Abstract
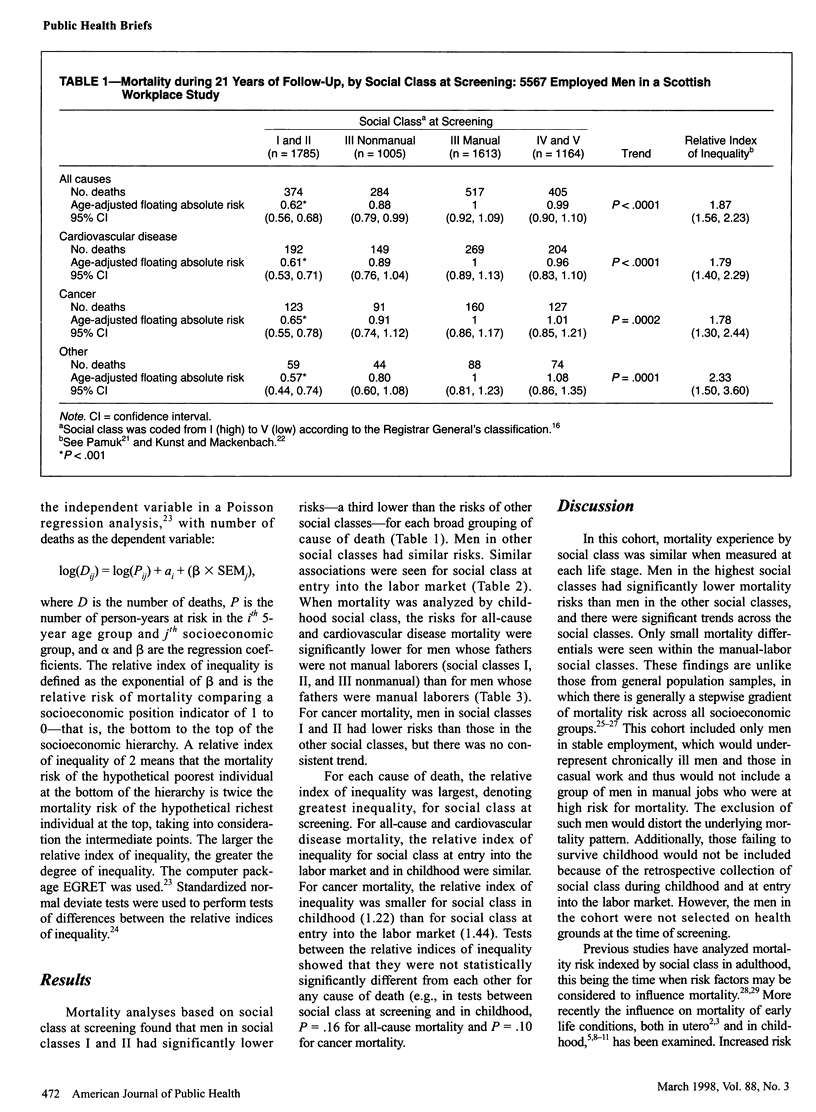
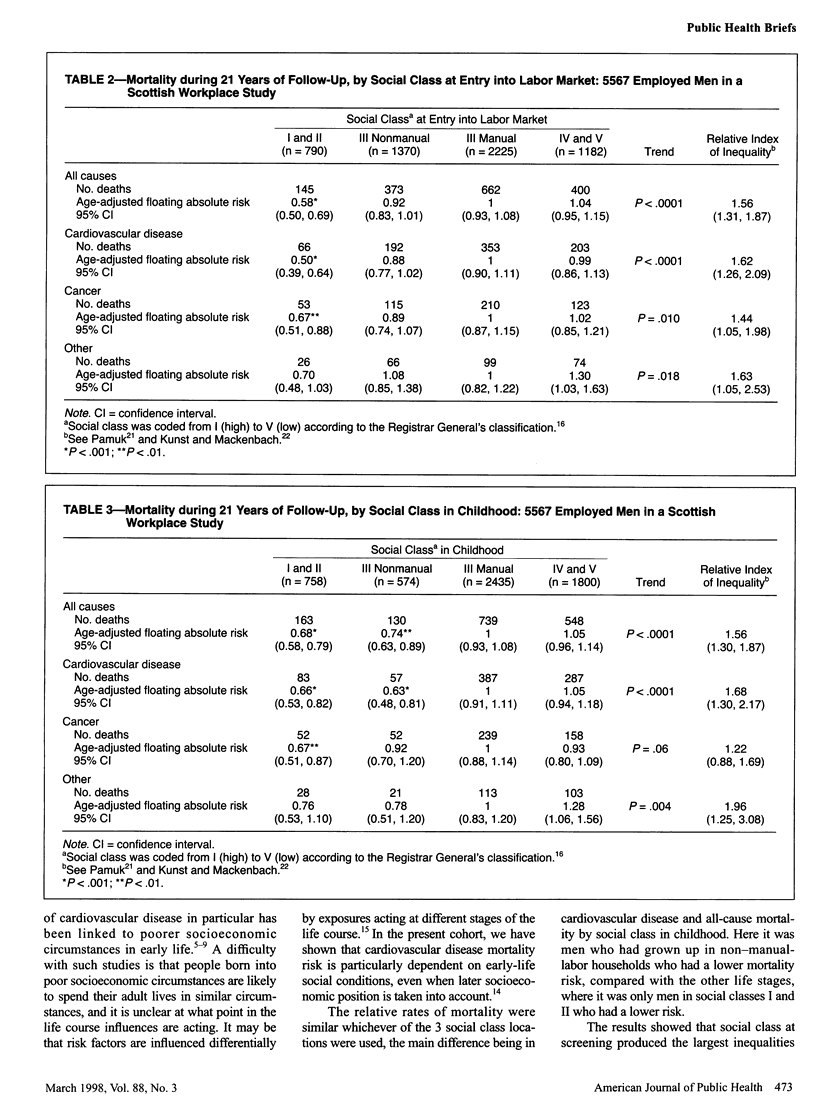
OBJECTIVES: This study examined how social class, measured at 3 staged of life, contributes to mortality risk. METHODS: A cohort of employed Scottish men (n = 5567) provided their fathers' occupation and their own first and current occupations, from which social class in childhood, at labor-market entry, and at screening (1970 to 1973) was determined. Relative rates of mortality and relative indices of inequality were calculated from 21 years of follow-up. RESULTS: Mortality risk was similar at each stage of life, with men in the higher social classes having the lowest risk. Social class at screening produced the greatest relative indices of inequality. CONCLUSIONS: The widening of inequalities in mortality in adulthood suggests the importance of the accumulation of poor socioeconomic circumstances throughout life.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. J., Bull A. R., Osmond C., Simmonds S. J. Fetal and placental size and risk of hypertension in adult life. BMJ. 1990 Aug 4;301(6746):259–262. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6746.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley M., Power C., Blane D., Smith G. D., Shipley M. Birth weight and later socioeconomic disadvantage: evidence from the 1958 British cohort study. BMJ. 1994 Dec 3;309(6967):1475–1478. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6967.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shlomo Y., Smith G. D. Deprivation in infancy or in adult life: which is more important for mortality risk? Lancet. 1991 Mar 2;337(8740):530–534. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91307-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blane D., Hart C. L., Smith G. D., Gillis C. R., Hole D. J., Hawthorne V. M. Association of cardiovascular disease risk factors with socioeconomic position during childhood and during adulthood. BMJ. 1996 Dec 7;313(7070):1434–1438. doi: 10.1136/bmj.313.7070.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blane D., Smith G. D., Bartley M. Social class differences in years of potential life lost: size, trends, and principal causes. BMJ. 1990 Sep 1;301(6749):429–432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6749.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr M. L., Sweetnam P. M. Family size and paternal unemployment in relation to myocardial infarction. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1980 Jun;34(2):93–95. doi: 10.1136/jech.34.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easton D. F., Peto J., Babiker A. G. Floating absolute risk: an alternative to relative risk in survival and case-control analysis avoiding an arbitrary reference group. Stat Med. 1991 Jul;10(7):1025–1035. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780100703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elo I. T., Preston S. H. Effects of early-life conditions on adult mortality: a review. Popul Index. 1992 Summer;58(2):186–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fall C. H., Barker D. J., Osmond C., Winter P. D., Clark P. M., Hales C. N. Relation of infant feeding to adult serum cholesterol concentration and death from ischaemic heart disease. BMJ. 1992 Mar 28;304(6830):801–805. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6830.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsdahl A. Living conditions in childhood and subsequent development of risk factors for arteriosclerotic heart disease. The cardiovascular survey in Finnmark 1974-75. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1978 Mar;32(1):34–37. doi: 10.1136/jech.32.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliksman M. D., Kawachi I., Hunter D., Colditz G. A., Manson J. E., Stampfer M. J., Speizer F. E., Willett W. C., Hennekens C. H. Childhood socioeconomic status and risk of cardiovascular disease in middle aged US women: a prospective study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1995 Feb;49(1):10–15. doi: 10.1136/jech.49.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G. A., Salonen J. T. Socioeconomic conditions in childhood and ischaemic heart disease during middle age. BMJ. 1990 Nov 17;301(6761):1121–1123. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6761.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. B., Middle L. A. Evaluation of thymidine kinase and neomycin phosphotransferase II positive selection systems for recovery of genetically atypical and recombinant DNA vaccine viruses. Biologicals. 1990 Oct;18(4):301–304. doi: 10.1016/1045-1056(90)90033-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuh D., Smith G. D. When is mortality risk determined? Historical insights into a current debate. Soc Hist Med. 1993 Apr;6(1):101–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst A. E., Mackenbach J. P. International variation in the size of mortality differences associated with occupational status. Int J Epidemiol. 1994 Aug;23(4):742–750. doi: 10.1093/ije/23.4.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg O. The impact of childhood living conditions on illness and mortality in adulthood. Soc Sci Med. 1993 Apr;36(8):1047–1052. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(93)90122-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. W., Kaplan G. A., Cohen R. D., Kauhanen J., Wilson T. W., Smith N. L., Salonen J. T. Childhood and adult socioeconomic status as predictors of mortality in Finland. Lancet. 1994 Feb 26;343(8896):524–527. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkola V., Punsar S., Karvonen M. J., Haapakoski J. Socio-economic conditions in childhood and mortality and morbidity caused by coronary heart disease in adulthood in rural Finland. Soc Sci Med. 1985;21(5):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(85)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamuk E. R. Social class inequality in mortality from 1921 to 1972 in England and Wales. Popul Stud (Camb) 1985 Mar;39(1):17–31. doi: 10.1080/0032472031000141256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Bartley M., Blane D. The Black report on socioeconomic inequalities in health 10 years on. BMJ. 1990 Aug 18;301(6748):373–377. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6748.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Hart C., Blane D., Gillis C., Hawthorne V. Lifetime socioeconomic position and mortality: prospective observational study. BMJ. 1997 Feb 22;314(7080):547–552. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7080.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Neaton J. D., Wentworth D., Stamler R., Stamler J. Socioeconomic differentials in mortality risk among men screened for the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial: I. White men. Am J Public Health. 1996 Apr;86(4):486–496. doi: 10.2105/ajph.86.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Wentworth D., Neaton J. D., Stamler R., Stamler J. Socioeconomic differentials in mortality risk among men screened for the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial: II. Black men. Am J Public Health. 1996 Apr;86(4):497–504. doi: 10.2105/ajph.86.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


