Abstract
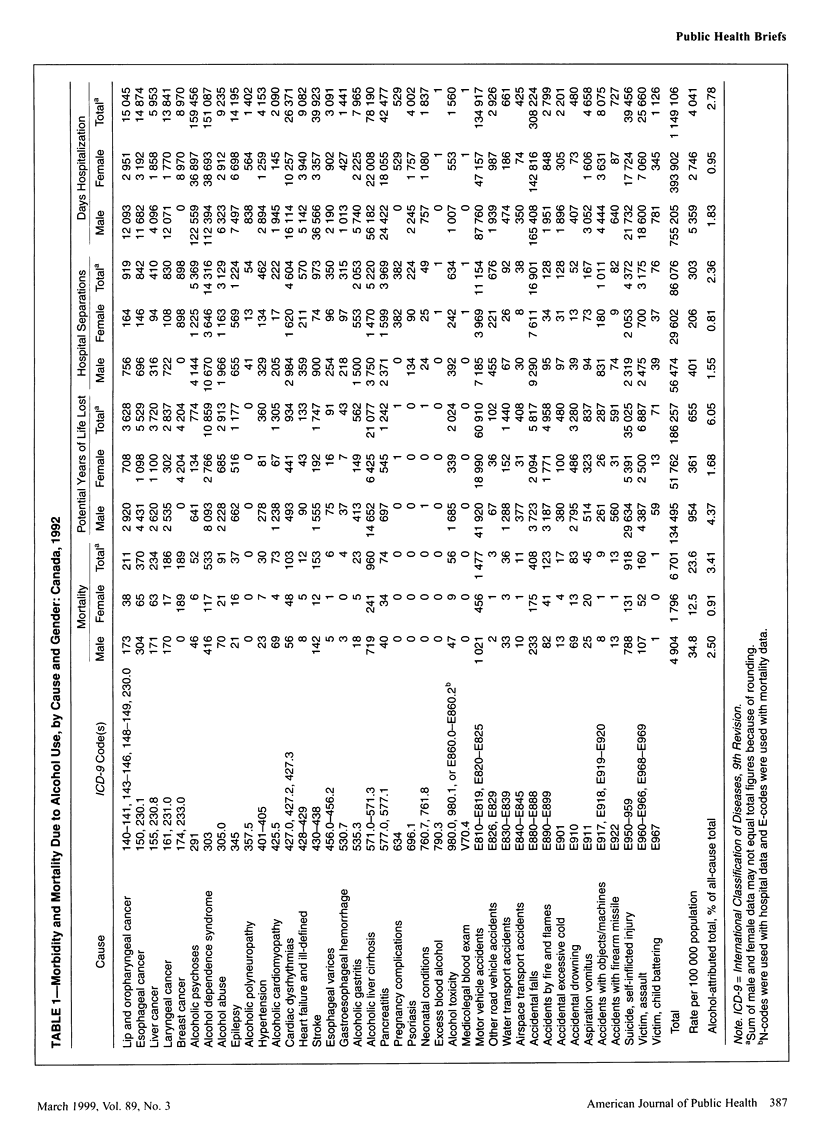
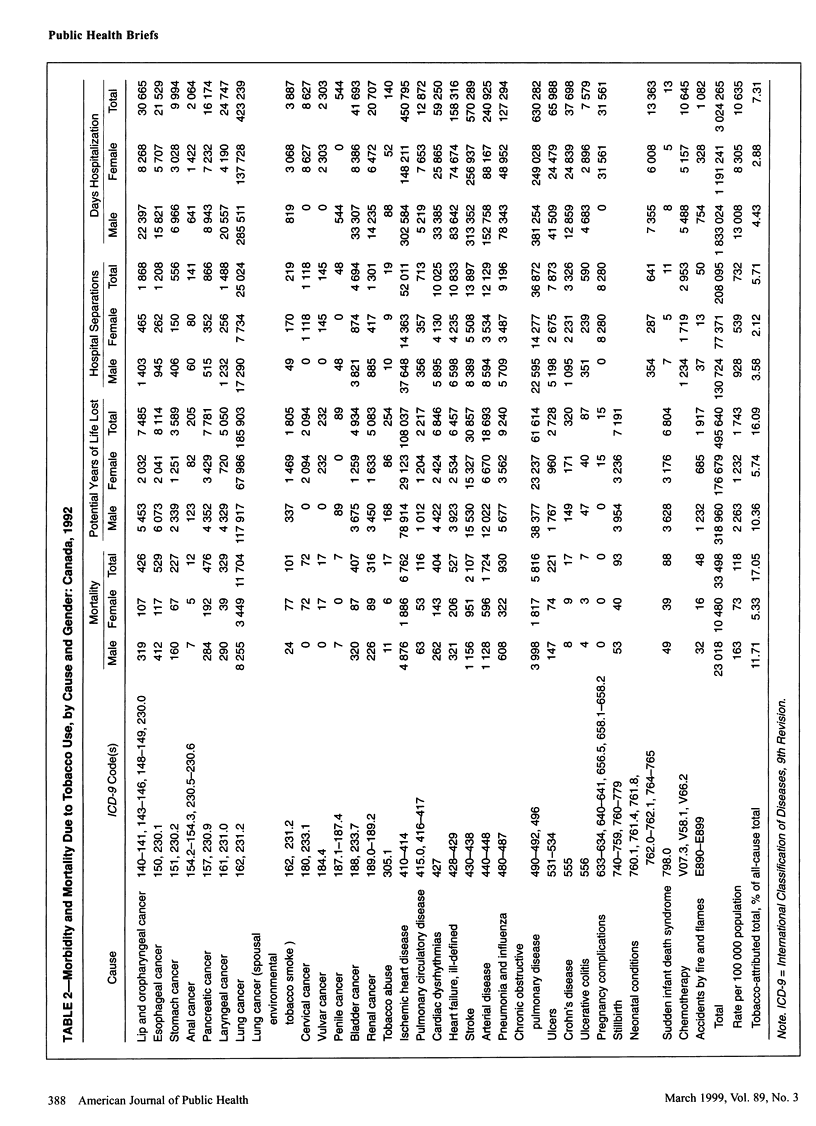
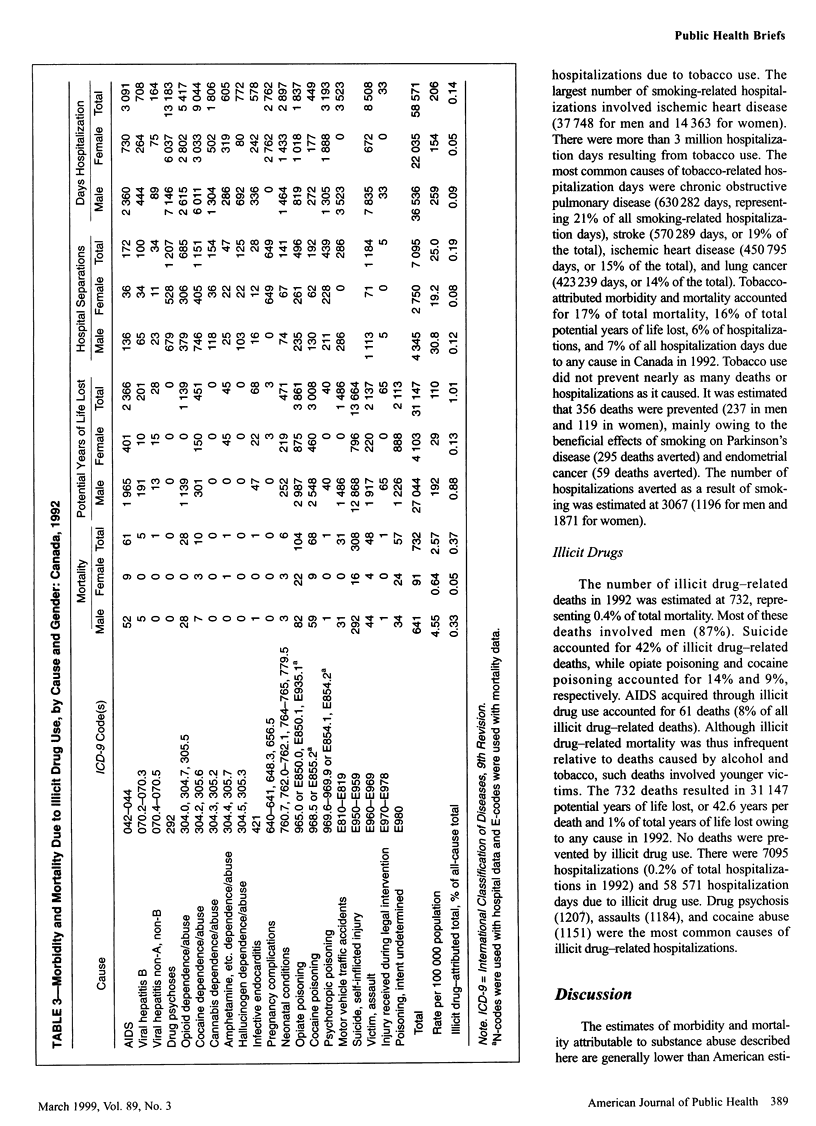
OBJECTIVES: This study estimated morbidity and mortality attributable to substance abuse in Canada. METHODS: Pooled estimates of relative risk were used to calculate etiologic fractions by age, gender, and province for 91 causes of disease or death attributable to alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drugs. RESULTS: There were 33,498 deaths and 208,095 hospitalizations attributed to tobacco, 6701 deaths and 86,076 hospitalizations due to alcohol, and 732 deaths and 7095 hospitalizations due to illicit drugs in 1992. CONCLUSIONS: Substance abuse exacts a considerable toll on Canadian society in terms of morbidity and mortality, accounting for 21% of deaths, 23% of years of potential life lost, and 8% of hospitalizations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Economic impact of motor-vehicle crashes--United States, 1990. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1993 Jun 18;42(23):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K., Merrill J. C., Chang H. H., Califano J. A., Jr Estimating the costs of substance abuse to the Medicaid hospital care program. Am J Public Health. 1995 Jan;85(1):48–54. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illing E. M., Kaiserman M. J. Mortality attributable to tobacco use in Canada and its regions, 1991. Can J Public Health. 1995 Jul-Aug;86(4):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz J. M., Novotny T. E., Rice D. P. Quantifying the disease impact of cigarette smoking with SAMMEC II software. Public Health Rep. 1991 May-Jun;106(3):326–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz J. M., Rice D. P., Parker D. L., Goodman R. A., Stroh G., Jr, Chalmers N. Quantifying the disease impact of alcohol with ARDI software. Public Health Rep. 1991 Jul-Aug;106(4):443–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


