Abstract
We examined the interaction of ethanol with the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic system in neurons of slices of the rat central amygdala nucleus (CeA), a brain region thought to be critical for the reinforcing effects of ethanol. Brief superfusion of 11–66 mM ethanol significantly increased GABA type A (GABAA) receptor-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) and currents (IPSCs) in most CeA neurons, with a low apparent EC50 of 20 mM. Acute superfusion of 44 mM ethanol increased the amplitude of evoked GABAA IPSPs and IPSCs in 70% of CeA neurons. The ethanol enhancement of IPSPs and IPSCs occurred to a similar extent in the presence of the GABA type B (GABAB) receptor antagonist CGP 55845A, suggesting that this receptor is not involved in the ethanol effect on CeA neurons. Ethanol superfusion also decreased paired-pulse facilitation of evoked GABAA IPSPs and IPSCs and always increased the frequency and sometimes the amplitude of spontaneous miniature GABAA IPSCs as well as responses to local GABA application, indicating both presynaptic and postsynaptic sites of action for ethanol. Thus, the CeA is the first brain region to reveal, without conditional treatments such as GABAB antagonists, consistent, low-dose ethanol enhancement of GABAergic transmission at both pre- and postsynaptic sites. These findings add further support to the contention that the ethanol–GABA interaction in CeA plays an important role in the reinforcing effects of ethanol.
Keywords: alcohol‖GABA IPSP/Cs‖paired-pulse facilitation‖miniature synaptic current‖electrophysiology
The amygdala formation is a complex of interconnected nuclei that has been implicated in various physiological functions such as attention (1), memory (1–4), emotion (5–7), and autonomic control (3). This complex has been linked to the motivational effects of drugs of abuse and alcoholism in particular (8).
The γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic system, particularly in the central amygdala nucleus (CeA), has been implicated in the expression of emotionality, including behavioral states of fear and anxiety, as well as states associated with consummatory responses (9). The CeA is considered to be crucial in mediating the behavioral effects of acute and chronic ethanol consumption (10, 11). Because stress reduction has long been considered to contribute to ethanol-seeking behavior in humans, researchers hypothesized that the CeA and its connections might be sites for a GABA-like action of ethanol to mediate ethanol reinforcement. Behavioral studies indicate that injection of GABAergic antagonists directly into the CeA decreases motivated responding for oral self-administration of ethanol in rats, whereas infusion of GABA agonists and benzodiazepines decreased anxiety (11, 12). Thus, these studies suggest that GABAergic systems in the CeA play a major role in the acute reinforcing effects of ethanol (13) and in the anxiogenic response to ethanol withdrawal (14).
There has been a continuing controversy over the ability of ethanol to enhance GABAergic neurotransmission [inhibitory postsynaptic potentials/inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSP/Cs)] in CNS neurons under basal conditions in other brain regions (see Discussion and refs. 15–18). Therefore, we have investigated effects of acute ethanol on basic membrane properties and on inhibitory GABAergic transmission within the CeA in a slice preparation.
Here we report that, in contrast to other brain regions, acute superfusion of low ethanol concentrations augments three measures of GABAergic neurotransmission (spontaneous and evoked IPSP/Cs and responses to exogenously applied GABA) in most CeA neurons in brain slices taken from rats. These findings add further support for the contention that GABA–ethanol interactions in central amygdala play some role in the reinforcing effects of ethanol.
Materials and Methods
Slice Preparation.
We prepared amygdala slices from male Sprague–Dawley rats (100–300 g) that were anesthetized with halothane (3%) and decapitated, and the brains were rapidly removed into ice-cold artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) gassed with 95% O2/5% CO2. Transverse slices 400 μm thick were cut on a Vibroslicer (Campden) or a Leica VT 1000S (McBain Instruments, Chatsworth, CA), incubated in an interface configuration for ≈30 min, and then submerged completely and superfused continuously (flow rate, 2–4 ml/min) with warm (31°C) gassed ACSF. The ACSF was composed of 130 mM NaCl, 3.5 mM KCl, 1.25 mM NaH2PO4, 1.5 mM MgSO4⋅7H2O, 2.0 mM CaCl2, 24 mM NaHCO3, and 10 mM glucose. The inner chamber had a total volume of 0.8 ml; at the superfusion rates used, 90% replacement of the chamber solution could be obtained within 1 min. Drugs were added to the ACSF from stock solutions at known concentrations.
Intracellular Recording.
We recorded from CeA neurons with sharp micropipettes (containing 3 M KCl) using discontinuous voltage- or current-clamp mode. In voltage-clamp mode, we used a switching frequency of 3–5 kHz and continuously monitored, on a separate oscilloscope, electrode settling time and capacitance neutralization at the head stage. The data were acquired with an Axoclamp-2A preamplifier (Axon Instruments, Foster City, CA) and stored for later analysis by using PCLAMP software (Axon Instruments). We evoked pharmacologically isolated IPSP/Cs by stimulating locally within the CeA through a bipolar stimulating electrode and superfusing the glutamate receptor blockers 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX, 10 μM) and dl-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (APV, 30 μM) to isolate GABAergic IPSP/Cs. In five cells, we also applied 1 μM CGP 55845A [a GABA type B (GABAB) antagonist], to further isolate GABA type A (GABAA) receptor-mediated IPSP/Cs.
In most neurons, we held the cells near their resting membrane potential (RMP) and applied hyperpolarizing and depolarizing voltage commands or current steps (200-pA increments, 750-msec duration) to generate current–voltage and/or voltage–current curves, respectively. The evoked IPSP/C amplitudes and current–voltage or voltage–current responses were quantified by CLAMPFIT software (Axon Instruments). We also used a paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) protocol with an interstimulus interval of 50 msec and stimulus strength adjusted such that the amplitude of the first IPSP/C of the pair was 50% of maximal amplitude of the IPSP/C determined in the input/output (I/O) relationship. We took measures before ethanol (control), during ethanol (5–15 min), and after (20–30 min) ethanol washout and calculated the ratio between the second and first IPSP/C (IPSP/C2 to IPSP/C1). We express all values as mean ± SEM. We subjected data to a between-subject or within-subject ANOVA with repeated measures, and the Newman–Keuls post hoc test with P < 0.05 considered statistically significant. When appropriate we used the Student's paired or unpaired t test.
Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Recording of Miniature IPSCs (mIPSCs).
In another set of neurons, we recorded from CeA using the “blind” method of whole-cell patch-clamp in the presence of 10 μM CNQX, 30 μM APV, 1 μM CGP 55845A, and 1 μM tetrodotoxin (TTX). All GABAA IPSC recordings were made with electrodes filled with an internal solution containing 135 mM KCl, 10 mM Hepes, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EGTA, 5 mM ATP, and 1 mM GTP (the latter two added fresh on the day of recording), with pH values of 7.2–7.3 and osmolarity of 275–290. We pulled patch pipettes on a Flaming/Brown puller from borosilicate glass (input resistance 2–3 MΩ). The data were acquired with an Axoclamp-2A preamplifier (Axon Instruments) and analyzed by using MINI 5.1 software (Synaptosoft, Leona, NJ). We evaluated ethanol effects on frequency and amplitude of mIPSCs within individual neurons using cumulative probability analysis, with statistical significance determined by using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov nonparametric two-sample test (P < 0.05 is considered significant).
GABA Pressure Application.
We applied GABA (5 μM in the pipette) locally near the recorded neuron by pressure (pipette tip diameter, 2–4 μm; pressure, 1–10 psi; duration, 0.5–3 sec). The GABA responses were recorded in current-clamp mode and in the presence of glutamate receptor blockers APV (30 μM) and CNQX (10 μM), together with 1 μM CGP 55845A and 1 μM TTX (to minimize presynaptic effects). The neurons were held near their RMPs (≈−77 mV) where, with Cl−-containing recording pipettes, GABA responses were depolarizing. After stable responses were achieved, we took current and voltage measurements at several time points before, during, and after ethanol application. We defined ethanol potentiation of GABA responses as a 10% increase in peak response.
Drugs.
CGP 55845A was a gift from Novartis Pharma (Basel). We purchased APV and CNQX from Tocris Cookson (Ellison, MO), bicuculline and GABA from Sigma, TTX from Calbiochem, and ethanol from Remet (La Mirada, CA). To avoid loss of ethanol by evaporation, we diluted solutions in gassed ACSF from sealed stock solutions of reagent-grade 95% ethyl alcohol in water immediately before administration.
Results
CeA Neuronal Properties.
We recorded from a total of 99 CeA neurons; they had a mean RMP of −76 ± 2 mV and mean input resistance (with sharp pipettes) of 105 ± 5 MΩ. In current-clamp mode, these CeA neurons had several distinctive characteristics. The spike firing during a depolarizing voltage step was either accommodating or nonaccommodating and was followed by either a large after-hyperpolarizing potential (AHP) (38%) or very small AHP (62%). We defined the AHP as large when the amplitude was ≈5–6 mV (duration ≥ 500 msec) and small when at ≈1 mV (duration ≈250 msec), measured at 200 msec after the depolarizing step. Generally, neurons with accommodated spike firing also had larger AHPs compared with the nonaccommodating neurons. These characteristics are consistent with previous reports of diverse cell types in the CeA (19–21). To date, we have not seen any correlation between the cell type (based on AHP size) and the responsivity to ethanol (described below).
Ethanol: Evoked IPSP/Cs.
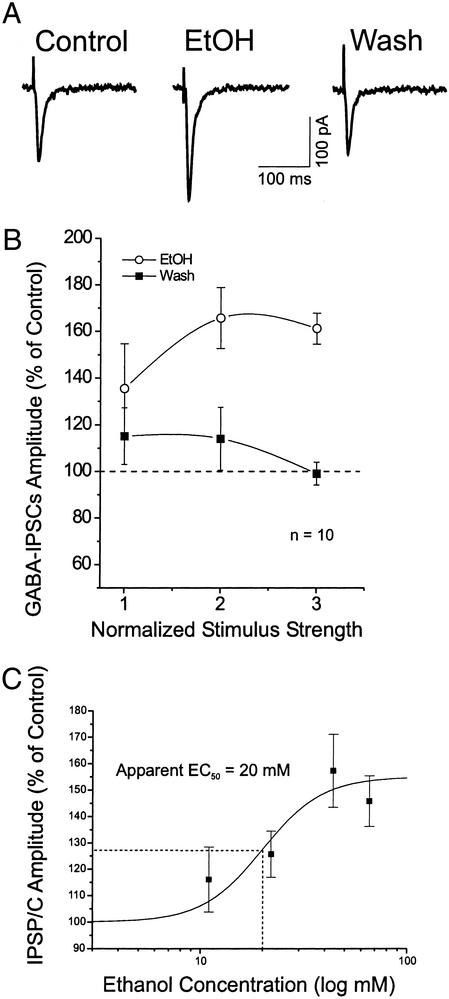
We examined the acute effects of 44 mM ethanol on basic membrane properties of CeA neurons. Ethanol had no significant (P > 0.1) effect on membrane potential, voltage–current and current–voltage curves, input resistance, or spike amplitudes (data not shown). However, in the presence of glutamate receptor blockers CNQX and APV, 44 mM ethanol clearly enhanced the isolated GABA-mediated IPSC amplitudes (Fig. 1A) in 7 of 10 neurons tested (Table 1). Statistical analysis done on all 10 neurons showed that ethanol significantly [F(1, 23) = 7.205, P < 0.05] increased mean evoked IPSC amplitudes over all stimulus strengths (to 161 ± 7% of control at maximal stimulus intensity), with recovery on washout for 12 min (99 ± 4% of control at maximal strength; Fig. 1B). The ethanol-induced enhancement of IPSCs was measurable at ≈4 min (including the inflow “dead time”) after the onset of ethanol superfusion and was maximal at 6–8 min; it recovered after 10–15 min of washout. We saw no signs of acute tolerance even with long ethanol applications.
Figure 1.
Acute superfusion of ethanol increases the amplitude of evoked GABA IPSCs, revealed in the presence of glutamatergic blockers. (A) Superfusion of 44 mM ethanol (EtOH) for 10 min increased the IPSC amplitude, with recovery on washout (12 min). (B) Mean percent increases of IPSC amplitudes elicited by 44 mM ethanol, averaged from 10 CeA neurons. (C) Dose–response relationship for ethanol enhancement of mean IPSP/C amplitudes in CeA neurons, expressed as percent of control. Ethanol superfused for 7–10 min. Number of neurons for each ethanol concentration: 11 mM, n = 5; 22 mM, n = 5; 44 mM, n = 8; and 66 mM, n = 4. The logistic curve, plotted by ORIGIN software (Microcal Software, Northampton, MA) using y = (A1 − A2)/[1 + (x/xo)p + A2], gives an apparent EC50 of 20 mM ethanol for IPSP/C enhancement. Parameters of the logistic curve were set at 155% (upper asymptote fixed) and 100% (lower asymptote fixed). The rate was fixed at 3.0, with “center” unfixed. Error bars, SEM.
Table 1.
Differential ethanol sensitivity of CeA neurons
| Acute ethanol (44 mM) effects on | Increase, % cells | No change or decrease, % cells | No. of cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evoked IPSP/Cs | 70 | 30 | 10 |
| Responses to exogenous GABA | 69 | 31 | 16 |
| Frequency of miniature IPSCs | 100 | 0 | 6 |
| Amplitude of miniature IPSCs | 67 | 33 | 6 |
A dose–response analysis also showed that ethanol (11–66 mM) significantly enhanced the GABAergic IPSPs across the neuronal population as a whole (both ethanol-sensitive and -insensitive; Fig. 1C). The highest ethanol concentration, 66 mM, actually enhanced GABA IPSPs to a lesser extent than did 44 mM ethanol, reminiscent of the inverted U-shaped dose–response curve obtained from nucleus accumbens neurons (22). This ethanol–IPSP interaction in CeA had an apparent EC50 of 20 mM (Fig. 1C), lower than reported for most other neuron types.
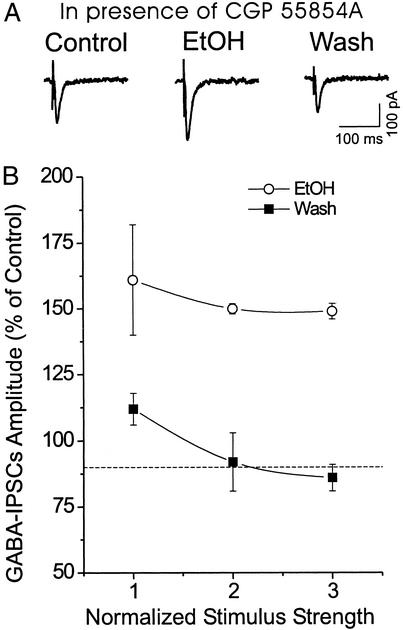
We reported previously that in rat hippocampal slices, ethanol enhanced isolated GABAA IPSCs only if GABAB receptors were blocked (16). However, as indicated above, in 70% of CeA neurons ethanol increased IPSCs even without blocking GABAB receptors. To determine whether the enhancement might be increased further if GABAB receptors were blocked, in five neurons we superfused the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP 55845A (1 μM) together with the glutamate receptor blockers. Under these conditions, ethanol still enhanced the mean IPSC amplitude to 148 ± 3% of control (measured at maximal stimulus intensity; Fig. 2). Thus, in contrast to hippocampus (16) and nucleus accumbens (15), in CeA GABAB receptors do not seem to regulate ethanol enhancement of isolated IPSC amplitudes.
Figure 2.
(A) Representative synaptic current traces before, during, and after ethanol (EtOH) application (44 mM, 8 min), all in the continued presence of the GABAB receptor antagonist 1 μM CGP 55845A together with the glutamate receptor blockers APV and CNQX. Ethanol superfusion increased the amplitude of evoked GABAA IPSCs, with recovery on washout (15 min). RMP = holding potential (Vh) = −72 mV. (B) Pooled data from five CeA neurons showing that, in the presence CGP 55845A (1 μM), ethanol enhanced GABAA IPSCs by about the same percentage as without the blocker (see Fig. 1B); this effect was reversible after washout.
Paired-Pulse Studies.
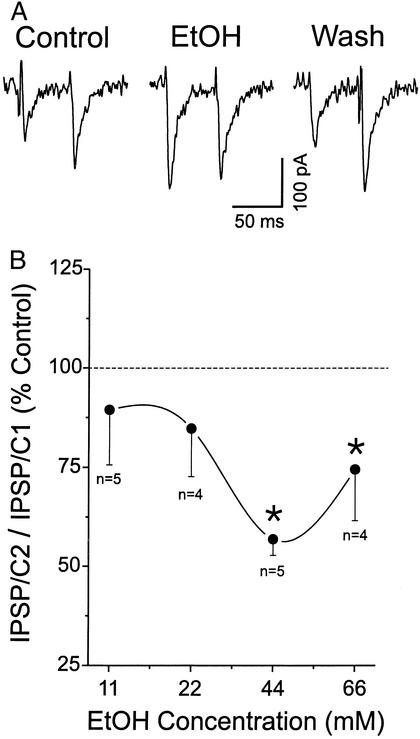
Ethanol could act at either pre- or postsynaptic sites to enhance IPSP size. To determine whether ethanol changes the probability of GABA release at CeA synapses, we carried out three types of experiments. In the first set of experiments we examined PPF (at an interpulse interval of 50 msec), a phenomenon whereby a secondary synaptic response is increased by a preceding primary stimulation of equal intensity (23–25). Changes in PPF are inversely related to transmitter release such that a reduction of PPF is associated with an increased probability of transmitter release (26, 27). We found that superfusion of either 44 or 66 mM ethanol significantly decreased PPF of GABAA IPSP/Cs (relative to the control; P < 0.05; Fig. 3B), suggesting an increased GABA release. In two cells we observed PPF to become paired-pulse inhibition (Fig. 3A). A slight decrease of PPF was observed also in neurons superfused with lower concentrations of ethanol (11 or 22 mM), but this did not reach statistical significance (P > 0.05; Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Ethanol (EtOH) increased the amplitude of evoked GABAA IPSP/Cs (see Fig. 1) and decreased the PPF ratio of IPSP/Cs (IPSP/C2 to IPSP/C1) during ethanol application. Results are the average from different groups of neurons for each ethanol concentration tested: 11 mM, n = 5; 22 mM, n = 4; 44 mM, n = 5; and 66 mM, n = 4. Mean ± SEM paired-pulse ratio is expressed as percentage of the mean baseline value (dashed line). The asterisk denotes statistical significance (P < 0.05, ANOVA).
Spontaneous IPSCs.
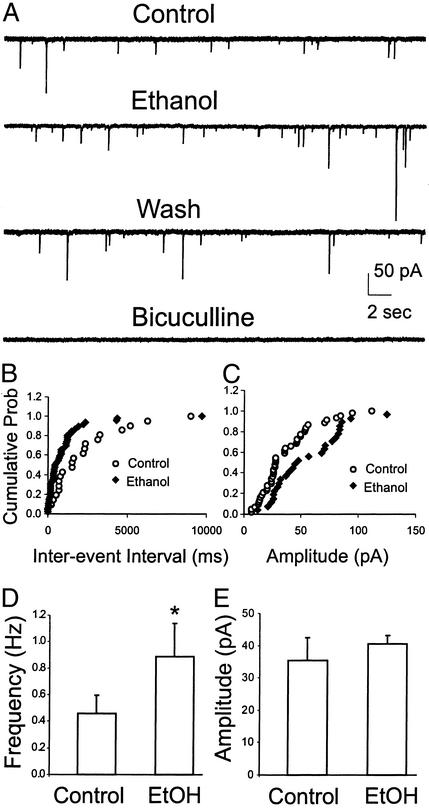
In recordings with sharp pipettes, the majority of neurons from control rats exhibited spontaneous synaptic events completely blocked by superfusion of bicuculline. Interestingly, in approximately half of neurons recorded, 44 mM ethanol clearly increased the frequency of these spontaneous IPSP/Cs (data not shown), suggesting a possible presynaptic site of action. In a second set of experiments, to quantify spontaneous mIPSCs, we recorded from six CeA neurons using whole-cell patch-clamp in the presence of 1 μM TTX, 1 μM CGP 55845A, and glutamatergic blockers (30 μM APV and 10 μM CNQX). Generally, a change in the frequency of mIPSCs implicates an altered probability of transmitter release, and a change in the amplitude of mIPSCs reflects alterations in the sensitivity of postsynaptic GABAA receptors (28, 29). Superfusion of 44 mM ethanol for 6–10 min increased the mean frequency of mIPSCs to 223 ± 31% of control and significantly shifted the cumulative frequency distribution to shorter interevent intervals in all six neurons (means: control, 0.46 ± 0.14 Hz; 44 mM ethanol, 0.89 ± 0.25 Hz; P < 0.05; Fig. 4 A, B, and D; Table 1), supporting the PPF data indicating an increased presynaptic release of GABA. These mIPSCs were blocked totally by superfusion of bicuculline (Fig. 4A). Furthermore, ethanol induced spontaneous mIPSC activity in one of the neurons that was silent during the control period.
Figure 4.
Ethanol (44 mM) increased the frequency and amplitude of spontaneous mIPSCs. (A) Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from a representative CeA neuron in the presence of 1 μM TTX, 30 μM APV, 10 μM CNQX, and 1 μM CGP 55845A. Acute superfusion of 44 mM ethanol onto this cell increased the frequency and amplitude of the mIPSCs, with partial recovery on washout. These mIPSCs were totally blocked by superfusion of 30 μM bicuculline. (B) Cumulative frequency histogram for a representative neuron showing a shift to the left, indicating a shorter interevent interval (higher frequencies) during the application of 44 mM ethanol. The data shown are means from one 2-min recording each from control baseline and during ethanol superfusion. (C) Cumulative amplitude histogram from the same neuron showing a significant increase in the distribution of mIPSC amplitudes. (D) Pooled data showing the mean increase of mIPSC frequency by 44 mM ethanol (EtOH, n = 6). The asterisk denotes statistical significance by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov nonparametric two-sample test (P < 0.05). (E) Mean amplitudes of mIPSCs from the same six neurons. When averaged over all cells, ethanol did not significantly increase the mIPSC amplitude (P > 0.05).
There was also a significant increase in the mIPSC amplitudes during ethanol application, to 150 ± 12% of control (P < 0.05) in four of the six neurons, suggesting a postsynaptic as well as a presynaptic ethanol effect in some of these neurons. However, averaged over all six neurons, the mean amplitude of mIPSCs in the controls and during 44 mM ethanol superfusion was 35 ± 7 and 40 ± 3 pA, respectively, which was not statistically significant (Fig. 4E). To verify that the apparent changes in frequency were not due to amplitude increases bringing detectable events out of the baseline noise into the discrimination window, we examined mIPSCs in the same cell recorded at different holding potentials. As the membrane potential is shifted away from equilibrium, a change in the amplitude of the events should be detected, whereas the frequency should stay the same (29). In fact, the amplitudes of mIPSCs in one neuron voltage-clamped at −50 and −65 mV were significantly different (P < 0.05), whereas the ethanol-induced frequency increase was not (P > 0.05), further suggesting that increased frequency was independent of changes in amplitude.
GABA Responses.
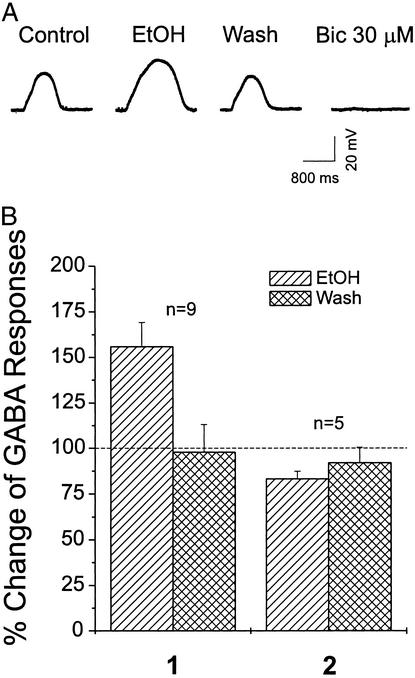
In a different set of CeA neurons, to verify postsynaptic actions of ethanol further, we evoked GABAA responses by local application of 5 μM GABA from a pipette in the presence of 1 μM TTX to minimize presynaptic effects. Under these conditions, exogenous GABA evoked reproducible depolarizing potentials (in current-clamp mode) in CeA neurons that were nearly totally blocked by 30 μM bicuculline (Fig. 5A), suggesting that these responses were mediated primarily by GABAA receptors. In 11 of 16 neurons tested, 44 mM ethanol significantly [F(1, 44) = 7.279, P < 0.01] increased the mean GABA-induced potentials to 158 ± 9% of control (Fig. 5B, 1). In most (69%) of these cells (Table 1), ethanol potentiation of GABA responses occurred within 5 min and recovered to control levels (97 ± 3% of control) on washout (5–15 min). In two of these neurons (not included in the graph of Fig. 5B), the potentiation was followed by a depression, suggesting the development of rapid tolerance to ethanol in these CeA neurons. In the remaining five cells, 44 mM ethanol slightly decreased GABA responses to 83 ± 4% (Fig. 5B, 2). Thus, acute superfusion of 44 mM ethanol increased the amplitude of both GABAA IPSP/Cs and responses to exogenous GABA in almost the same percentage of neurons (Table 1), indicating that ethanol acts at the postsynaptic as well as the presynaptic level in these CeA neurons.
Figure 5.
Amplitudes of exogenous GABA-induced depolarizing potentials in current-clamped CeA neurons are enhanced by 44 mM ethanol (EtOH) superfusion. (A) Representative potential records from a CeA neuron. Local application of GABA (5 μM) from a pipette (every 2 min) during superfusion of ACSF containing APV, CNQX, CGP 55845A, and TTX (control); during ethanol (44 mM) application plus blockers; then during washout of ethanol. Bicuculline (Bic, 30 μM) superfusion totally blocks the GABA response. 1, pooled data from nine ethanol-sensitive CeA neurons showing that ethanol superfusion increased the mean amplitude of exogenous GABA-induced responses, with recovery on washout; 2, in the remaining five cells, 44 mM ethanol slightly decreased mean GABA responses by 17%. The mean ± SEM of GABA responses is plotted as the percent change over the baseline level (dotted line).
Discussion
This study has revealed direct effects of ethanol on GABAergic mechanisms in the rat CeA nucleus. Based on their electrophysiological properties, we found evidence for diverse cell types within the CeA, consistent with results of previous studies (19–21). Although we have observed no correlation between the cell type and sensitivity to ethanol, the two cell types could play a different role in the physiology of this brain region. We hypothesize that the cells with small AHPs will support higher firing frequencies consistent with their role as classical inhibitory interneurons. Our current studies using an infrared video-microscopic setup will help to correlate the physiology and morphology of these cell types better. Stimulation within the CeA elicited synaptic responses mediated by both glutamate (data not shown) and GABA receptors. Acute superfusion of low ethanol concentrations dose-dependently augmented GABAergic neurotransmission, as assessed by several methods, in most CeA neurons, with recovery after washout. Ethanol had no effect on basic membrane properties regardless of cell type recorded, consistent with findings in other brain regions (16–18, 30–35).
Ethanol has been reported to allosterically modulate the GABAA receptor complex and potentiate the effects of GABA in some preparations (36, 37). Nonetheless, in many brain areas other than amygdala, acute ethanol effects on GABAA synaptic responses were either negligible (22, 30, 32) or contingent on additional manipulations such as blockade of GABAB receptors (15, 16, 22) or stimulation in discrete segments of the neuronal afferents (17). In fact, ethanol did not alter currents evoked by exogenous GABA in hippocampus even with GABAB receptor blockade, suggesting that the ethanol–IPSP interaction seen there was mediated presynaptically (15, 16). O. J. Ariwodola and J. L. Weiner have found in rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons that ethanol significantly potentiates presynaptic GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of GABAA IPSCs, effectively decreasing the overall enhancement effect of ethanol on GABA receptor-mediated neurotransmission at these synapses (personal communications). Our present results show that GABAB receptor blockade was not required in the CeA for the enhancement of IPSP/Cs by ethanol, nor did it potentate this effect, which suggests that the ethanol–IPSP interaction was exerted at least in part postsynaptically and that presynaptic GABAB receptors may not be involved in ethanol effects or may not be present on the GABA terminals in CeA. Nor did we observe, with the stimulus parameters used, evidence of a GABAB receptor-mediated postsynaptic component.
Our study has shown that in ≈70% of the CeA neurons tested, acute superfusion of 44 mM ethanol augments the amplitudes of both evoked and spontaneous GABAA receptor-mediated IPSP/Cs and responses to exogenous GABA in the presence of TTX, indicating that ethanol exerts a significant postsynaptic effect in this brain region. A substantial literature has reported inconsistent ethanol effects on postsynaptic responses to exogenous GABA application (15, 22, 38–44). The reasons for these discrepancies are not clear. It should be noted that the concentrations of ethanol applied in most of our experiments were relatively moderate (44 mM or less).
In many CeA neurons, we observed spontaneous events that were blocked completely by CNQX and GABAA receptor blockers. Further, the spontaneous bicuculline-sensitive IPSP/Cs were observed frequently, consistent with previous demonstrations of high numbers of GABA-containing neurons in the CeA (45, 46). With sharp pipettes, ethanol increased the frequency of such spontaneous GABAA receptor-mediated events in most neurons, in parallel with the enhancement of evoked IPSP/Cs in our recordings. This ethanol effect was confirmed by whole-cell recordings and quantification of mIPSCs (in TTX) in all CeA neurons. In fact, we found that ethanol increased mIPSC frequencies sometimes without significantly altering their amplitude distribution. These findings demonstrate that ethanol-induced enhancement of GABAA IPSP/Cs appears to be in part through presynaptic increase of GABA release. An increase in probability of GABA release also would account for the reduction of PPF of IPSP/Cs seen during acute ethanol. Ethanol also increased the mIPSC amplitudes in 67% of the cells tested. These data are consistent with the ethanol-induced increase of responses to exogenous GABA and further support the hypothesis that ethanol also has a postsynaptic effect.
Ethanol interactions with GABA receptors in CeA have been correlated with ethanol reinforcement, and adaptive changes in the GABAergic system seem to be involved in ethanol dependence (11, 36, 47). Our findings agree with behavioral studies suggesting an interaction between ethanol and the GABAergic system in the CeA (11, 12): GABAA receptor antagonists infused into the amygdala reduced ethanol consumption (12), whereas infusion of GABAA agonists and benzodiazepines decreased anxiety (11). It is worth emphasizing that quite low concentrations of ethanol (apparent EC50 = 20 mM), thought to be sedative in vivo, enhanced GABA-mediated IPSP/Cs in CeA neurons. This high ethanol sensitivity lends support to the hypothesis that this brain region is involved in the well known anxiolytic effect of ethanol.
In conclusion, we have shown that ethanol, at low concentrations, markedly enhances multiple measures of GABAergic inhibition at both the pre- and postsynaptic level in the CeA. Such effects are consistent with an overall reduction in the activity and output of the central nucleus [see also recent in vivo studies (48)] and may account in part for the anxiolytic or “tension-reducing” effect of ethanol consumption (11–13, 49). Further study of ethanol effects on the network characteristics of the amygdala may elucidate the biological and molecular substrates of the reinforcing effects of ethanol consumption and how those effects change during the development of dependence.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. G. Koob for critical comments and Drs. W. Fröstl and A. Suter (Novartis Pharma) for the gift of CGP-55854A. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants AA06420, AA10994, DA03665, and NS38633 and the Veterans Affairs Merit Review.
Abbreviations
- GABA
γ-aminobutyric acid
- CeA
central amygdala nucleus
- IPSP
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
- IPSC
inhibitory postsynaptic current
- ACSF
artificial cerebrospinal fluid
- CNQX
6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione
- APV
dl-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate
- GABAB
GABA type B
- GABAA
GABA type A
- RMP
resting membrane potential
- PPF
paired-pulse facilitation
- mIPSC
miniature GABAA IPSC
- TTX
tetrodotoxin
- AHP
after-hyperpolarizing potential
References
- 1.McDonald A J. Prog Neurobiol. 1998;55:257–332. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Henke P G. Behav Brain Res. 1985;16:19–24. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(85)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Liubashina O, Jolkkonen E, Pitkanen A. Neurosci Lett. 2000;291:85–88. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Holland P C, Gallagher M. Trends Cogn Sci. 1999;3:65–73. doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(98)01271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gentile C G, Jarrell T W, Teich A, McCabe P M, Schneiderman N. Behav Brain Res. 1986;20:263–273. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(86)90226-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.LeDoux J E. Annu Rev Psychol. 1995;46:209–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.46.020195.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goosens K A, Holt W, Maren S. Behav Brain Res. 2000;114:145–152. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(00)00224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Koob G F, Roberts A J, Schulteis G, Parsons L H, Heyser C J, Hyytia P, Merlo-Pich E, Weiss F. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:3–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Davis M, Rainnie D, Cassell M. Trends Neurosci. 1994;17:208–214. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rassnick S, Heinrichs S C, Britton K T, Koob G F. Brain Res. 1993;605:25–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91352-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hyytia P, Koob G F. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;283:151–159. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00314-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roberts A J, Cole M, Koob G F. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:1289–1298. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb01125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Koob G F, Rassnick S, Heinrichs S, Weiss F. EXS. 1994;71:103–114. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7330-7_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pich E M, Lorang M, Yeganeh M, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Raber J, Koob G F, Weiss F. J Neurosci. 1995;15:5439–5447. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-08-05439.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Siggins G, Nie Z, Madamba S. In: The “Drunken” Synapse: Studies of Alcohol Related Disorders. Liu Y, Hunt W, editors. New York: Kluwer/Plenum; 1999. pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wan F J, Berton F, Madamba S G, Francesconi W, Siggins G R. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:5049–5054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.5049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weiner J L, Gu C, Dunwiddie T V. J Neurophysiol. 1997;77:1306–1312. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.3.1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Soldo B L, Proctor W R, Dunwiddie T V. Synapse. 1994;18:94–103. doi: 10.1002/syn.890180204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schiess M C, Callahan P M, Zheng H. J Neurosci Res. 1999;58:663–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rainnie D G, Fernhout B J, Shinnick-Gallagher P. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;263:846–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Martina M, Royer S, Pare D. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82:1843–1854. doi: 10.1152/jn.1999.82.4.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nie Z, Madamba S G, Siggins G R. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;293:654–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zucker R S. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:13–31. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Debanne D, Guerineau N C, Gahwiler B H, Thompson S M. J Physiol (London) 1996;491:163–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jiang L, Sun S, Nedergaard M, Kang J. J Physiol (London) 2000;523:425–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00425.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Andreasen M, Hablitz J J. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:326–336. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.1.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mennerick S, Zorumski C F. J Physiol (London) 1995;488:85–101. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.De Koninck Y, Mody I. J Neurophysiol. 1994;71:1318–1335. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.4.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Otis T S, De Koninck Y, Mody I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:7698–7702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Siggins G R, Pittman Q J, French E D. Brain Res. 1987;414:22–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91323-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Siggins G R, Bloom F E, French E D, Madamba S G, Mancillas J, Pittman Q J, Rogers J. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1987;492:350–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb48692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Proctor W R, Allan A M, Dunwiddie T V. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992;16:480–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1992.tb01405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Proctor W R, Soldo B L, Allan A M, Dunwiddie T V. Brain Res. 1992;595:220–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91053-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nie Z, Madamba S G, Siggins G R. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;271:1566–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nie Z, Yuan X, Madamba S G, Siggins G R. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;266:1705–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Deitrich R A, Dunwiddie T V, Harris R A, Erwin V G. Pharmacol Rev. 1989;41:489–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Harris R A, Allan A M. Brain Res. 1989;490:26–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mihic S J. Neurochem Int. 1999;35:115–123. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(99)00053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Marszalec W, Aistrup G L, Narahashi T. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:1516–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Aguayo L G. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;187:127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90349-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Reynolds J N, Prasad A. Brain Res. 1991;564:138–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reynolds J N, Prasad A, MacDonald J F. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;224:173–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90802-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Soldo B L, Proctor W R, Dunwiddie T V. Brain Res. 1998;800:187–197. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(98)00455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Signore A P, Yeh H H. J Neurophysiol. 2000;84:247–254. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.1.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nitecka L, Ben-Ari Y. J Comp Neurol. 1987;266:45–55. doi: 10.1002/cne.902660105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ben-Ari Y, Zigmond R E, Shute C C, Lewis P R. Brain Res. 1977;120:435–444. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tabakoff B, Hoffman P L. Neuron. 1996;16:909–912. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Naylor J C, Simson P E, Gibson B, Schneider A M, Wilkins E, Firestone A, Choy M. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:1683–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Moller C, Wiklund L, Sommer W, Thorsell A, Heilig M. Brain Res. 1997;760:94–101. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)00308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]