Abstract
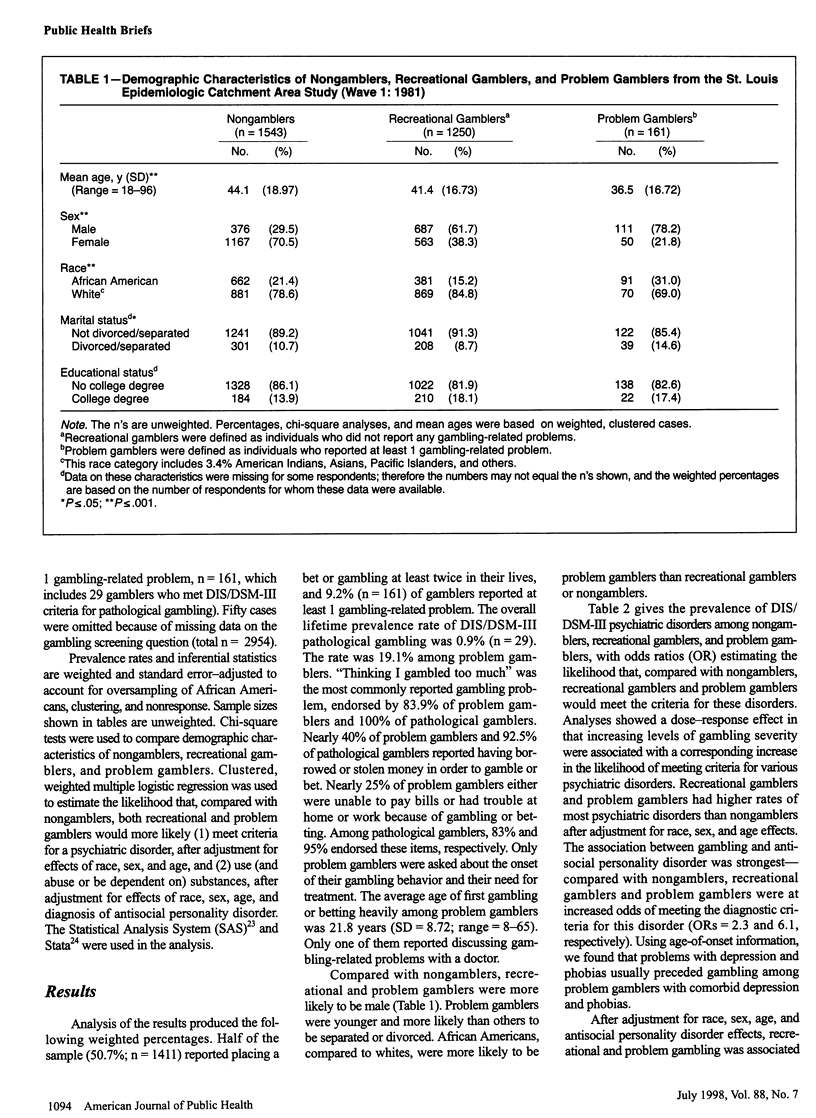
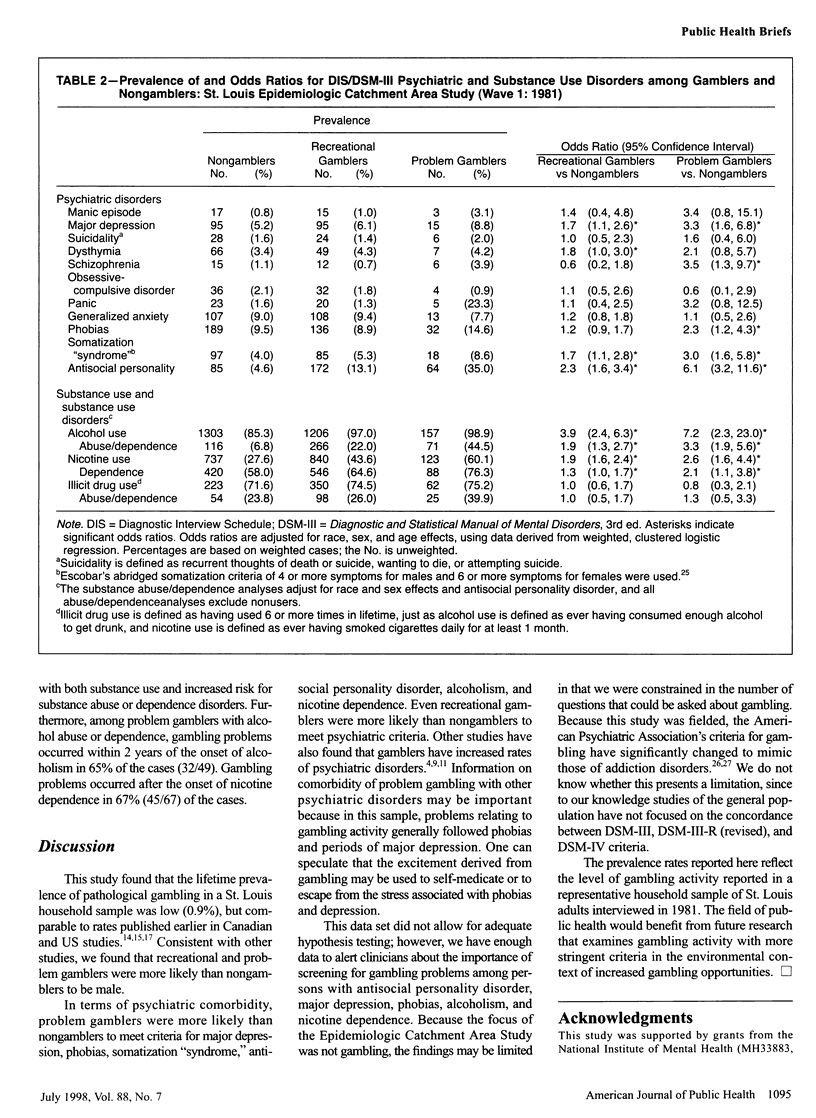
OBJECTIVES: This study determined prevalence estimates of problem gambling and relationships to other psychiatric and substance use disorders. METHODS: In 1981, the Diagnostic Interview Schedule was used to collect epidemiological information on problem gambling and other disorders from 3004 adults in St. Louis, Mo. RESULTS: The lifetime prevalence of pathological gambling was 0.9%; 46% of those surveyed gambled recreationally. Problem gamblers (those reporting at least one gambling-related problem) were 9.2% of the sample and were predominately White (69%), male (78.2%), and young than nongamblers. They were at increased risk for several psychiatric diagnoses, especially for antisocial personality disorder, alcoholism, and tobacco dependence. CONCLUSIONS: Clinicians treating alcoholism and tobacco dependence may need to screen for problem gambling. Additional research in the context of increased gambling opportunities is needed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bland R. C., Newman S. C., Orn H., Stebelsky G. Epidemiology of pathological gambling in Edmonton. Can J Psychiatry. 1993 Mar;38(2):108–112. doi: 10.1177/070674379303800207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaszczynski A., McConaghy N., Frankova A. Boredom proneness in pathological gambling. Psychol Rep. 1990 Aug;67(1):35–42. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1990.67.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J. H., Burke J. D., Jr, Gruenberg E., Holzer C. E., 3rd, Rae D. S., George L. K., Karno M., Stoltzman R., McEvoy L., Nestadt G. Exclusion criteria of DSM-III. A study of co-occurrence of hierarchy-free syndromes. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Oct;41(10):983–989. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790210065008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elia C., Jacobs D. F. The incidence of pathological gambling among Native Americans treated for alcohol dependence. Int J Addict. 1993 May;28(7):659–666. doi: 10.3109/10826089309039654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar J. I., Burnam M. A., Karno M., Forsythe A., Golding J. M. Somatization in the community. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 Aug;44(8):713–718. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800200039006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigelman W., Kleinman P. H., Lesieur H. R., Millman R. B., Lesser M. L. Pathological gambling among methadone patients. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1995 Aug;39(2):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0376-8716(95)01141-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladouceur R., Dubé D., Bujold A. Prevalence of pathological gambling and related problems among college students in the Quebec metropolitan area. Can J Psychiatry. 1994 Jun;39(5):289–293. doi: 10.1177/070674379403900509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladouceur R. Prevalence estimates of pathological gambling in Quebec. Can J Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;36(10):732–734. doi: 10.1177/070674379103601007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur H. R., Blume S. B. Characteristics of pathological gamblers identified among patients on a psychiatric admissions service. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1990 Sep;41(9):1009–1012. doi: 10.1176/ps.41.9.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur H. R., Blume S. B. The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): a new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. Am J Psychiatry. 1987 Sep;144(9):1184–1188. doi: 10.1176/ajp.144.9.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur H. R., Blume S. B., Zoppa R. M. Alcoholism, drug abuse, and gambling. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1986 Jan-Feb;10(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1986.tb05610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur H. R., Heineman M. Pathological gambling among youthful multiple substance abusers in a therapeutic community. Br J Addict. 1988 Jul;83(7):765–771. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1988.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick R. A., Russo A. M., Ramirez L. F., Taber J. I. Affective disorders among pathological gamblers seeking treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 1984 Feb;141(2):215–218. doi: 10.1176/ajp.141.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. B. Review of research on pathological gambling. Psychol Rep. 1993 Jun;72(3 Pt 1):791–810. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1993.72.3.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins L. N., Helzer J. E., Croughan J., Ratcliff K. S. National Institute of Mental Health Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Its history, characteristics, and validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Apr;38(4):381–389. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780290015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. J., Lorenz V. C. The pathological gambler as criminal offender. Comments on evaluation and treatment. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1992 Sep;15(3):647–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volberg R. A. The prevalence and demographics of pathological gamblers: implications for public health. Am J Public Health. 1994 Feb;84(2):237–241. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


