Abstract
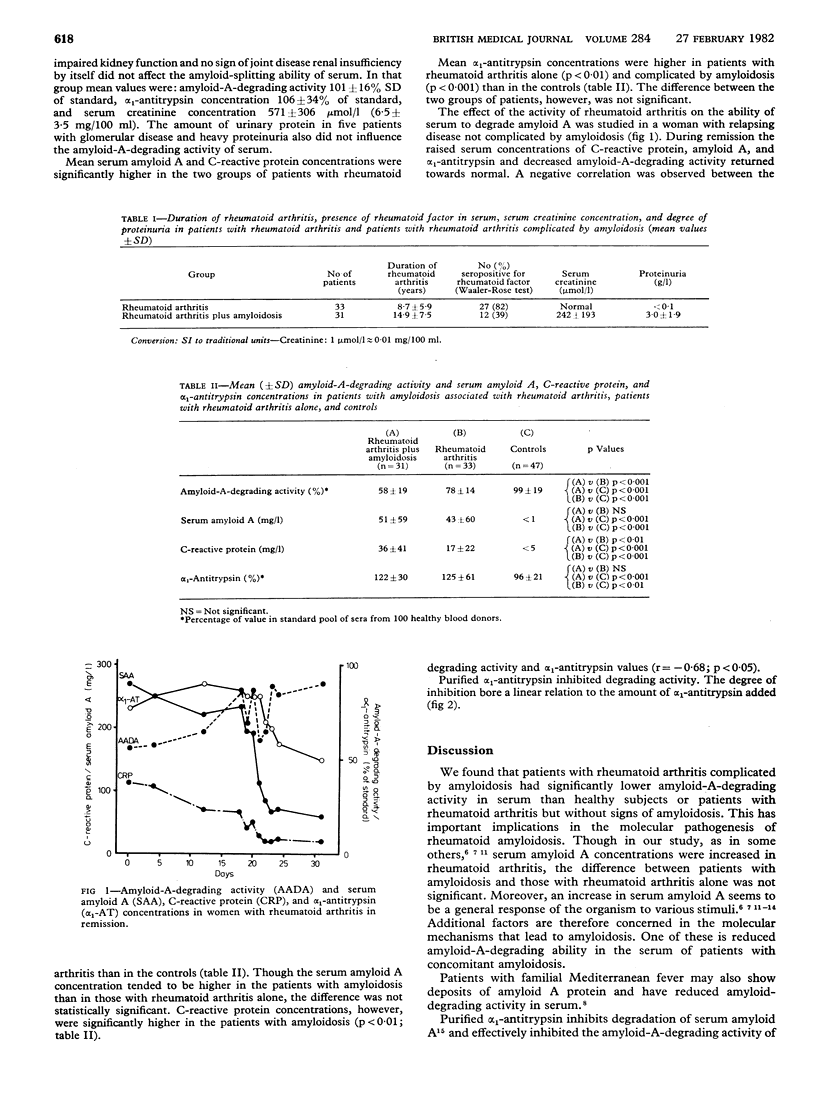
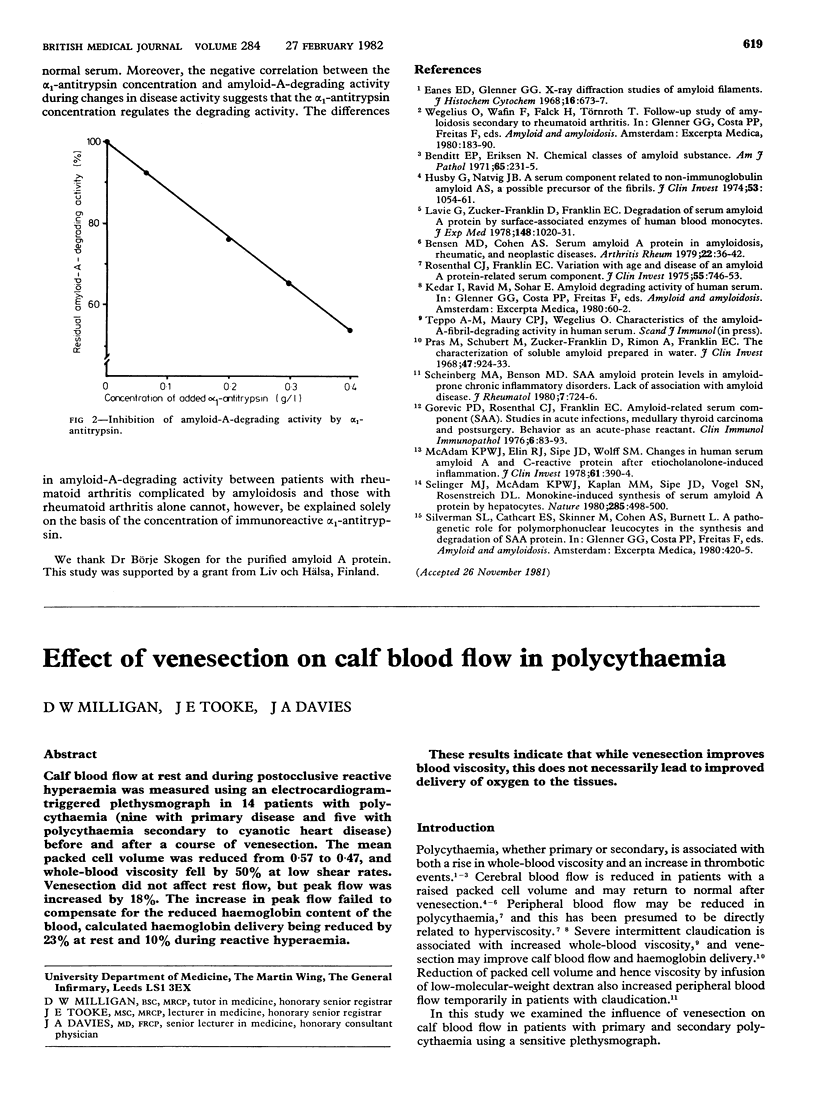
The ability to degrade amyloid A fibrils was studied in the serum of 31 patients with amyloidosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis, 33 patients with rheumatoid arthritis without amyloidosis, and 47 healthy controls. Fibrillar amyloid A protein and the radial diffusion method were used. The mean degrading activity in serum was significantly lower in patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated by amyloidosis (58 +/- 19% SD of the activity in a pooled sample of sera from 100 healthy blood donors used as standard) than in patients with rheumatoid arthritis alone (78 +/- 14%; p less than 0.001) or controls (99 +/- 19%; p less than 0.001). Alpha 1-antitrypsin, concentrations of which were raised in both groups of patients, inhibited the degrading activity in serum even in low concentrations. A negative correlation between degrading activity and alpha 1-antitrypsin concentrations was observed. These findings suggest that reduced amyloid-A-degrading activity is due to inhibition rather than to deficiency of enzyme.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Chemical classes of amyloid substance. Am J Pathol. 1971 Oct;65(1):231–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Cohen A. S. Serum amyloid A protein in amyloidosis, rheumatic, and enoplastic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jan;22(1):36–42. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eanes E. D., Glenner G. G. X-ray diffraction studies on amyloid filaments. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Nov;16(11):673–677. doi: 10.1177/16.11.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Amyloid-related serum component (SAA)--studies in acute infections, medullary thyroid carcinoma, and postsurgery. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Jul;6(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Natvig J. B. A serum component related to nonimmunoglobulin amyloid protein AS, a possible precursor of the fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1054–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI107642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Degradation of serum amyloid A protein by surface-associated enzymes of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1020–1031. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Elin R. J., Sipe J. D., Wolff S. M. Changes in human serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein after etiocholanolone-induced inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):390–394. doi: 10.1172/JCI108949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Variation with age and disease of an amyloid A protein-related serum component. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):746–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI107985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg M. A., Benson M. D. SAA amyloid protein levels in amyloid-prone chronic inflammatory disorders. Lack of association with amyloid disease. J Rheumatol. 1980 Sep-Oct;7(5):724–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger M. J., McAdam K. P., Kaplan M. M., Sipe J. D., Vogel S. N., Rosenstreich D. L. Monokine-induced synthesis of serum amyloid A protein by hepatocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):498–500. doi: 10.1038/285498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


