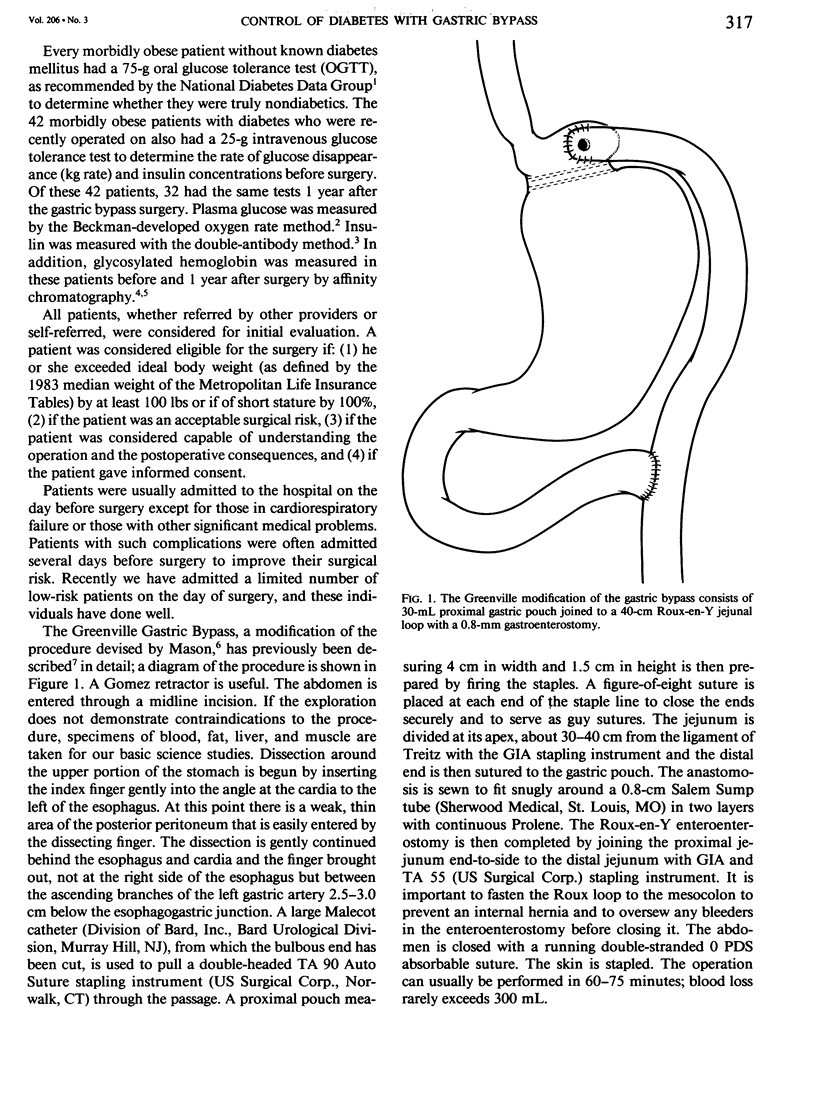
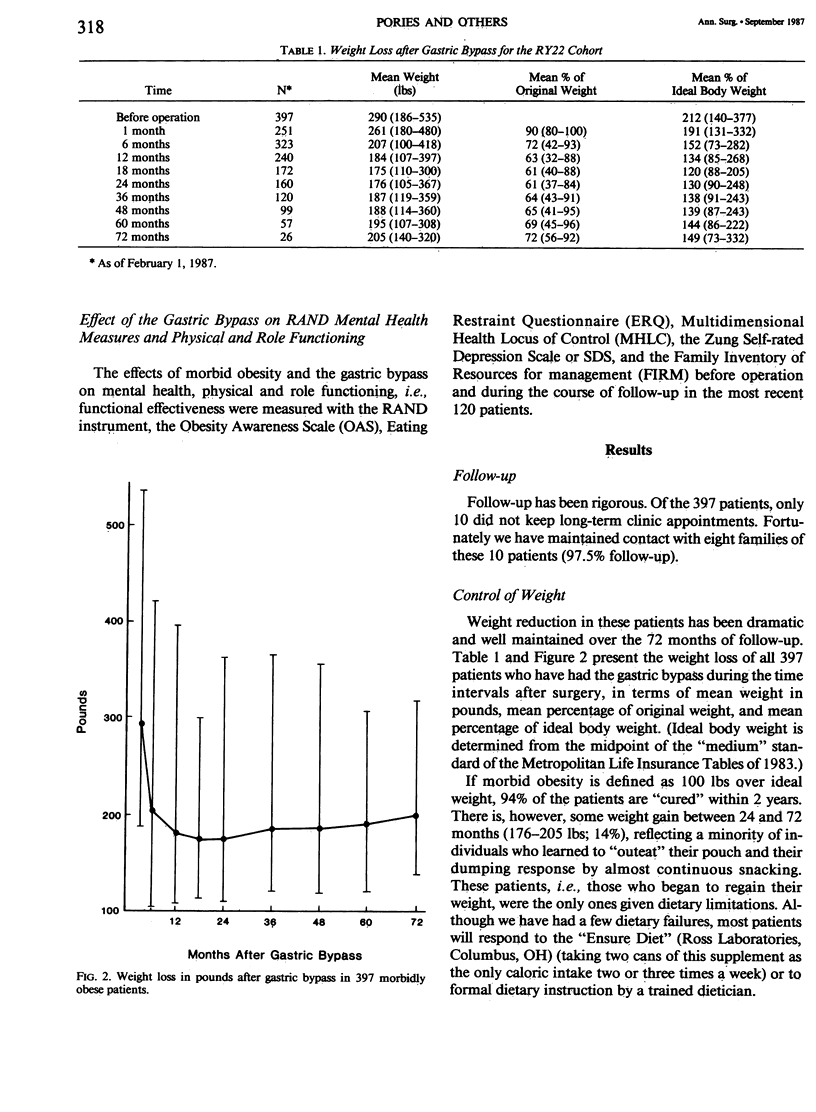
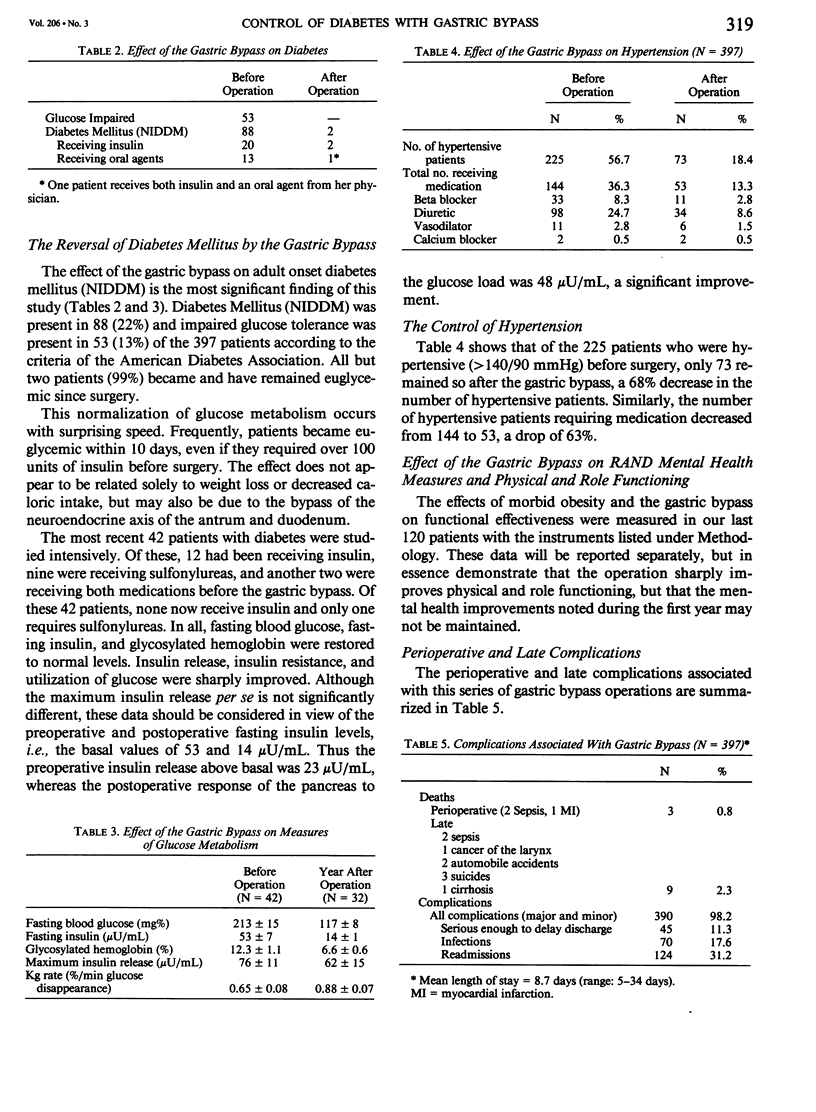
Abstract
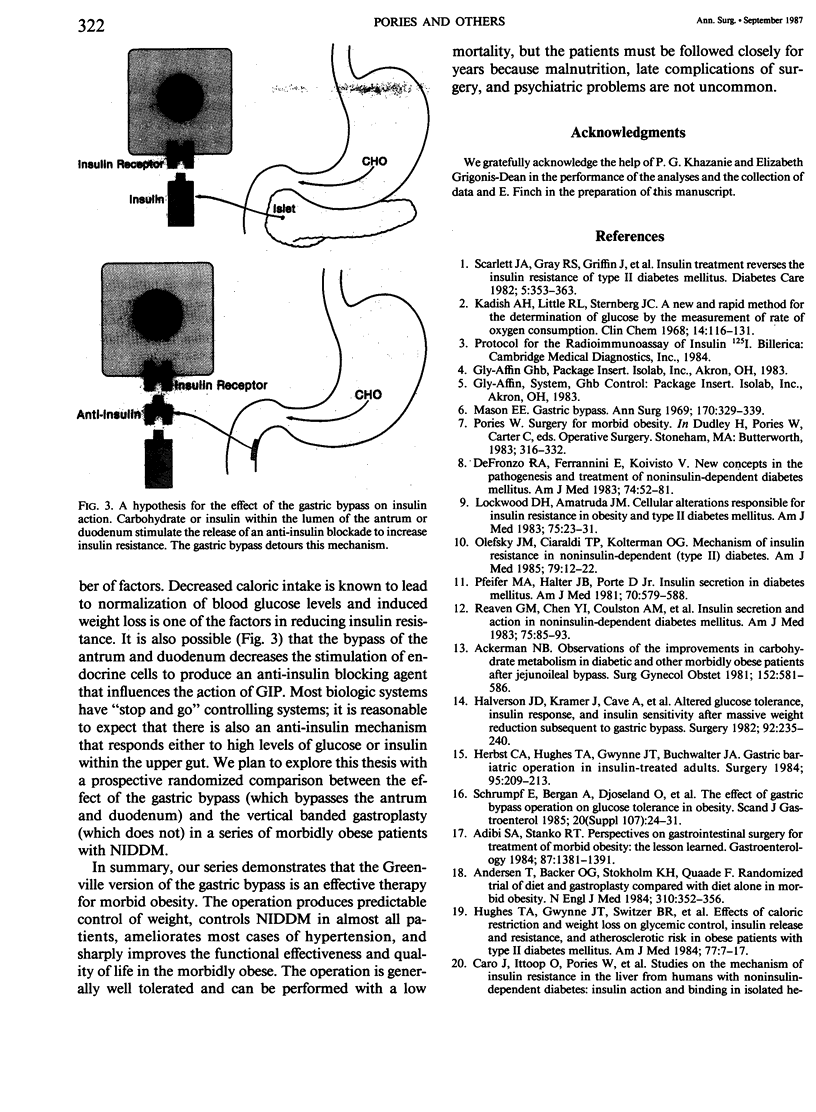
Since February 1, 1980, the identical standardized Greenville Gastric Bypass has been performed in 397 morbidly obese patients with an operative mortality rate of 0.8%. The operation effectively controlled weight and maintained satisfactory weight loss even after 6 years (mean weights and ranges: Preoperative: 290 lbs (196-535); 18 months: 175 lbs (110-300); 72 months: 205 lbs (140-320). The gastric bypass favorably affected non-insulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM), hypertension, physical and role functioning, and several measures of mental health. Rigorous follow-up (97.5% over 6 years) revealed that health problems were common in postoperative patients; there were nine late deaths. Abnormal glucose metabolism was present in 141 (36%) of 397 patients before surgery: NIDDM was present in 88 patients (22%) and 53 patients (14%) were glucose impaired. Of these, all but two became euglycemic within 4 months after surgery without any diabetic medication or special diets. The most recent 42 morbidly obese patients with NIDDM were studied intensively. In that cohort, fasting blood glucose, fasting insulin, and glycosylated hemoglobin returned to normal after surgery; insulin release, insulin resistance, and utilization of glucose improved sharply. The normalization of glucose metabolism after gastric bypass may not be related solely to weight loss and restriction of caloric intake, but may also be due to the bypass of the antrum and duodenum.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman N. B. Observations on the improvements in carbohydrate metabolism in diabetic and other morbidly obese patients after jejunoileal bypass. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981 May;152(5):581–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adibi S. A., Stanko R. T. Perspectives on gastrointestinal surgery for treatment of morbid obesity: the lesson learned. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1381–1391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen T., Backer O. G., Stokholm K. H., Quaade F. Randomized trial of diet and gastroplasty compared with diet alone in morbid obesity. N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 9;310(6):352–356. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402093100604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Meelheim D., Flickinger E. G., Thomas F., Jenquin M., Silverman J. F., Khazanie P. G., Sinha M. K. Studies on the mechanism of insulin resistance in the liver from humans with noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Insulin action and binding in isolated hepatocytes, insulin receptor structure, and kinase activity. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):249–258. doi: 10.1172/JCI112558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Sinha M. K., Raju S. M., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Dohm G. L. Insulin receptor kinase in human skeletal muscle from obese subjects with and without noninsulin dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1330–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI112958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Koivisto V. New concepts in the pathogenesis and treatment of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1983 Jan 17;74(1A):52–81. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90654-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson J. D., Kramer J., Cave A., Permutt A., Santiago J. Altered glucose tolerance, insulin response, and insulin sensitivity after massive weight reduction subsequent to gastric bypass. Surgery. 1982 Aug;92(2):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst C. A., Hughes T. A., Gwynne J. T., Buckwalter J. A. Gastric bariatric operation in insulin-treated adults. Surgery. 1984 Feb;95(2):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes T. A., Gwynne J. T., Switzer B. R., Herbst C., White G. Effects of caloric restriction and weight loss on glycemic control, insulin release and resistance, and atherosclerotic risk in obese patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1984 Jul;77(1):7–17. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood D. H., Amatruda J. M. Cellular alterations responsible for insulin resistance in obesity and type II diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1983 Nov 30;75(5B):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason E. E., Ito C. Gastric bypass. Ann Surg. 1969 Sep;170(3):329–339. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196909010-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Ciaraldi T. P., Kolterman O. G. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent (type II) diabetes. Am J Med. 1985 Sep 20;79(3B):12–22. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(85)80003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer M. A., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr Insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90579-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Chen Y. I., Coulston A. M., Greenfield M. S., Hollenbeck C., Lardinois C., Liu G., Schwartz H. Insulin secretion and action in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Is insulin resistance secondary to hypoinsulinemia? Am J Med. 1983 Nov 30;75(5B):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlett J. A., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G. Insulin treatment reverses the insulin resistance of type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1982 Jul-Aug;5(4):353–363. doi: 10.2337/diacare.5.4.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrumpf E., Bergan A., Djøseland O., Fausa O., Flaten O., Skagen D. W., Tronier B. The effect of gastric bypass operation on glucose tolerance in obesity. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1985;107:24–31. doi: 10.3109/00365528509099748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha M. K., Pories W. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Caro J. F. Insulin-receptor kinase activity of adipose tissue from morbidly obese humans with and without NIDDM. Diabetes. 1987 May;36(5):620–625. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.5.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]