Abstract
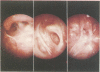
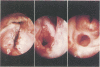
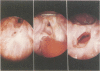
Eighteen cases of severe chronic caustic stenosis of the hypopharynx and esophagus are presented. Restoration of digestive continuity was accomplished by retrosternal ileocolic transposition. The cervical approach and the position of anastomosis depended on the status of the hypopharynx. When one pyriform sinus remained open (type I, N = 4), an anterior suprahyoid approach was used in conjunction with lateral hypopharyngotomy because it facilitated the anastomosis and additional minor surgical procedures. When the hypopharynx was completely stenosed (type II, N = 14), a transepiglottic approach consisting of partial horizontal laryngectomy was used because it allowed excision of the supraglottic stricture, restoration of the oropharyngeal cavity, anastomosis to the posterior oropharyngeal wall, management of an eventual laryngotracheal stenosis, and elevation of the laryngeal inlet above the digestive anastomosis. After operation, several endoscopic examinations were required, sometimes combined with reoperation. Return of deglutition assuring normal nutrition was obtained in 61% of patients: 3 of 4 type I and in 8 of 14 type II.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowitz W. P., Roper C. L., Sessions D. G., Spector G. J., Ogura J. H. Surgical management of severe lye burns of the esophagus by colon interposition. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1975 Sep-Oct;84(5 Pt 1):576–582. doi: 10.1177/000348947508400502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borja A. R., Ransdell H. T., Jr, Thomas T. V., Johnson W. Lye injuries of the esophagus. Analysis of ninety cases of lye ingestion. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1969 Apr;57(4):533–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardona J. C., Daly J. F. Current management of corrosive esophagitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1971 Aug;80(4):521–527. doi: 10.1177/000348947108000414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gago O., Ritter F. N., Martel W., Orvald T. O., Delavan J. W., Dieterle R. V., Kirsh M. M., Kahn D. R., Sloan H. Aggressive surgical treatment for caustic injury of the esophagus and stomach. Ann Thorac Surg. 1972 Mar;13(3):243–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64845-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehanno P., Guedon C. Inhibition of experimental esophageal lye strictures by penicillamine. Arch Otolaryngol. 1981 Mar;107(3):145–147. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1981.00790390011004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossot D., Sarfati E., Celerier M. Early blunt esophagectomy in severe caustic burns of the upper digestive tract. Report of 29 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1987 Aug;94(2):188–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C. W., Harris A. S. Relief of stricture in the cervical esophagus by Z-plasty technique. Laryngoscope. 1971 May;81(5):658–662. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197105000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. Total obliteration of esophagus and hypopharynx due to corrosives. A new technique of reconstruction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1970 Aug;60(2):264–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPER C. L., BERK P. D., HOWES E. L. Strength of esophageal anastomoses repaired with autogenous pericardial grafts. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963 Jul;117:83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaker R. C., Conley J. Surgical treatment of hypopharyngeal stenosis in children. Laryngoscope. 1979 Oct;89(10 Pt 1):1593–1599. doi: 10.1002/lary.5540891007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D. B., Demeter M. J., Barnett T. E. Caustic ingestion: controversies in management. A review of 214 cases. Laryngoscope. 1980 Jan;90(1):98–109. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198001000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsh M. M., Peterson A., Brown J. W., Orringer M. B., Ritter F., Sloan H. Treatment of caustic injuries of the esophagus: a ten year experience. Ann Surg. 1978 Nov;188(5):675–678. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197811000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAFARGUE P., DUFOUR R., CABANIE H., CHAVANNAZ J. Oesphagoplastie préthoracique à l'aide du côlon droit et de l'iléon terminal. Mem Acad Chir (Paris) 1951 Apr 11;77(12-13):362–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGURA J. H., ROPER C. L., BURFORD T. H. Functional restoration of the food passages in extensive stenosing caustic burns of the pharynx and esophagus. Laryngoscope. 1961 Aug;71:885–902. doi: 10.1288/00005537-196108000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabuzzi D. D., Camp H. L. Repair of hypopharyngeal stenosis. Arch Otolaryngol. 1973 Mar;97(3):256–258. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1973.00780010264007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati E., Gossot D., Assens P., Celerier M. Management of caustic ingestion in adults. Br J Surg. 1987 Feb;74(2):146–148. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild J. A. Caustic ingestion in adult patients. Laryngoscope. 1985 Oct;95(10):1199–1201. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198510000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symbas P. N., Vlasis S. E., Hatcher C. R., Jr Esophagitis secondary to ingestion of caustic material. Ann Thorac Surg. 1983 Jul;36(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)60653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. N., Dedo H. H., Lim R. C., Jr, Steele M. Pharyngoesophageal caustic stricture. Treatment by pharyngogastrostomy compared to colon interposition combined with free bowel graft. Am J Surg. 1976 Aug;132(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran Ba Huy P., Assens P., Mislawski R., Brun J. G., Frachet B., Beutter P., Brasnu D., Celerier M. L'oesopharyngoplastie par transplantation d'un greffon iléo-colique droit dans le traitement des séquelles des sténoses caustiques de l'oesophage et de l'hypopharynx. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 1982;99(10-11):489–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. J., Welsh L. W. Endoscopic examination of corrosive injuries of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Laryngoscope. 1978 Aug;88(8 Pt 1):1300–1309. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197808000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarington C. T., Jr The experimental causticity of sodium hypochlorite in the esophagus. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1970 Oct;79(5):895–899. doi: 10.1177/000348947007900503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]