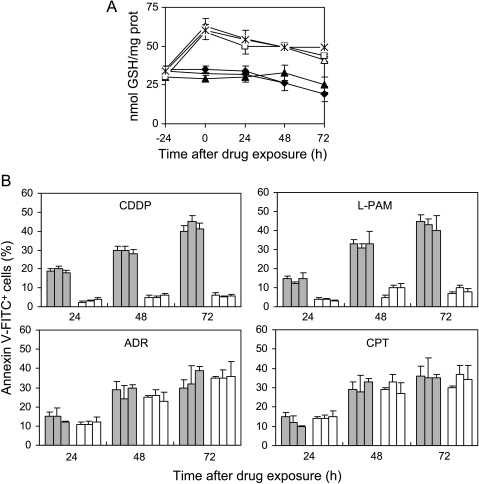
Figure 4.
GSH increase following ester administration protects c-Myc transfectants from CDDP- and l-PAM-triggered apoptosis, without altering topoisomerase inhibitor-induced cell death. (A) Intracellular GSH content evaluated in the untreated MAS51 (▲), MAS53 (◆), and MAS69 (-) c-Myc transfectants and GSH ester-treated MAS51 (△), MAS53 (◊), and MAS69 (*) c-Myc transfectants before (-24 hours) and from 0 to 72 hours following exposure to GSH ethyl ester (5 mM; 24 hours). Statistical analysis: P < .01 at 24 to 72 hours after drug exposure for GSH ester-exposed c-Myc antisense transfectants when compared to unexposed ones. (B) Cytofluorimetric evaluation of apoptotic (annexin V+/PI-) MAS51, MAS53, and MAS69 c-Myc low-expressing clones cells preincubated (white bars) or not (gray bars) with GSH ester and treated with the IC50 doses of CDDP, l-PAM, ADR, or CPT. Analysis was performed from 24 to 72 hours following the end of the treatments. Values for c-Myc transfectants, both unexposed and exposed to GSH ester, are always below 10%; thus, they have not been included in the histograms. Statistical analysis: P < .05 at 24 hours, < .01 at 48 to 72 hours after exposure to CDDP and l-PAM calculated for GSH ester-exposed c-Myc antisense transfectants when compared to unexposed ones.