Abstract
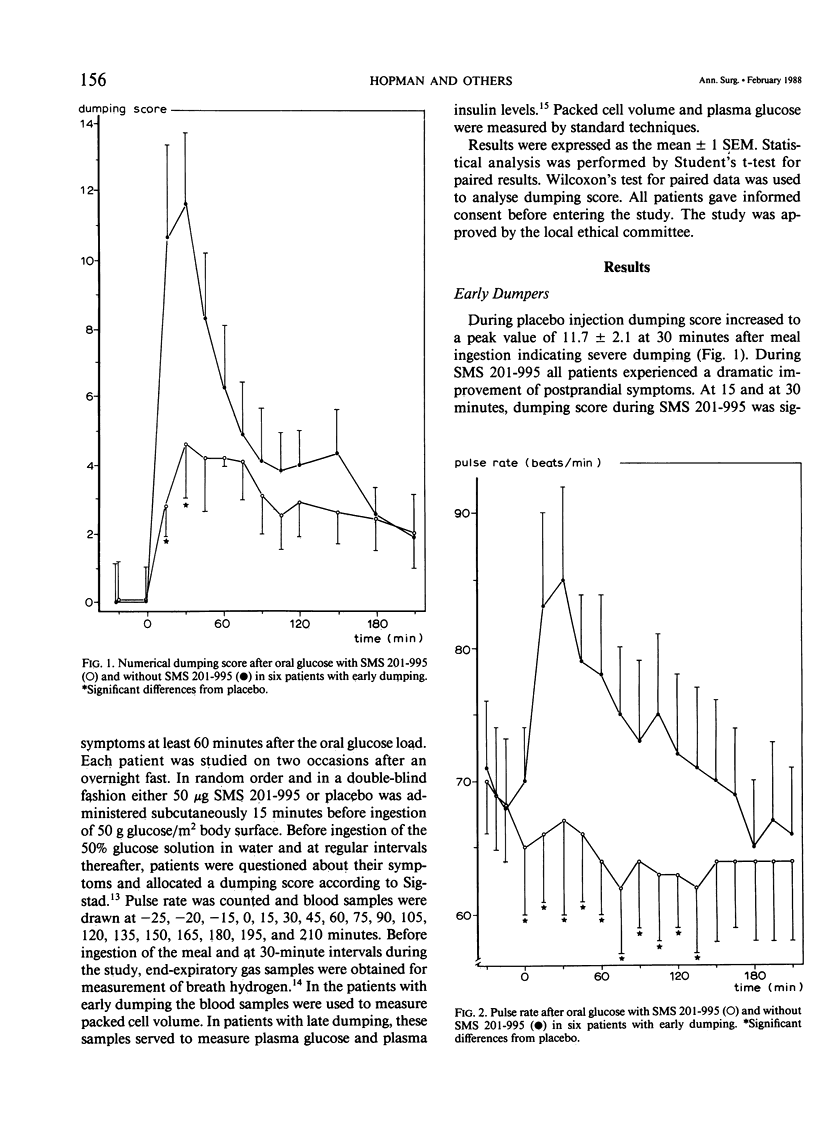
In six patients suffering from severe early dumping and six patients with late dumping after peptic ulcer surgery, the effect of the somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995 was compared with placebo. In early dumpers subcutaneous administration of 50 micrograms SMS 201-995 prior to meal ingestion induced a strong improvement of dumping symptoms as reflected by a decrease of the Sigstad dumping score from 12 +/- 2 during placebo to 5 +/- 2 (p less than 0.05). Furthermore, the postprandial increase of pulse rate was abolished; maximum pulse rate decreased from 85 +/- 7 beats/min to 67 +/- 7 beats/min (p less than 0.05). SMS 201-995 did not significantly affect postprandial changes in packed cell volume. In late dumpers 50 micrograms SMS 201-995 reduced peak plasma insulin after oral glucose from 173 +/- 16 mU/L during placebo to 35 +/- 9 mU/L during SMS 201-995 (p less than 0.05) and increased individual plasma glucose nadirs from 1.9 +/- 0.3 mmol/L to 7.5 +/- 3.3 mmol/L (p less than 0.01). Both in early and late dumpers SMS 201-995 improved postprandial expiratory breath hydrogen excretion indicating slowing of gastrointestinal hurry. SMS 201-995 is a powerful therapeutic agent for the management of patients suffering from the dumping syndrome after gastric surgery.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. V., Bloom S. R. Neuroendocrine tumours of the gut: long-term therapy with the somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;119:115–128. doi: 10.3109/00365528609087439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W., Briner U., Doepfner W., Haller R., Huguenin R., Marbach P., Petcher T. J., Pless SMS 201-995: a very potent and selective octapeptide analogue of somatostatin with prolonged action. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 13;31(11):1133–1140. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn A. M., Christofides N. D., Ghatei M. A., Sarson D. L., Ebeid F. H., Ralphs D. N., Bloom S. R. Elevation of plasma neurotensin in the dumping syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Oct;59(4):237–243. doi: 10.1042/cs0590237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeldtke R. D., O'Dorisio T. M., Boden G. Treatment of autonomic neuropathy with a somatostatin analogue SMS-201-995. Lancet. 1986 Sep 13;2(8507):602–605. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. J., Gassull M. A., Leeds A. R., Metz G., Dilawari J. B., Slavin B., Blendis L. M. Effect of dietary fiber on complications of gastric surgery: prevention of postprandial hypoglycemia by pectin. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):215–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson C., Wisén O., Efendić S., Uvnäs-Wallensten K. Effects of somatostatin on gastrointestinal propagation and absorption of oral glucose in man. Digestion. 1981;22(3):126–137. doi: 10.1159/000198619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvols L. K., Moertel C. G., O'Connell M. J., Schutt A. J., Rubin J., Hahn R. G. Treatment of the malignant carcinoid syndrome. Evaluation of a long-acting somatostatin analogue. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 11;315(11):663–666. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609113151102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberts S. W., Uitterlinden P., Verschoor L., van Dongen K. J., del Pozo E. Long-term treatment of acromegaly with the somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1576–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawaetz O., Aritas Y., Blackburn A. M., Ralphs D. N. Gastric emptying after peptic ulcer surgery. Some pathophysiological mechanisms of the dumping syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1982 Nov;17(8):1065–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawaetz O., Blackburn A. M., Bloom S. R., Aritas Y., Ralphs D. N. Gut hormone profile and gastric emptying in the dumping syndrome. A hypothesis concerning the pathogenesis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Jan;18(1):73–80. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long R. G., Adrian T. E., Bloom S. R. Somatostatin and the dumping syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Mar 23;290(6472):886–888. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6472.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons T. J., McLoughlin J. C., Shaw C., Buchanan K. D. Effect of acarbose on biochemical responses and clinical symptoms in dumping syndrome. Digestion. 1985;31(2-3):89–96. doi: 10.1159/000199185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoughlin J. C., Buchanan K. D., Alam M. J. A glycoside-hydrolase inhibitor in treatment of dumping syndrome. Lancet. 1979 Sep 22;2(8143):603–605. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz G., Gassull M. A., Leeds A. R., Blendis L. M., Jenkins D. J. A simple method of measuring breath hydrogen in carbohydrate malabsorption by end-expiratory sampling. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Mar;50(3):237–240. doi: 10.1042/cs0500237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagor G. R., Bryant M. G., Ghatei M. A., Kirk R. M., Bloom S. R. Release of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the dumping syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Feb 14;282(6263):507–510. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6263.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigstad H. A clinical diagnostic index in the diagnosis of the dumping syndrome. Changes in plasma volume and blood sugar after a test meal. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Dec;188(6):479–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth P. A., Jansen J. B., Lamers C. B. Effect of acarbose, pectin, a combination of acarbose with pectin, and placebo on postprandial reactive hypoglycaemia after gastric surgery. Gut. 1983 Sep;24(9):798–802. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.9.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschoor L., Lamberts S. W., Uitterlinden P., Del Pozo E. Glucose tolerance during long term treatment with a somatostatin analogue. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Nov 22;293(6558):1327–1328. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6558.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Eriksson L. S. The influence of a long-acting somatostatin analogue on splanchnic haemodynamics and metabolism in healthy subjects and patients with liver cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;119:103–108. doi: 10.3109/00365528609087437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J. Influence of somatostatin on carbohydrate disposal and absorption in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1976 Dec 4;2(7997):1213–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G., Fuessl H., Kraenzlin M., Bloom S. R. Postprandial effects of SMS 201-995 on gut hormones and glucose tolerance. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;119:73–83. doi: 10.3109/00365528609087434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



