Abstract
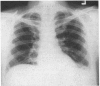
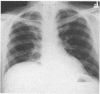
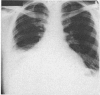
Roentgen findings in subphrenic abscess, in the order of their specificity and clinical value, are subphrenic air-fluid level, elevation and restriction of motion of the diaphragm, pleural reaction with congestion, segmental atelectasis or pneumonitis at the lung base and upper abdominal mass. Less frequently there may be empyema or bronchopleural fistula.
Suppression of the infection by antibiotics may protract the course and obscure the clinical findings. Serial x-ray and fluoroscopic studies are recommended when a patient who has had rupture of a viscus or previous abdominal operation does not completely recover or has a persistent lowgrade fever.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERENS J. J., GRAY H. K., DOCKERTY M. B. Subphrenic abscess. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1953 Apr;96(4):463–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD D. P. The intrathoracic complications of subphrenic abscess. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1959 Dec;38:771–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER R., BREWER L. A., 3rd SUBPHRENIC ABSCESS: A THORACOABDOMINAL CLINICAL COMPLEX: THE CHANGING PICTURE WITH ANTIBIOTICS. Am J Surg. 1964 Aug;108:165–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(64)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINEEN P., McSHERRY C. K. Subdiaphragmatic abscess. Ann Surg. 1962 Apr;155:506–517. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196204000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]