Abstract
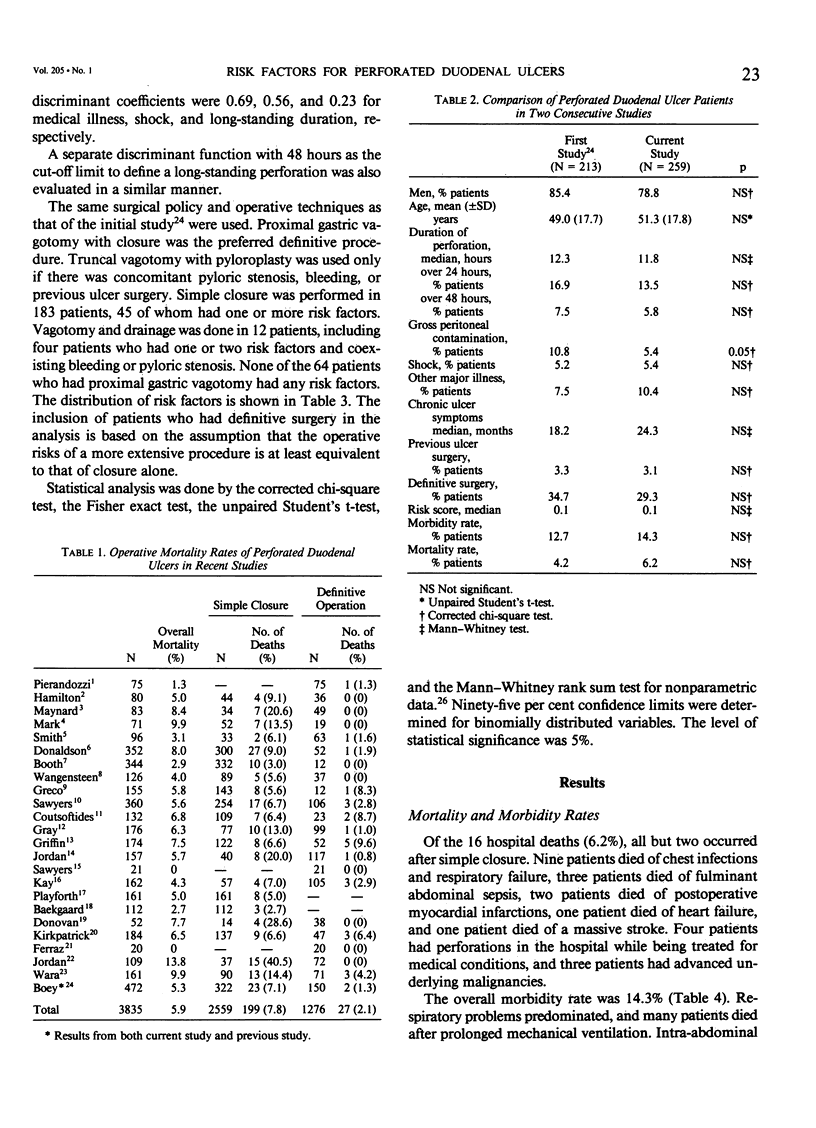
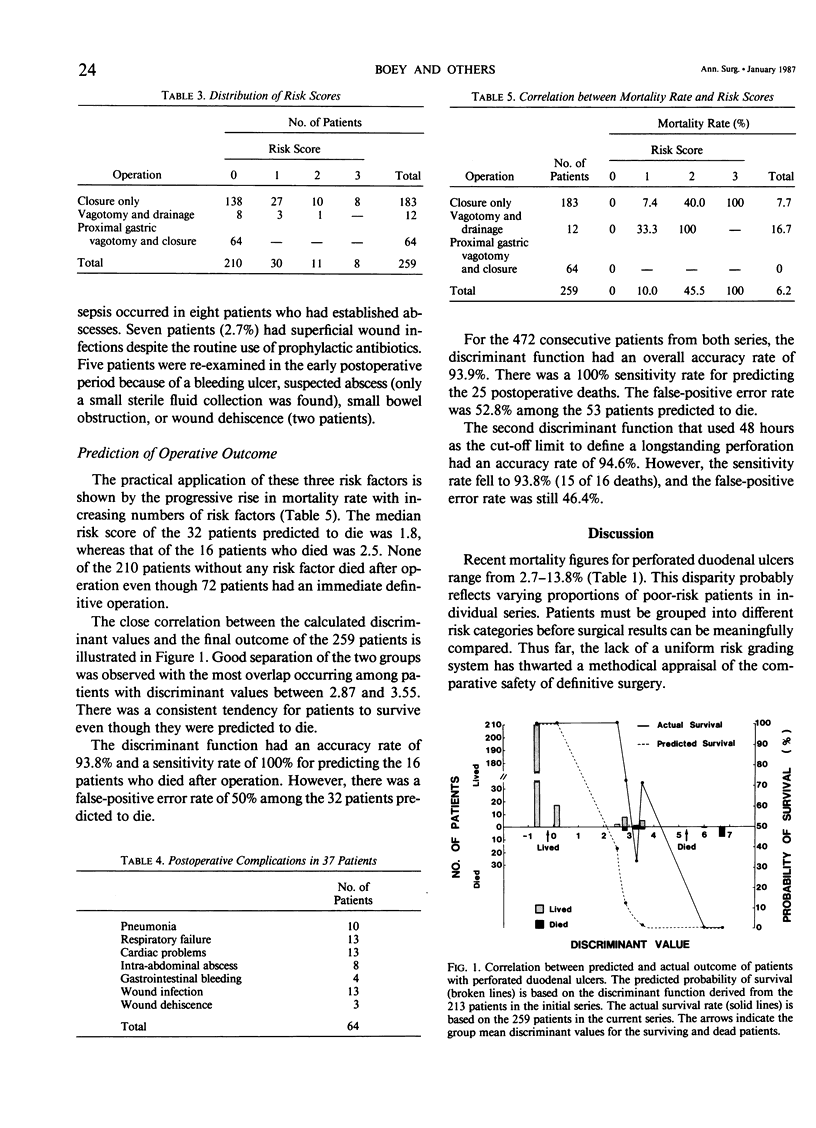
In order to validate a previously derived set of risk factors, 259 consecutive patients who had simple closure or definitive operation for perforated duodenal ulcers were studied prospectively. Major medical illness, preoperative shock, and longstanding perforation (more than 24 hours) correctly predicted the outcome in 93.8% of patients. Most importantly, 16 patients (6.2%) who died after operation could be identified (no false-negative error). The mortality rate increased progressively with increasing numbers of risk factors: 0%, 10%, 45.5%, and 100% in patients with none, one, two, and all three risk factors, respectively. These findings underscore the importance of patient selection and the feasibility of a risk grading system in guiding surgical management. Definitive surgery can be done safely in good-risk patients. Simple closure is preferable in those patients with uncomplicated perforations if any risk factor is present. Truncal vagotomy and drainage may be required if there is coexisting bleeding or stenosis. Nonoperative treatment deserves re-evaluation in patients with all three risk factors because of their uniformly dismal outcome after operation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baekgaard N., Lawaetz O., Poulsen P. E. Simple closure or definitive surgery for perforated duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1979;14(1):17–20. doi: 10.3109/00365527909179841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boey J., Lee N. W., Wong J., Ong G. B. Perforations in acute duodenal ulcers. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Aug;155(2):193–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boey J., Wong J., Ong G. B. A prospective study of operative risk factors in perforated duodenal ulcers. Ann Surg. 1982 Mar;195(3):265–269. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198203000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boey J., Wong J., Ong G. B. Bacteria and septic complications in patients with perforated duodenal ulcers. Am J Surg. 1982 May;143(5):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth R. A., Williams J. A. Mortality of perforated duodenal ulcer treated by simple suture. Br J Surg. 1971 Jan;58(1):42–44. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutsoftides T., Himal H. S. Perforated gastroduodenal ulcers. Factors affecting morbidity and mortality and the role of definitive surgery. Am J Surg. 1976 Nov;132(5):575–576. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEAN A. C., CLARK C. G., SINCLAIR-GIEBEN A. H. The late prognosis of perforated duodenal ulcer. Gut. 1962 Mar;3:60–64. doi: 10.1136/gut.3.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson G. A., Jarrett F. Perforated gastroduodenal ulcer disease at the Massachusetts General Hospital from 1952 to 1970. Am J Surg. 1970 Sep;120(3):306–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan A. J., Vinson T. L., Maulsby G. O., Gewin J. R. Selective treatment of duodenal ulcer with perforation. Ann Surg. 1979 May;189(5):627–636. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197905000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz E. M., Ferreira Filho H. A., Bacelar T. S., Lacerda C. M., Ponce de Souza A., Kelner S. Proximal gastric vagotomy in stenosed or perforated duodenal ulcer. Br J Surg. 1981 Jul;68(7):452–454. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. G., Roberts A. K. Definitive emergency treatment of perforated duodenal ulcer. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Dec;143(6):890–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco R. S., Cahow C. E. Alternatives in the management of acute perforated duodenal ulcer. Am J Surg. 1974 Jan;127(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Organ C. H., Jr The natural history of the perforated duodenal ulcer treated by suture plication. Ann Surg. 1976 Apr;183(4):382–385. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197604000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. E., Harbrecht P. J. Growing indications for vagotomy in perforated peptic ulcer. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967 Jan;124(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth C. F., Scott L. D., Jamieson R. A. Progress after Perforated Peptic Ulcer. Br Med J. 1946 May 25;1(4455):787–790. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan G. L., Jr, DeBakey M. E., Duncan J. M., Jr Surgical management of perforated peptic ulcer. Ann Surg. 1974 May;179(5):628–633. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197405000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. H., Jr, Korompai F. L. Evolvement of a new treatment for perforated duodenal ulcer. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Mar;142(3):391–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. H., Jr Proximal Gastric vagotomy without drainage for treatment of perforated duodenal ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jul;83(1 Pt 2):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay P. H., Moore K. T., Clark R. G. The treatment of perforated duodenal ulcer. Br J Surg. 1978 Nov;65(11):801–803. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800651111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick J. R., Bouwman D. L. A logical solution to the perforated ulcer controversy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1980 May;150(5):683–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen E. S. Conservative treatment of 155 cases of perforated peptic ulcer. Acta Chir Scand. 1980;146(3):189–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark J. B. Factors influencing the treatment of perforated duodenal ulcer. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 Aug;129(2):325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard A. D., Froix C. J., Oropeza G. Gastroduodenal perforation. Arch Surg. 1968 Jul;97(1):96–104. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01340010126014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemanich G. J., Nicoloff D. M. Perforated duodenal ulcer: long-term follow-up. Surgery. 1970 May;67(5):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIERANDOZZI J. S., HINSHAW D. B., STAFFORD C. E. Vagotomy and pyloroplasty for acute perforated duodenal ulcer. A report of seventy-five cases. Am J Surg. 1960 Aug;100:245–250. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(60)90297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playforth M. J., McMahon M. J. The indications for simple closure of perforated duodenal ulcers. Br J Surg. 1978 Oct;65(10):699–701. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800651009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers J. L., Herrington J. L., Jr Perforated duodenal ulcer managed by proximal gastric vagotomy and suture plication. Ann Surg. 1977 Jun;185(6):656–660. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197706000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers J. L., Herrington J. L., Mulherin J. L., Jr, Whitehead W. A., Mody B., Marsh J. Acute perforated duodenal ulcer. An evaluation of surgical management. Arch Surg. 1975 May;110(5):527–530. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360110073013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L., Beehan P. J. Definitive operations for perforated duodenal ulcers. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 Sep;129(3):465–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabile B. E., Hardy H. J., Passaro E., Jr 'Kissing' duodenal ulcers. Arch Surg. 1979 Oct;114(10):1153–1156. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370340059010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangensteen S. L., Wray R. C., Golden G. T. Perforated duodenal ulcer. Am J Surg. 1972 May;123(5):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(72)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wara P., Kristensen E. S., Sørensen F. H., Boné J., Skovgaard S., Amdrup E. The value of parietal cell vagotomy compared to simple closure in a selective approach to perforated duodenal ulcer. Operative morbidity and recurrence rate. Acta Chir Scand. 1983;149(6):585–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


