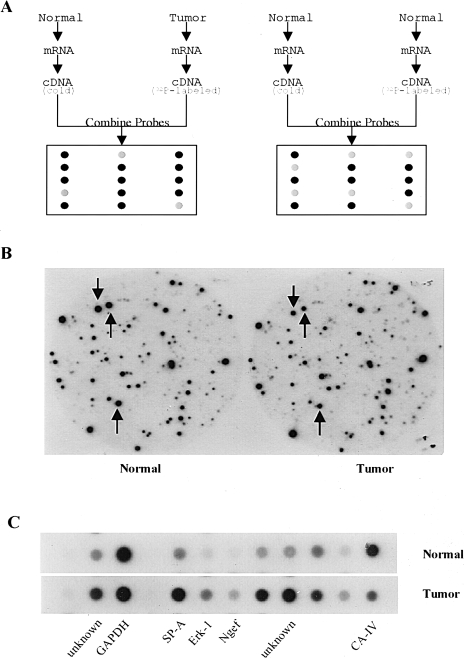
Figure 2.
Analysis of differentially expressed genes in mouse lung adenomas using CCLS. (A) Schematic illustration of CCLS. Equal amounts of total RNA from lung tumors and normal tissues were converted to cDNA probes with incorporation of 32P into the cDNA strands during RT. Two competitors were also generated from normal lung tissues using the same procedure except for 32P incorporation. Probes 1 and 2 were used to perform differential hybridization against a mouse lung cDNA library. (B) An example of data from CCLS. Two identical filters were differentially hybridized with the cDNA probes. The left one represents hybridization with the probe generated from normal tissue, whereas the right one represents hybridization with the probe derived from a lung tumor. The three spots indicated by arrows show three differentially expressed clones that were identified by CCLS. (C) Results of dot blot analysis. Dot blot analysis was conducted as one confirmation step. Differentially expressed clones selected from CCLS were confirmed by dot blot analysis. The GAPDH was used as an internal control.