Abstract
Thirty-three children with steroid-dependent or steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrosis were treated with a combination of cyclophosphamide and prednisone. Remission occurred in all 23 steroid-dependent patients and, at last report, 12 had gone without any medication for periods of from two months to 21 months without relapse. Remission occurred in five of ten steroid-resistant patients.
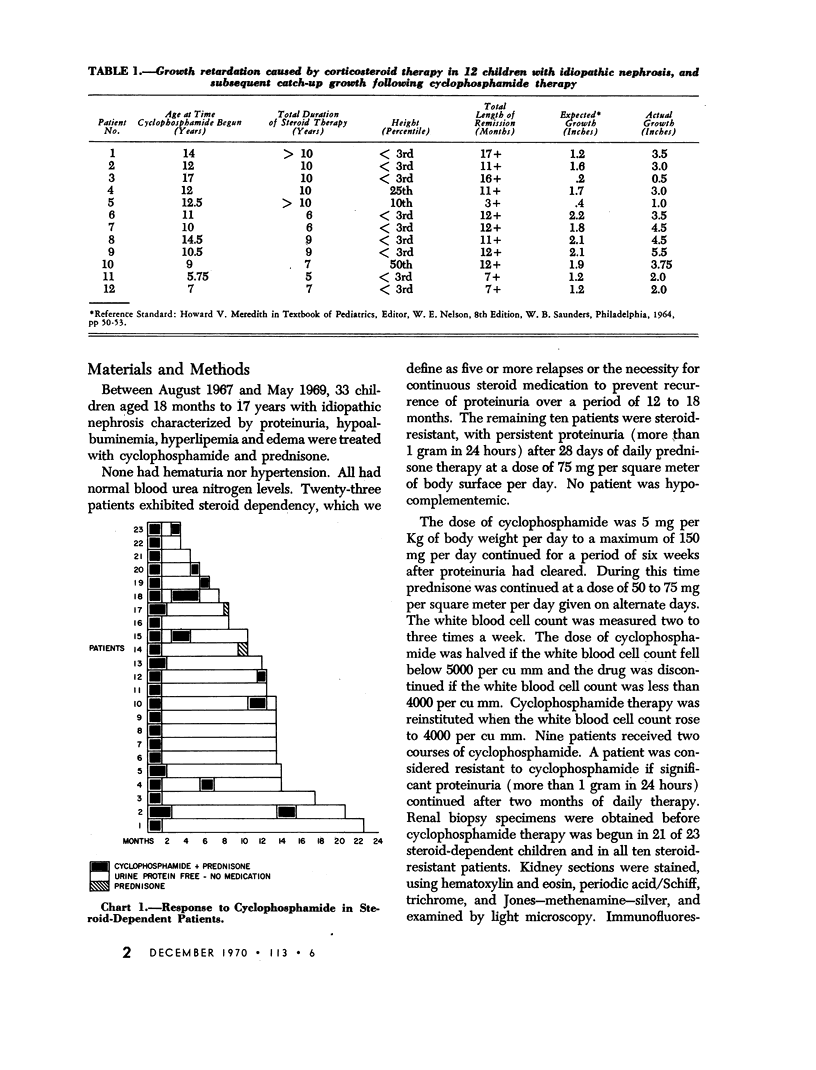
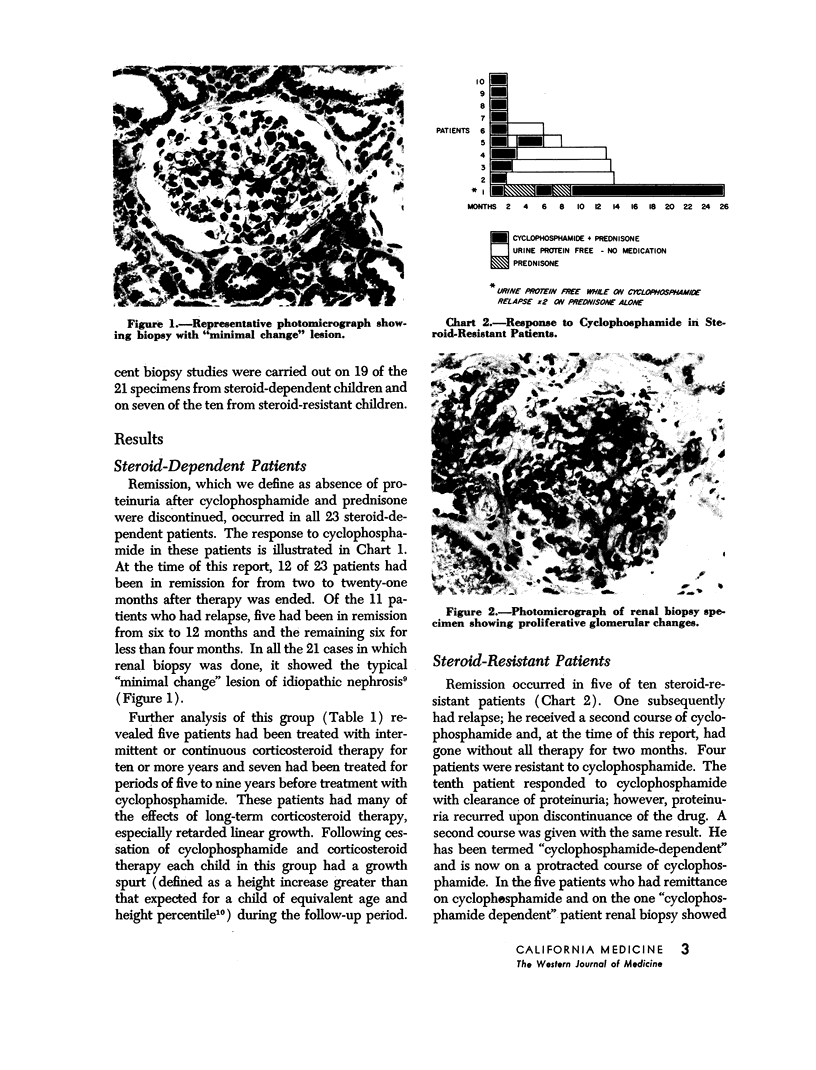
The renal biopsy findings in these patients demonstrate a correlation between the “minimal change” lesion and a positive response to cyclophosphamide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHASIS H., GOLDRING W., BALDWIN D. S. The effect of nitrogen mustard on renal manifestations of human glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1950 Jun;29(6):804–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLDBECK J. H. EXPERIENCE WITH ALKYLATING AGENTS IN THE TREATMENT OF CHILDREN WITH THE NEPHROTIC SYNDROME. Med J Aust. 1963 Dec 14;2:987–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churg J., Habib R., White R. H. Pathology of the nephrotic syndrome in children: a report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet. 1970 Jun 20;760(1):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond K. N., Hillman D. A., Marchessault J. H., Feldman W. Cyclophosphamide in the nephrotic syndrome of childhood: its use in two groups of patients defined by clinical, light microscopic and immunopathologic findings. Can Med Assoc J. 1968 Mar 16;98(11):524–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etteldorf J. N., Roy S., 3rd, Summitt R. L., Sweeney M. J., Wall H. P., Berton W. M. Cyclophosphamide in the treatment of idiopathic lipoid nephrosis. J Pediatr. 1967 May;70(5):758–766. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD R. A., SMITH R. T., VERNIER R. L. Serious untoward reactions to therapy with cortisone and adrenocorticotropin in pediatric practice. II. Pediatrics. 1957 Feb;19(2):272–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupe W. E., Heymann W. Cytotoxic drugs in steroid-resistant renal disease. Alkylating and antimetabolic agents in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome, lupus nephritis, chronic glomerulonephritis, and purpura nephritis in children. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Nov;112(5):448–458. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090140120011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman E., Heuser E., Gilchrist G. S., Donnell G. N., Landing B. H. Thrombosis, nephrosis, and corticosteroid therapy. J Pediatr. 1968 Sep;73(3):320–328. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadow S. R., Weller R. O., Archibald R. W. Fatal systemic measles in a child receiving cyclophosphamide for nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1969 Oct 25;2(7626):876–878. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncrieff M. W., White R. H., Oggs C. S., Cameron J. S. Cyclophosphamide therapy in the nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 15;1(5645):666–671. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5645.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northway J. D., McAdams A. J., Forristal J., West C. D. A "silent" phase of hypocomplementemic persistent nephritis detectable by reduced serum beta-1c-globulin levels. J Pediatr. 1969 Jan;74(1):28–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Stamler F. W. Cyclophosphamide and fatal varicella. J Pediatr. 1969 Jan;74(1):117–119. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Acker K. J., Hooft C. The influence of hormone treatment on the natural evolution of the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1968 Nov;57(6):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1968.tb06966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]