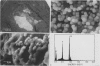
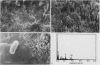
Abstract
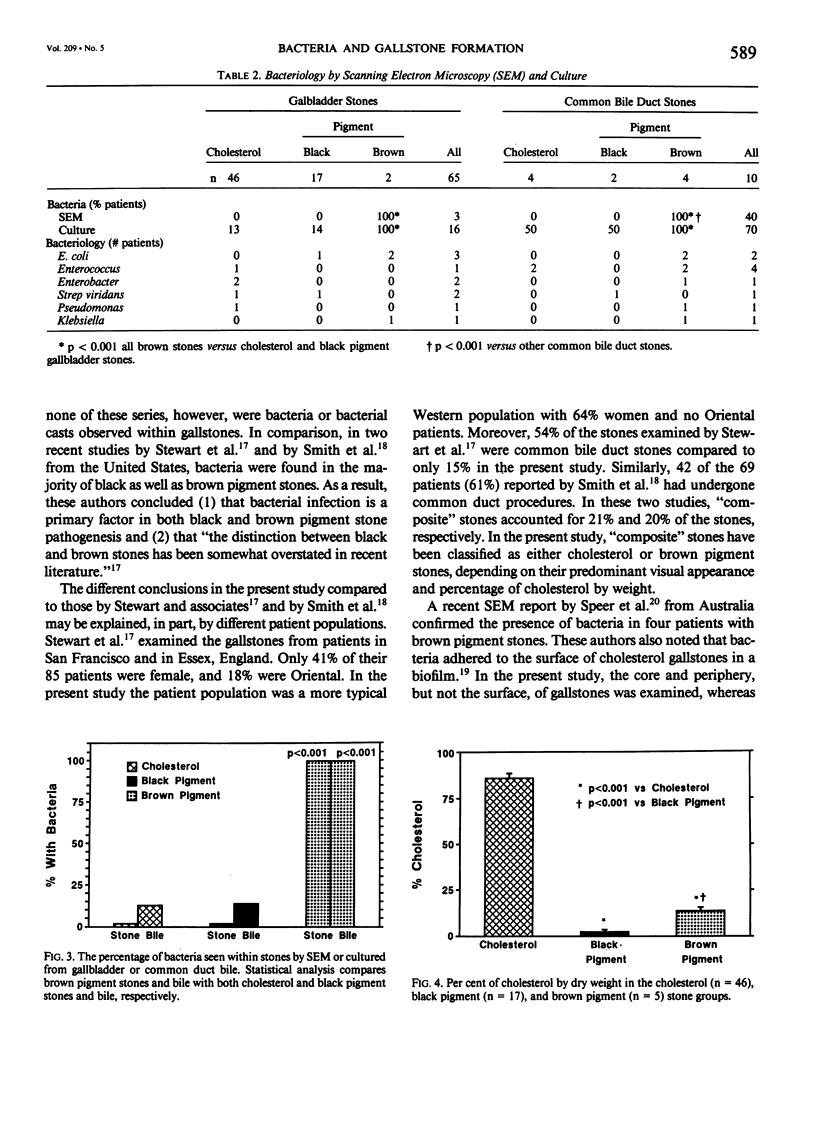
Debate continues as to the role that bacteria play in gallstone pathogenesis in Western countries. We therefore, examined gallbladder and common duct stones from 67 consecutive patients undergoing cholecystectomy and/or common bile duct exploration. Bile was cultured and stone cholesterol content was measured. Stones were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for bacteria. Individual calcium salts were classified by windowless energy-dispersive x-ray microanalysis. Gallbladder stones in 65 patients were identified as cholesterol in 46 (71%), black pigment in 17 (26%), and brown pigment in 2 patients (3%). Common bile duct stones from ten patients were cholesterol in 4, black pigment in 2, and brown pigment in 4 patients. The five patients with brown pigment stones were significantly (p less than 0.05) older, more likely to be men and to present with bile duct obstruction. Bile cultures were positive in 13% of patients with cholesterol stones, in 14% of those with black pigment stones, and in all of the patients with brown pigment stones (p less than 0.001). By SEM, bacteria were observed only within the calcium bilirubinate-protein matrix of brown pigment stones (p less than 0.001). In comparison to black pigment stones, brown stones were more likely to contain calcium palmitate (p less than 0.005) and cholesterol (p less than 0.001). We conclude that black and brown pigment stones have different pathogenic mechanisms and that bacterial infection is important only in the formation of brown pigment stones.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballantyne B., Wood W. G. Biochemical and histochemical observations on Beta-glucuronidase in the mammalian gallbladder. Am J Dig Dis. 1968 Jun;13(6):551–557. doi: 10.1007/BF02233068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhoft R. A., Pellegrini C. A., Motson R. W., Way L. W. Composition and morphologic and clinical features of common duct stones. Am J Surg. 1984 Jul;148(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetta F. M. Bile infection documented as initial event in the pathogenesis of brown pigment biliary stones. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):482–489. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. T., Chan C. W. Recurrent pyogenic cholangitis: a necropsy study. Pathology. 1980 Jul;12(3):415–428. doi: 10.3109/00313028009077105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhart G. L., Levison M. E., Trotman B. W., Soloway R. D. Pigment vs cholesterol cholelithiasis: bacteriology of gallbladder stone, bile, and tissue correlated with biliary lipid analysis. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Oct;23(10):877–882. doi: 10.1007/BF01072459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSA B. U., DOE R. P., SEAL U. S. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF HUMAN LIVER BETA-GLUCURONIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2811–2816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki T., Matsushiro T., Suzuki N. Clarification of the nomenclature of pigment gallstones. Am J Surg. 1982 Sep;144(3):302–305. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki T. Pathogenesis of calcium bilirubinate gallstone: role of E. coli, beta-glucuronidase and coagulation by inorganic ions, polyelectrolytes and agitation. Ann Surg. 1966 Jul;164(1):90–100. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196607000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malet P. F., Dabezies M. A., Huang G. H., Long W. B., Gadacz T. R., Soloway R. D. Quantitative infrared spectroscopy of common bile duct gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1988 May;94(5 Pt 1):1217–1221. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malet P. F., Takabayashi A., Trotman B. W., Soloway R. D., Weston N. E. Black and brown pigment gallstones differ in microstructure and microcomposition. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):227–234. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malet P. F., Williamson C. E., Trotman B. W., Soloway R. D. Composition of pigmented centers of cholesterol gallstones. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):477–481. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Nakayama F. Composition of bile pigment in gallstones and bile and their etiological significance. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Mar;93(3):353–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase M., Hikasa Y., Soloway R. D., Tanimura H., Setoyama M., Kato H. Gallstones in Western Japan. Factors affecting the prevalence of intrahepatic gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):684–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase M., Tanimura H., Setoyama M., Hikasa Y. Present features of gallstones in Japan. A collective review of 2,144 cases. Am J Surg. 1978 Jun;135(6):788–790. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama F., Furusawa T., Nakama T. Hepatolithiasis in Japan: present status. Am J Surg. 1980 Feb;139(2):216–219. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow J. D. The etiology of pigment gallstones. Hepatology. 1984 Sep-Oct;4(5 Suppl):215S–222S. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., Postier R. G., Cameron J. L. Biliary bacteria: significance and alterations after antibiotic therapy. Arch Surg. 1982 Apr;117(4):445–449. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380280037008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potamitis G. S., Tsonis P. A., Arvanitis C. Molecular organization of gallstones. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Mar;32(3):332–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01297063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. J., Fasulo J. M., Patton G. M. Lipids of pigment gallstones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 20;712(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjödahl R., Tagesson C. On the mediation inflammatory reaction in the human gallbladder epithelium. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(3):321–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway R. D., Trotman B. W., Maddrey W. C., Nakayama F. Pigment gallstone composition in patients with hemolysis or infection/stasis. Dig Dis Sci. 1986 May;31(5):454–460. doi: 10.1007/BF01320307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway R. D., Trotman B. W., Ostrow J. D. Pigment gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jan;72(1):167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart L., Smith A. L., Pellegrini C. A., Motson R. W., Way L. W. Pigment gallstones form as a composite of bacterial microcolonies and pigment solids. Ann Surg. 1987 Sep;206(3):242–250. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198709000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata M., Nakayama F. Bacteria and gallstones. Etiological significance. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Mar;26(3):218–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01391633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotman B. W., Morris T. A., 3rd, Sanchez H. M., Soloway R. D., Ostrow J. D. Pigment versus cholesterol cholelithiasis: identification and quantification by infrared spectroscopy. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):495–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotman B. W., Soloway R. D. Pigment gallstone disease: Summary of the National Institutes of Health--international workshop. Hepatology. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):879–884. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Watts J. M. Chemical composition of common bile duct stones. Br J Surg. 1986 Mar;73(3):229–232. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosiewitz U. Scanning electron microscopy in gallstone research. Scan Electron Microsc. 1983;(Pt 1):419–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosiewitz U., Schenk J., Sabinski F., Schmack B. Investigations on common bile duct stones. Digestion. 1983;26(1):43–52. doi: 10.1159/000198867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Sakae T., Schäfer H. Analysis of vaterite microspherolith deposits on a pure cholesterol gallstone by X-ray diffraction, X-ray microanalysis and infrared absorption techniques. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985;405(4):463–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00737172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Yanagisawa J., Nakayama F. Composition of intrahepatic calculi. Etiological significance. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Apr;33(4):449–453. doi: 10.1007/BF01536030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]