Abstract
OBJECTIVES: The purpose of this study was to determine the efficacy of a college-based smokeless tobacco cessation intervention targeting college athletes. METHODS: Sixteen colleges were matched for prevalence of smokeless tobacco use in their combined baseball and football teams and randomly assigned within college pairs to the intervention or the control group. One-year prevalence of cessation among smokeless tobacco users was determined by self-report of abstinence for the previous 30 days. Differences between groups were analyzed in a weighted version of the Fisher 1-sided permutation test for paired samples after adjustment for significant predictors of quitting other than the intervention (i.e., smokeless tobacco uses per week and most frequently used brand). RESULTS: Cessation prevalences were 35% in the intervention colleges and 16% in the control colleges when subjects with unknown quit status were defined as nonquitters. After adjustment for other significant predictors of quitting, the difference of 19% increased to 21%. The intervention effect increased with level of smokeless tobacco use. CONCLUSIONS: This intervention was effective in promoting smokeless tobacco cessation, especially among those who were more frequent users.
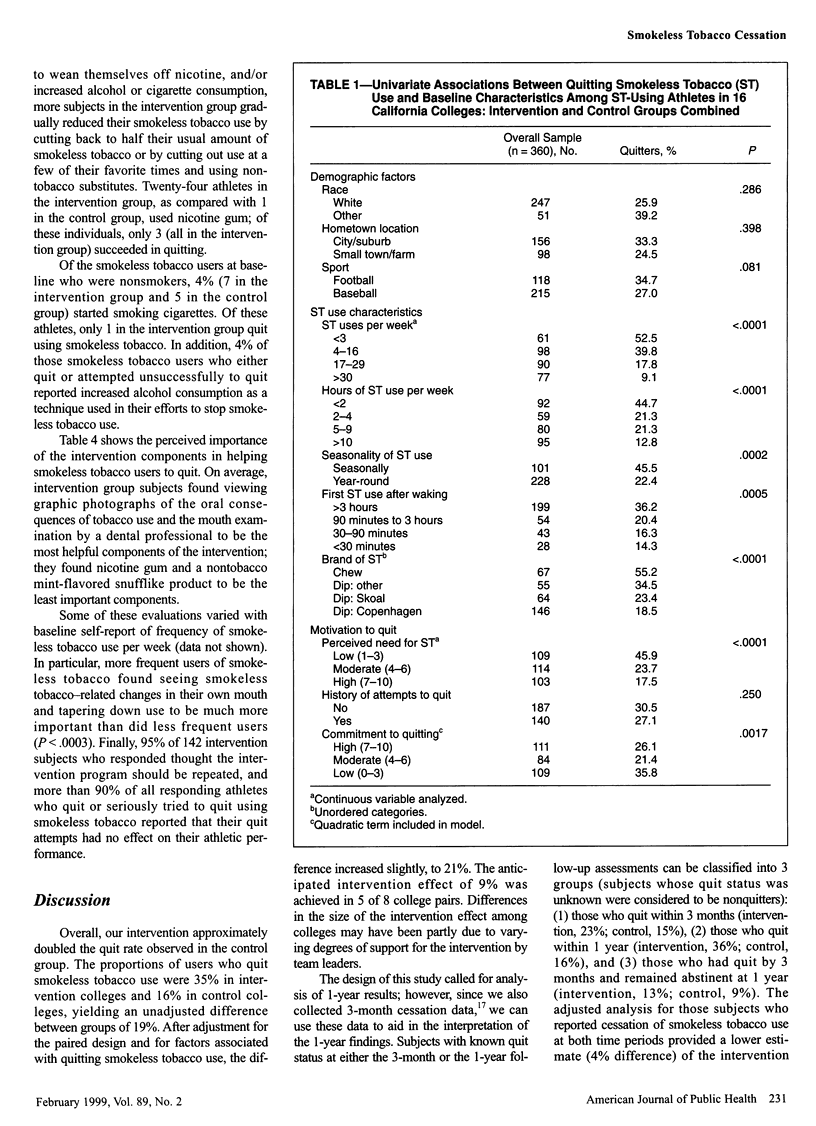
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton J., Chassin L., Presson C. C., Sherman S. J. Social image factors as motivators of smoking initiation in early and middle adolescence. Child Dev. 1982 Dec;53(6):1499–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder G., Alfredsson L., Englund A., de Faire U. Smokeless tobacco use and increased cardiovascular mortality among Swedish construction workers. Am J Public Health. 1994 Mar;84(3):399–404. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp D. E., Klesges R. C., Relyea G. The relationship between body weight concerns and adolescent smoking. Health Psychol. 1993 Jan;12(1):24–32. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.12.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiClemente C. C., Prochaska J. O. Self-change and therapy change of smoking behavior: a comparison of processes of change in cessation and maintenance. Addict Behav. 1982;7(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(82)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner A., Donald A. Analysis of data arising from a stratified design with the cluster as unit of randomization. Stat Med. 1987 Jan-Feb;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780060106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner A. Statistical methodology for paired cluster designs. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Nov;126(5):972–979. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakin E., Severson H., Glasgow R. E. Development and evaluation of a smokeless tobacco cessation program: a pilot study. NCI Monogr. 1989;(8):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. I., Hansen W. B., Mittelmark M. B. Increasing the validity of self-reports of smoking behavior in children. J Appl Psychol. 1977 Aug;62(4):521–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover E. D. Conducting smokeless tobacco cessation clinics. Am J Public Health. 1986 Feb;76(2):207–207. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady D., Greene J., Daniels T. E., Ernster V. L., Robertson P. B., Hauck W., Greenspan D., Greenspan J., Silverman S., Jr Oral mucosal lesions found in smokeless tobacco users. J Am Dent Assoc. 1990 Jul;121(1):117–123. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1990.0139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. C., Walsh M. M., Masouredis C. A program to help major league baseball players quit using spit tobacco. J Am Dent Assoc. 1994 May;125(5):559–568. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1994.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsukami D., Jensen J., Allen S., Grillo M., Bliss R. Effects of behavioral and pharmacological treatment on smokeless tobacco users. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1996 Feb;64(1):153–161. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.64.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton J. F., Walsh M. M., Masouredis C. M., Drues J. C., Grady D. G., Ernster V. L. Planning a spit tobacco cessation intervention: identification of beliefs associated with addiction. Addict Behav. 1994 Jul-Aug;19(4):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(94)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson-Gingiss P., Morrow J. R., Jr, Dratt L. M. Patterns of smokeless tobacco use among university athletes. J Am Coll Health. 1989 Sep;38(2):87–90. doi: 10.1080/07448481.1989.9938421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez L. C. Smokeless tobacco on campus. Psychol Rep. 1988 Oct;63(2):439–442. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1988.63.2.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maritz J. S., Jarrett R. G. The use of statistics to examine the association between fluoride in drinking water and cancer death rates. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat. 1983;32(2):97–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masouredis C. M., Hilton J. F., Grady D., Gee L., Chesney M., Hengl L., Ernster V., Walsh M. M. A spit tobacco cessation intervention for college athletes: three-month results. Adv Dent Res. 1997 Sep;11(3):354–359. doi: 10.1177/08959374970110030801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray D. M., Perry C. L. The measurement of substance use among adolescents: when is the 'bogus pipeline' method needed? Addict Behav. 1987;12(3):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(87)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska J. O., DiClemente C. C., Velicer W. F., Ginpil S., Norcross J. C. Predicting change in smoking status for self-changers. Addict Behav. 1985;10(4):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(85)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson P. B., Walsh M., Greene J., Ernster V., Grady D., Hauck W. Periodontal effects associated with the use of smokeless tobacco. J Periodontol. 1990 Jul;61(7):438–443. doi: 10.1902/jop.1990.61.7.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Severson H., Lichtenstein E., Little S. J., Leben J. Making the most of a teachable moment: a smokeless-tobacco cessation intervention in the dental office. Am J Public Health. 1995 Feb;85(2):231–235. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velicer W. F., Prochaska J. O., Rossi J. S., Snow M. G. Assessing outcome in smoking cessation studies. Psychol Bull. 1992 Jan;111(1):23–41. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.111.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenaar A. C., Komro K. A., McGovern P., Williams C. L., Perry C. L. Effects of a saliva test pipeline procedure on adolescent self-reported alcohol use. Addiction. 1993 Feb;88(2):199–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1993.tb00803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. M., Hilton J. F., Ernster V. L., Masouredis C. M., Grady D. G. Prevalence, patterns, and correlates of spit tobacco use in a college athlete population. Addict Behav. 1994 Jul-Aug;19(4):411–427. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(94)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westman E. C. Does smokeless tobacco cause hypertension? South Med J. 1995 Jul;88(7):716–720. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199507000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn D. M., Blot W. J., Shy C. M., Pickle L. W., Toledo A., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Snuff dipping and oral cancer among women in the southern United States. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 26;304(13):745–749. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



