Abstract
Net fluxes of sodium and potassium ions were determined in sodium-loaded, potassium-depleted erythrocytes from 370 white subjects, 194 of whom had essential hypertension or had been born to parents with essential hypertension. Findings were compared with those in 86 controls who were normotensive and did not have a family history of hypertension. Compared with controls all patients with essential hypertension had a low sodium to potassium ratio secondary to a deficit in the sodium-potassium cotransport system. A similar abnormality was found in subjects born to parents with essential hypertension, the prevalences of a deficient cotransport system in such subjects being 53.6% (52 out of 97) among those with one hypertensive parent and 73.7% (14 out of 19) among those with two hypertensive parents. Both sexes were equally affected. Studies in 14 families over two or three generations showed the erythrocyte cation abnormality in one or more members of each consecutive generation. No close association was evident between the deficient erythrocyte sodium-potassium cotransport system and either blood groups ABO, Rh, Kidd, Duffy, P, and MNS or the major histocompatibility HLA antigens. Out of 90 consecutive unrelated and normotensive white blood donors, 36 showed a low erythrocyte sodium-potassium net flux ratio. It is concluded that in white people abnormal erythrocyte cation transport is a biochemical disorder characteristic of essential hypertension and transmitted by a dominant and autosomal mode expressing a single abnormal gene.
Full text
PDF
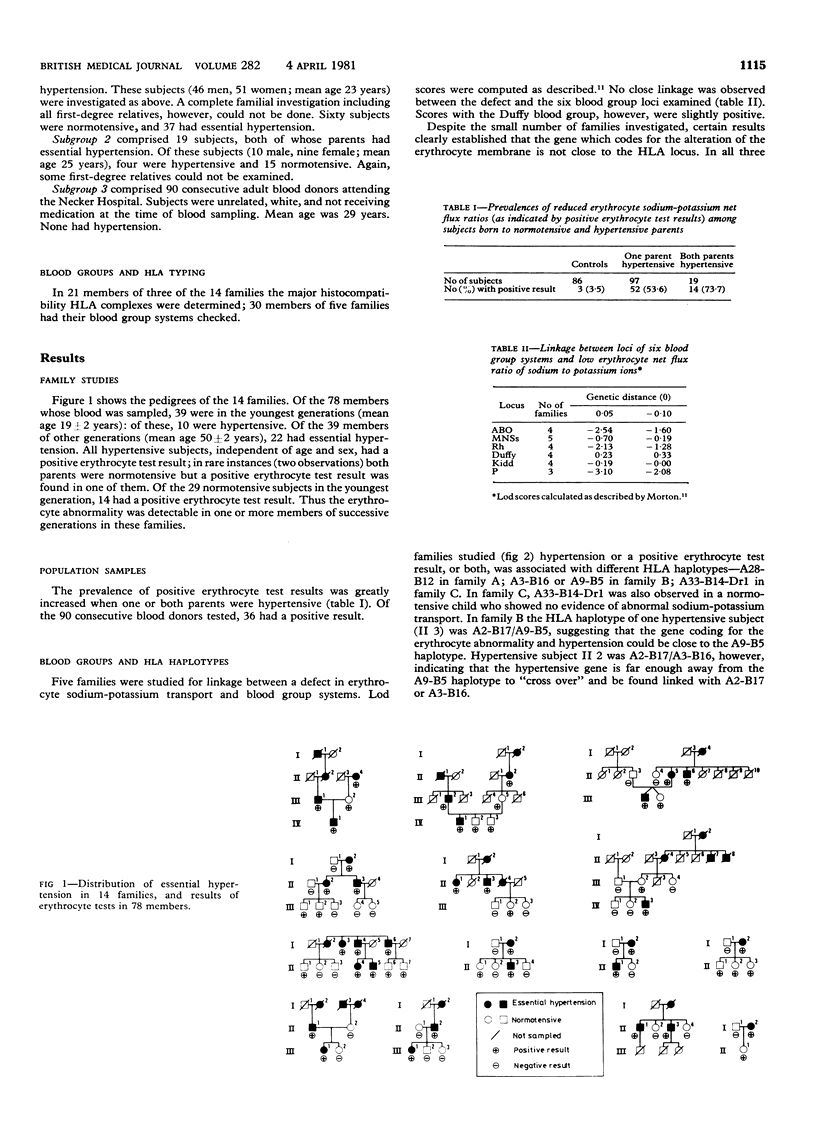
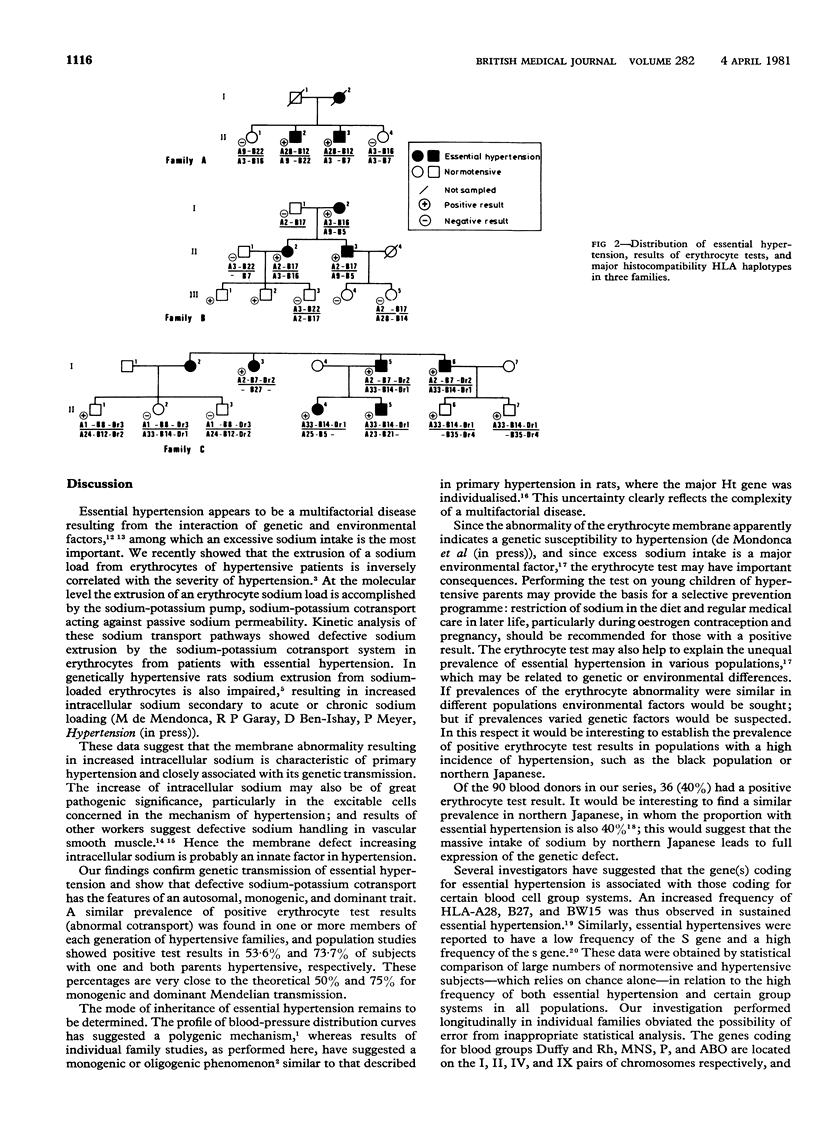

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André J. L., Deschamps J. P., Gueguen R. Pression artérielle chez l'enfant. Valeurs rapportées à la taille. Nouv Presse Med. 1980 Jun 28;9(28):1958–1959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa M., Adragna N., Solomon H. S., Connolly T. M., Tosteson D. C. Increased sodium-lithium countertransport in red cells of patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 3;302(14):772–776. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004033021403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAUSSET J. Iso-leuco-anticorps. Acta Haematol. 1958 Jul-Oct;20(1-4):156–166. doi: 10.1159/000205478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mendonca M., Grichois M. L., Garay R. P., Sassard J., Ben-Ishay D., Meyer P. Abnormal net Na+ and K+ fluxes in erythrocytes of three varieties of genetically hypertensive rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4283–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Dagher G., Pernollet M. G., Devynck M. A., Meyer P. Inherited defect in a Na+, K-co-transport system in erythrocytes from essential hypertensive patients. Nature. 1980 Mar 20;284(5753):281–283. doi: 10.1038/284281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Elghozi J. L., Dagher G., Meyer P. Laboratory distinction between essential and secondary hypertension by measurement of erythrocyte cation fluxes. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 3;302(14):769–771. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004033021402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Meyer P. A new test showing abnormal net Na+ and K+ fluxes in erythrocytes of essential hypertensive patients. Lancet. 1979 Feb 17;1(8112):349–353. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92891-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann M. C., Benson H. Interaction of environmental factors and systemic arterial blood pressure: a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971 Nov;50(6):543–553. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197111000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON M., PICKERING G. W., ROBERTS J. A. F., SOWRY G. S. The aetiology of essential hypertension. 4. The role of inheritance. Clin Sci. 1954 May;13(2):273–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. W. Reactivity of ion fluxes in rat aorta during hypertension and circulatory control. Fed Proc. 1974 Feb;33(2):133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen B. O., Andersen P. L., Lamm L. U., Kissmeyer-Nielsen F. HLA antigens in essential hypertension. Relation to familiar disposition and serum immunoglobulins. Tissue Antigens. 1977 Aug;10(2):70–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. Y., Belbeck L., Daniel E. E. Abnormal biochemistry of vascular smooth muscle plasma membrane isolated from hypertensive rats. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):137–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loggie J. M., New M. I., Robson A. M. Hypertension in the pediatric patient: a reappraisal. J Pediatr. 1979 May;94(5):685–699. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. Z., Grim C. E., Conneally P. M., Weinberger M. H. Association of blood groups with essential and secondary hypertension. A possible association of the MNS system. Hypertension. 1979 Sep-Oct;1(5):493–497. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.1.5.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLATT R. Heredity in hypertension. Lancet. 1963 Apr 27;1(7287):899–904. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91686-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


