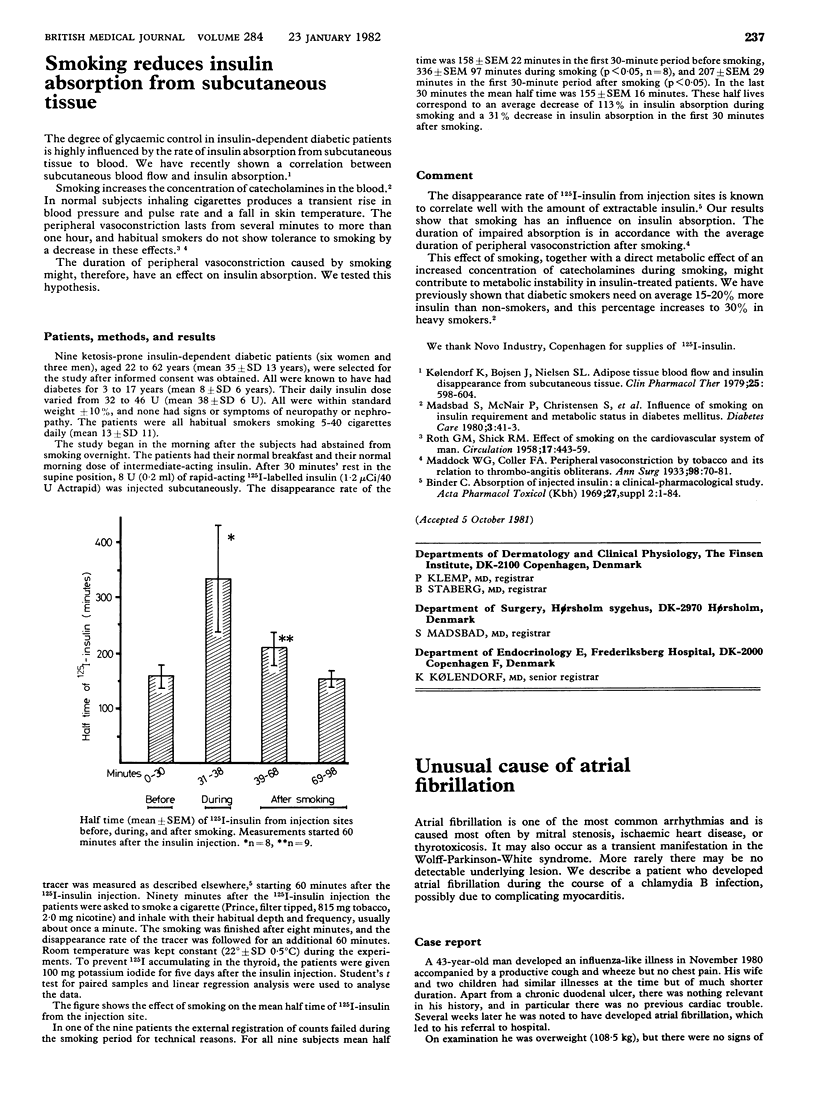
Full text
PDFPage 237
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binder C. Absorption of injected insulin. A clinical-pharmacological study. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1969;27 (Suppl 2):1–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1969.tb03069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kølendorf K., Bojsen J., Nielsen S. L. Adipose tissue blood flow and insulin disappearance from subcutaneous tissue. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 May;25(5 Pt 1):598–604. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979255part1598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddock W. G., Coller F. A. Peripheral Vasoconstriction by Tobacco and Its Relation to Thrombo-Angiitis Obliterans. Ann Surg. 1933 Jul;98(1):70–81. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193307000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsbad S., McNair P., Christensen M. S., Christiansen C., Faber O. K., Binder C., Transbøl I. Influence of smoking on insulin requirement and metbolic status in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1980 Jan-Feb;3(1):41–43. doi: 10.2337/diacare.3.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH G. M., SHICK R. M. Effect of smoking on the cardiovascular system of man. Circulation. 1958 Mar;17(3):443–459. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


