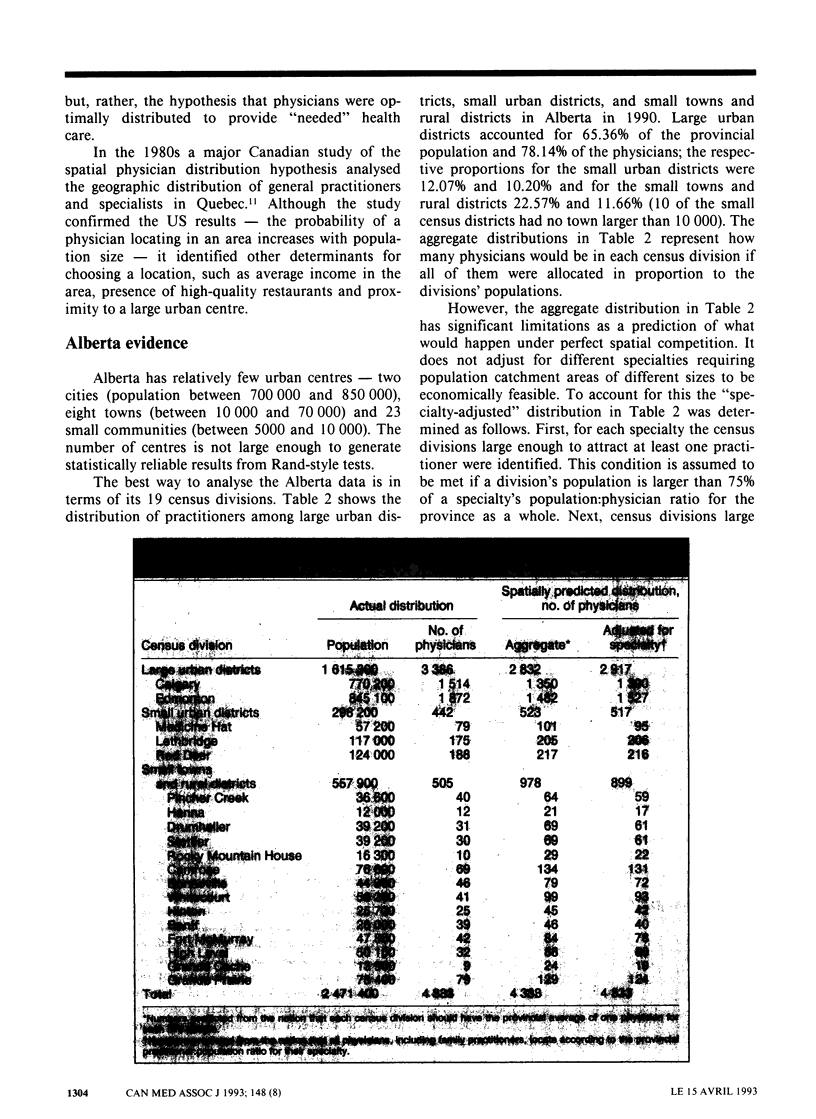
This article analyses how physicians choose locations of practice in response to spatial competition forces and considers the implications of such choices for public policy to alleviate shortages of practitioners in rural areas. The predicted geographic distribution of physicians, as determined through spatial competition modelling, was compared with the actual distribution of physicians in 1990 among Alberta's 19 census divisions. Physicians were found to respond to spatial competition forces in choosing where to practise, with the qualification that 1 urban patient had a demand weight equal to 2.32 rural patients. A policy to attract more physicians to rural areas by means of income subsidies is technically feasible but expensive. The high cost means that alternative policies such as a bigger and more effective ambulance network to transport patients to medical centres should become the focus of public policies to improve health care in rural areas.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dionne G., Langlois A., Lemire N. More on the geographical distribution of physicians. J Health Econ. 1987 Dec;6(4):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0167-6296(87)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhouse J. P., Williams A. P., Bennett B. W., Schwartz W. B. Where have all the doctors gone? JAMA. 1982 May 7;247(17):2392–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz W. B., Newhouse J. P., Bennett B. W., Williams A. P. The changing geographic distribution of board-certified physicians. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 30;303(18):1032–1038. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010303031803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. P., Schwartz W. B., Newhouse J. P., Bennett B. W. How many miles to the doctor? N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 20;309(16):958–963. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310203091606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


