Abstract
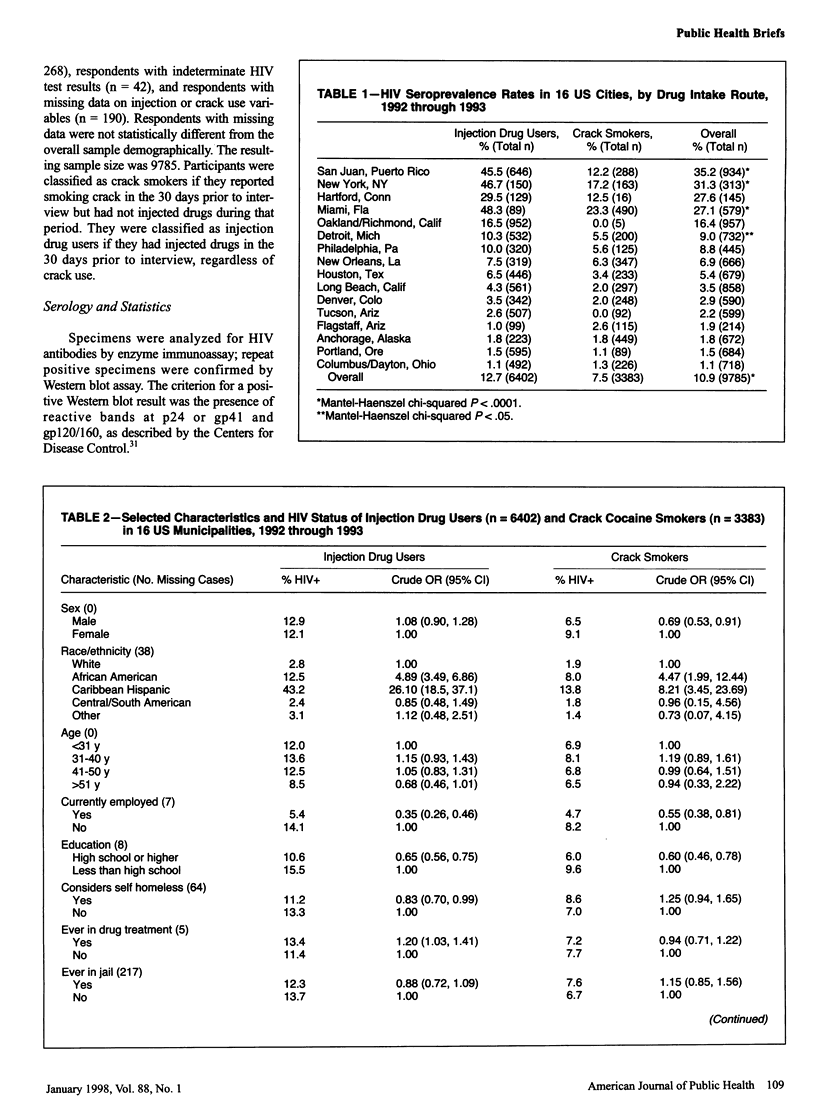
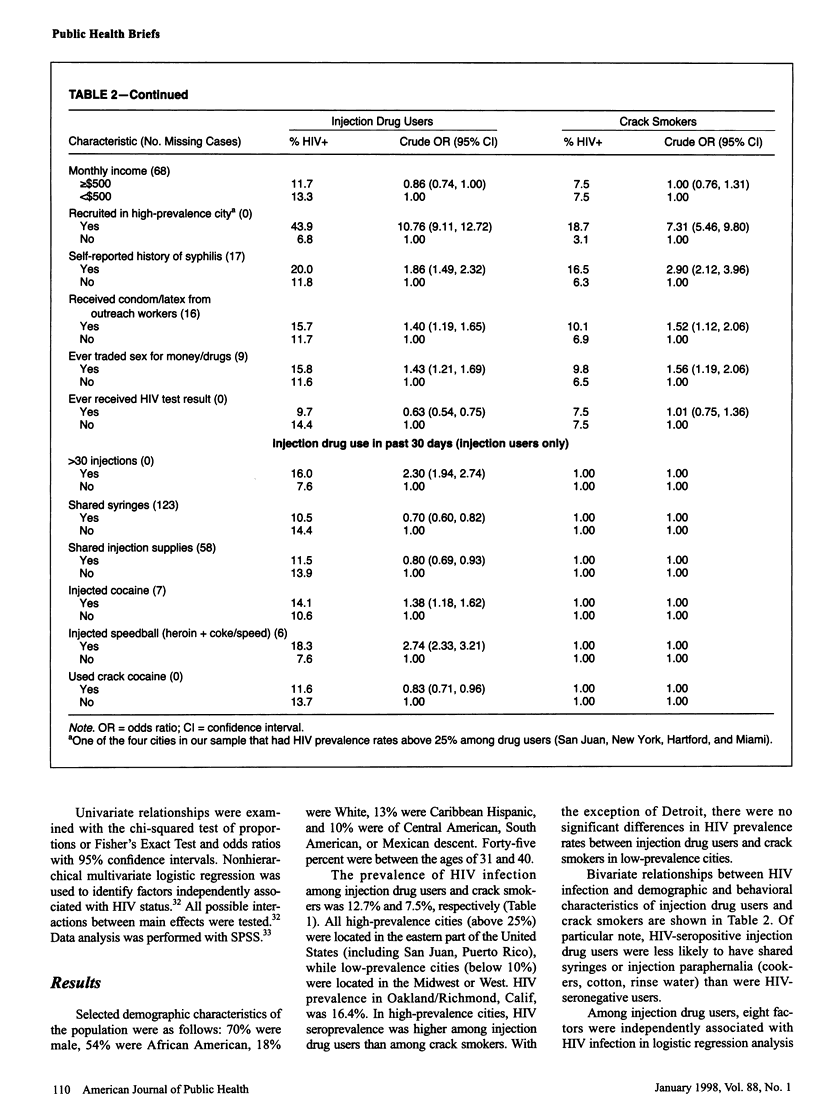
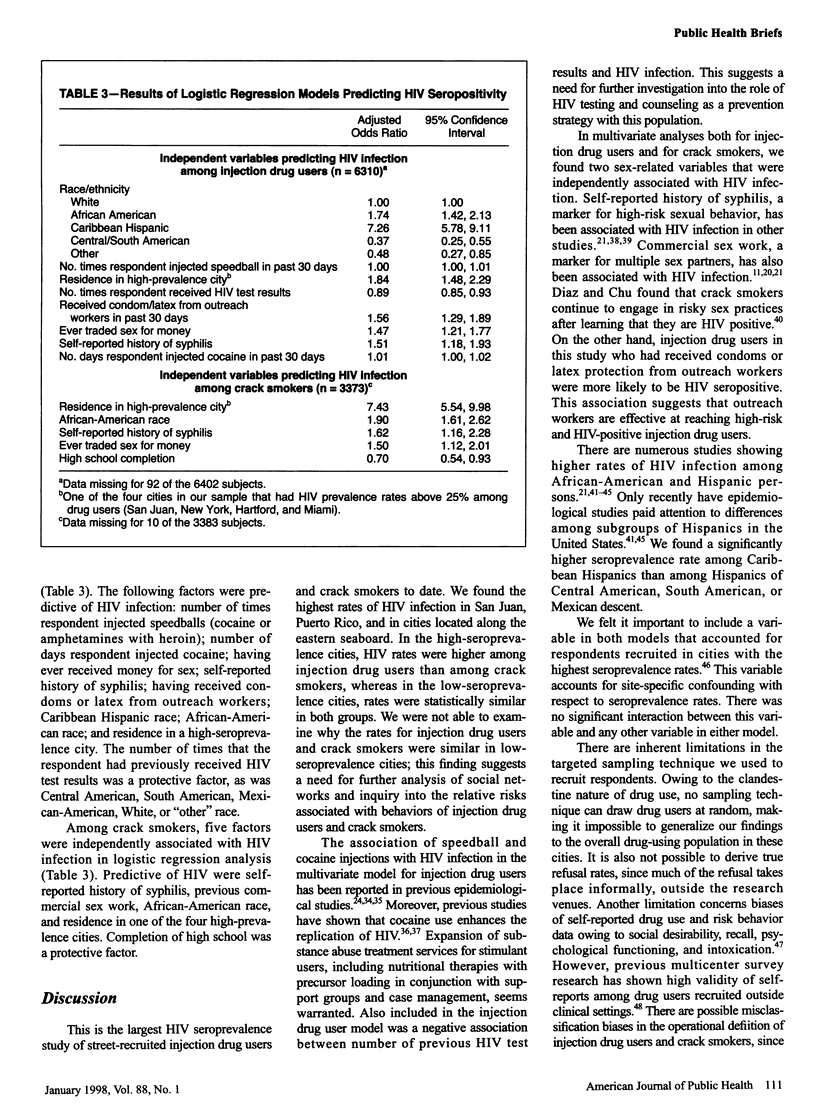
OBJECTIVES: This study deter- mined human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seroprevalence and factors associated with HIV infection among street-recruited injection drug users and crack cocaine smokers. METHODS: An analysis was performed on HIV serologies and risk behaviors of 6402 injection drug users and 3383 crack smokers in 16 US municipalities in 1992 and 1993. RESULTS: HIV seroprevalence was 12.7% among injection drug users and 7.5% among crack smokers. Most high-seroprevalence municipalities (>25%) were located along the eastern seaboard of the United States. In high-seroprevalence municipalities, but not in others, HIV seroprevalence was higher for injection drug users than for crack smokers. Among injection drug users, cocaine injection, use of speedballs (cocaine or amphetamines with heroin), and sexual risk behaviors were independently associated with HIV infection. Among crack smokers, sexual risk behaviors were associated with HIV infection. CONCLUSIONS: Injection drug users and crack smokers are at high risk for HIV infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagasra O., Pomerantz R. J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the presence of cocaine. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1157–1164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battjes R. J., Pickens R. W., Brown L. S., Jr HIV infection and AIDS risk behaviors among injecting drug users entering methadone treatment: an update. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Sep 1;10(1):90–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluthenthal R. N., Watters J. K. Multimethod research from targeted sampling to HIV risk environments. NIDA Res Monogr. 1995;157:212–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth R. E., Watters J. K., Chitwood D. D. HIV risk-related sex behaviors among injection drug users, crack smokers, and injection drug users who smoke crack. Am J Public Health. 1993 Aug;83(8):1144–1148. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.8.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., de Wolf F., Houweling J. T., Bakker M., Dekker J., Roos M. T., Coutinho R. A., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Antibody response to a synthetic peptide covering a LAV-1/HTLV-IIIB neutralization epitope and disease progression. AIDS. 1989 Feb;3(2):71–76. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198902000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson M. A., Stoneburner R. L., Hildebrandt D. S., Ewing W. E., Telzak E. E., Jaffe H. W. Heterosexual transmission of HIV-1 associated with the use of smokable freebase cocaine (crack). AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1121–1126. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199109000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin K., DeHovitz J. A., Dillon S., McCormack W. M. HIV infection, genital ulcer disease, and crack cocaine use among patients attending a clinic for sexually transmitted diseases. Am J Public Health. 1991 Dec;81(12):1576–1579. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.12.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choopanya K., Vanichseni S., Des Jarlais D. C., Plangsringarm K., Sonchai W., Carballo M., Friedmann P., Friedman S. R. Risk factors and HIV seropositivity among injecting drug users in Bangkok. AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1509–1513. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHovitz J. A., Kelly P., Feldman J., Sierra M. F., Clarke L., Bromberg J., Wan J. Y., Vermund S. H., Landesman S. Sexually transmitted diseases, sexual behavior, and cocaine use in inner-city women. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Dec 15;140(12):1125–1134. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz T., Buehler J. W., Castro K. G., Ward J. W. AIDS trends among Hispanics in the United States. Am J Public Health. 1993 Apr;83(4):504–509. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.4.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz T., Chu S. Y. Crack cocaine use and sexual behavior among people with AIDS. JAMA. 1993 Jun 9;269(22):2845–2846. doi: 10.1001/jama.1993.03500220031012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin B. R., Irwin K. L., Faruque S., McCoy C. B., Word C., Serrano Y., Inciardi J. A., Bowser B. P., Schilling R. F., Holmberg S. D. Intersecting epidemics--crack cocaine use and HIV infection among inner-city young adults. Multicenter Crack Cocaine and HIV Infection Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 24;331(21):1422–1427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411243312106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. R., Jose B., Deren S., Des Jarlais D. C., Neaigus A. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus seroconversion among out-of-treatment drug injectors in high and low seroprevalence cities. The National AIDS Research Consortium. Am J Epidemiol. 1995 Oct 15;142(8):864–874. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullilove R. E., Fullilove M. T., Bowser B. P., Gross S. A. Risk of sexually transmitted disease among black adolescent crack users in Oakland and San Francisco, Calif. JAMA. 1990 Feb 9;263(6):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullilove R. E., Fullilove M. T., Bowser B., Gross S. Crack users: the new AIDS risk group? Cancer Detect Prev. 1990;14(3):363–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkos H. W., Steel E. Crack cocaine, fellatio, and the transmission of HIV. Am J Public Health. 1991 Aug;81(8):1078–1079. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.8.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D. The estimated prevalence and incidence of HIV in 96 large US metropolitan areas. Am J Public Health. 1996 May;86(5):642–654. doi: 10.2105/ajph.86.5.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. H., Watters J. K., Case P. Psychological assessment and AIDS research with intravenous drug users: challenges in measurement. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1988 Apr-Jun;20(2):191–195. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1988.10524494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kral A. H., Lorvick J., Bluthenthal R. N., Watters J. K. HIV risk profile of drug-using women who have sex with women in 19 United States cities. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1997 Nov 1;16(3):211–217. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199711010-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss J. K., Koech D., Plummer F. A., Holmes K. K., Lightfoote M., Piot P., Ronald A. R., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Roberts P. AIDS virus infection in Nairobi prostitutes. Spread of the epidemic to East Africa. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):414–418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx R., Aral S. O., Rolfs R. T., Sterk C. E., Kahn J. G. Crack, sex, and STD. Sex Transm Dis. 1991 Apr-Jun;18(2):92–101. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199118020-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. E., Vlahov D., Cohn S., Odunmbaku M., Lindsay A., Antohony J. C., Hook E. W., 3rd Sexually transmitted diseases in a population of intravenous drug users: association with seropositivity to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):457–463. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D. M., Trigg H. L., Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Vlahov D., Kreek M. J. Cocaine injection and ethnicity in parenteral drug users during the early years of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epidemic in New York City. J Med Virol. 1989 Nov;29(3):181–185. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890290307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Gekker G., Chao C. C., Schut R., Molitor T. W., Balfour H. H., Jr Cocaine potentiates HIV-1 replication in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell cocultures. Involvement of transforming growth factor-beta. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfs R. T., Goldberg M., Sharrar R. G. Risk factors for syphilis: cocaine use and prostitution. Am J Public Health. 1990 Jul;80(7):853–857. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart R. G. Crack cocaine use: a review of prevalence and adverse effects. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1991;17(1):13–26. doi: 10.3109/00952999108992806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner L. A., Kessler R. C., Hughes M., Anthony J. C., Nelson C. B. Prevalence and correlates of drug use and dependence in the United States. Results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995 Mar;52(3):219–229. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950150051010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters J. K., Estilo M. J., Kral A. H., Lorvick J. J. HIV infection among female injection-drug users recruited in community settings. Sex Transm Dis. 1994 Nov-Dec;21(6):321–328. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199411000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters J. K., Needle R., Brown B. S., Weatherby N., Booth R., Williams M. The self-reporting of cocaine use. JAMA. 1992 Nov 4;268(17):2374–2376. doi: 10.1001/jama.268.17.2374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. H. Links between cocaine and retroviral infection. JAMA. 1989 Jan 27;261(4):607–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodak A., Moss A. HIV infection and injecting drug users: from epidemiology to public health. AIDS. 1990;4 (Suppl 1):S105–S109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


