Abstract
OBJECTIVES: This study estimated the lifetime health and economic benefits of sustained modest weight loss among obese persons. METHODS: We developed a dynamic model of the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and the risks and costs of 5 obesity-related diseases: hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease (CHD), and stroke. We then calculated the lifetime health and economic benefits of a sustained 10% reduction in body weight for men and women aged 35 to 64 years with mild, moderate, and severe obesity. RESULTS: Depending on age, gender, and initial BMI, a sustained 10% weight loss would (1) reduce the expected number of years of life with hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and type 2 diabetes by 1.2 to 2.9, 0.3 to 0.8, and 0.5 to 1.7, respectively; (2) reduce the expected lifetime incidence of CHD and stroke by 12 to 38 cases per 1000 and 1 to 13 cases per 1000, respectively; (3) increase life expectancy by 2 to 7 months; and (4) reduce expected lifetime medical care costs of these 5 diseases by $2200 to $5300. CONCLUSIONS: Sustained modest weight loss among obese persons would yield substantial health and economic benefits.
Full text
PDF
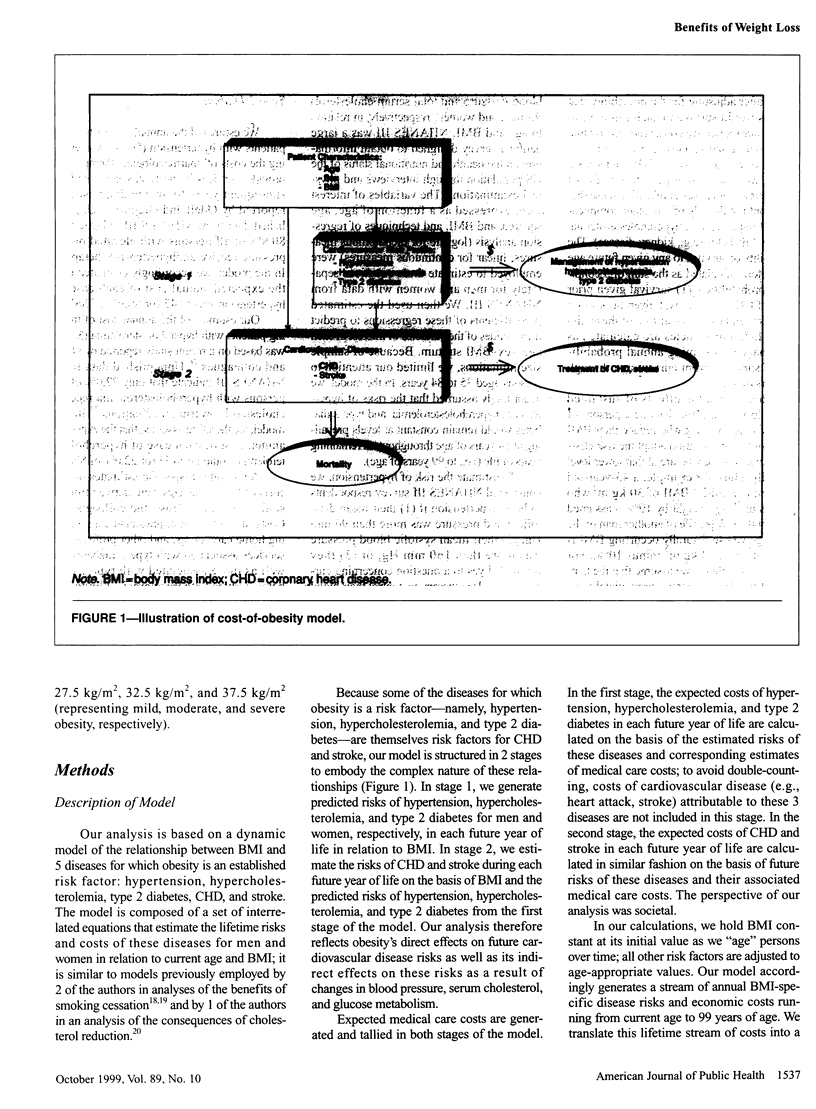

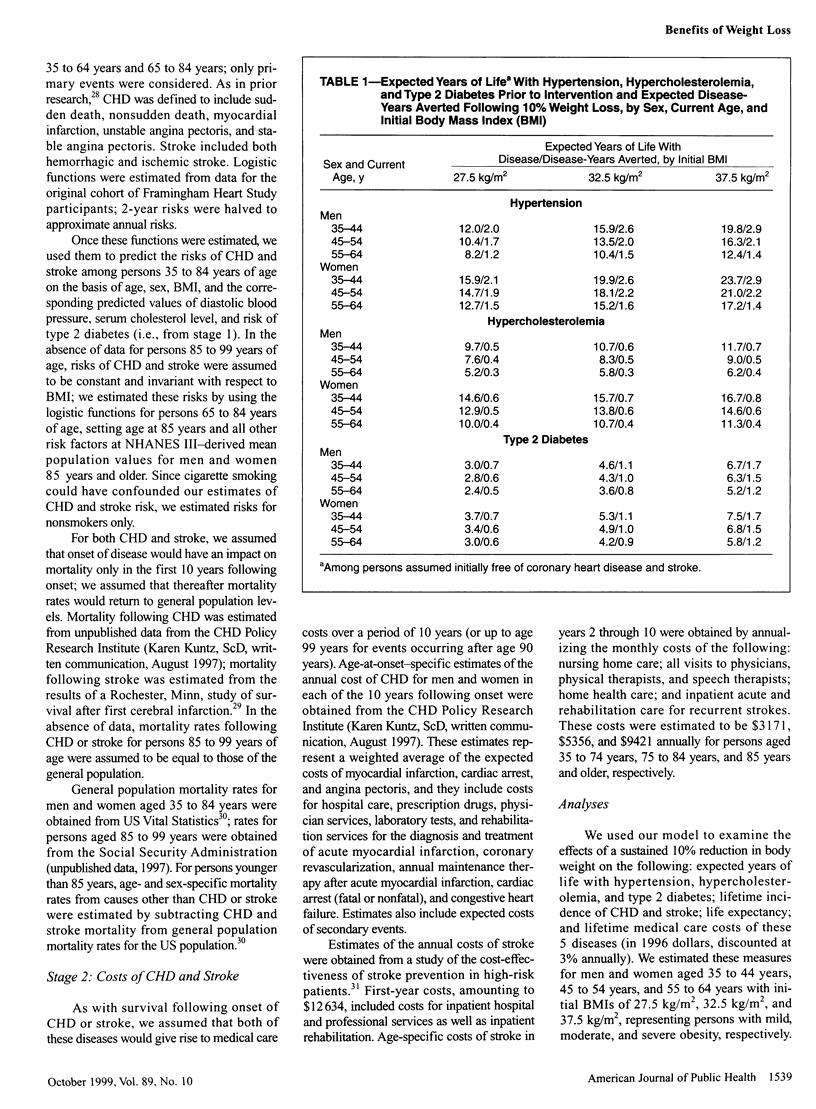
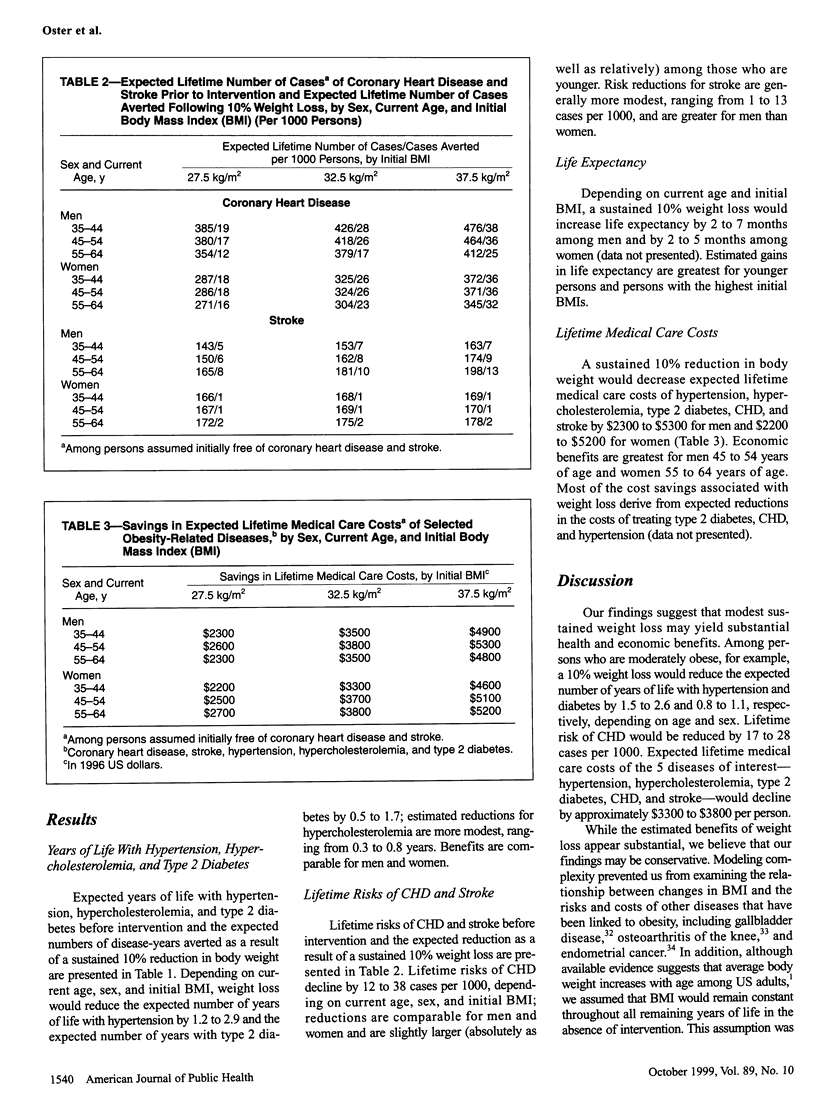


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres R., Muller D. C., Sorkin J. D. Long-term effects of change in body weight on all-cause mortality. A review. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Oct 1;119(7 Pt 2):737–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-7_part_2-199310011-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard-Barbash R., Swanson C. A. Body weight: estimation of risk for breast and endometrial cancers. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996 Mar;63(3 Suppl):437S–441S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/63.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz G. A., Willett W. C., Rotnitzky A., Manson J. E. Weight gain as a risk factor for clinical diabetes mellitus in women. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Apr 1;122(7):481–486. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-7-199504010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. W., Anderson J. W. Medication cost savings associated with weight loss for obese non-insulin-dependent diabetic men and women. Prev Med. 1995 Jul;24(4):369–374. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1995.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comuzzie A. G., Allison D. B. The search for human obesity genes. Science. 1998 May 29;280(5368):1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5368.1374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doar J. W., Wilde C. E., Thompson M. E., Sewell P. F. Influence of treatment with diet alone on oral glucose-tolerance test and plasma sugar and insulin levels in patients with maturity-onset diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1975 Jun 7;1(7919):1263–1266. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Naimark A., Walker A. M., Meenan R. F. Obesity and knee osteoarthritis. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 1;109(1):18–24. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegal K. M., Carroll M. D., Kuczmarski R. J., Johnson C. L. Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960-1994. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998 Jan;22(1):39–47. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0800541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm R. H., Jr, Flack J. M., Grandits G. A., Elmer P. J., Neaton J. D., Cutler J. A., Lewis C., McDonald R., Schoenberger J., Stamler J. Long-term effects on plasma lipids of diet and drugs to treat hypertension. Treatment of Mild Hypertension Study (TOMHS) Research Group. JAMA. 1996 May 22;275(20):1549–1556. doi: 10.1001/jama.1996.03530440029033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huse D. M., Oster G., Killen A. R., Lacey M. J., Colditz G. A. The economic costs of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 1989 Nov 17;262(19):2708–2713. doi: 10.1001/jama.262.19.2708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jama J. W., Launer L. J., Witteman J. C., den Breeijen J. H., Breteler M. M., Grobbee D. E., Hofman A. Dietary antioxidants and cognitive function in a population-based sample of older persons. The Rotterdam Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1996 Aug 1;144(3):275–280. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a008922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissner L., Odell P. M., D'Agostino R. B., Stokes J., 3rd, Kreger B. E., Belanger A. J., Brownell K. D. Variability of body weight and health outcomes in the Framingham population. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 27;324(26):1839–1844. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106273242602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon S. W., Macdonald G. J., Bernstein L., Andrews G., Blacket R. B. Comparison of weight reduction with metoprolol in treatment of hypertension in young overweight patients. Lancet. 1985 Jun 1;1(8440):1233–1236. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell T. W., Gregory M. C. Cost of hypertension treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 1995 Dec;10(12):686–688. doi: 10.1007/BF02602764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster G., Borok G. M., Menzin J., Heyse J. F., Epstein R. S., Quinn V., Benson V., Dudl R. J., Epstein A. M. Cholesterol-reduction intervention study (CRIS): a randomized trial to assess effectiveness and costs in clinical practice. Arch Intern Med. 1996 Apr 8;156(7):731–739. doi: 10.1001/archinte.156.7.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster G., Colditz G. A., Kelly N. L. The economic costs of smoking and benefits of quitting for individual smokers. Prev Med. 1984 Jul;13(4):377–389. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(84)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster G., Epstein A. M. Primary prevention and coronary heart disease: the economic benefits of lowering serum cholesterol. Am J Public Health. 1986 Jun;76(6):647–656. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.6.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster G., Huse D. M., Lacey M. J., Epstein A. M. Cost-effectiveness of ticlopidine in preventing stroke in high-risk patients. Stroke. 1994 Jun;25(6):1149–1156. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.6.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman J., Lin T., Nankin H. R., Brown K. A., Hornung C. A. Serum cholesterol profiles during treatment of obese outpatients with a very low calorie diet. Effect of initial cholesterol levels. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1992 Jan;16(1):49–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamuk E. R., Williamson D. F., Serdula M. K., Madans J., Byers T. E. Weight loss and subsequent death in a cohort of U.S. adults. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Oct 1;119(7 Pt 2):744–748. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-7_part_2-199310011-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty G. W., Brown R. D., Jr, Whisnant J. P., Sicks J. D., O'Fallon W. M., Wiebers D. O. Survival and recurrence after first cerebral infarction: a population-based study in Rochester, Minnesota, 1975 through 1989. Neurology. 1998 Jan;50(1):208–216. doi: 10.1212/wnl.50.1.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pi-Sunyer F. X. Medical hazards of obesity. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Oct 1;119(7 Pt 2):655–660. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-7_part_2-199310011-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pories W. J., MacDonald K. G., Jr, Morgan E. J., Sinha M. K., Dohm G. L., Swanson M. S., Barakat H. A., Khazanie P. G., Leggett-Frazier N., Long S. D. Surgical treatment of obesity and its effect on diabetes: 10-y follow-up. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Feb;55(2 Suppl):582S–585S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/55.2.582s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm E. B., Stampfer M. J., Giovannucci E., Ascherio A., Spiegelman D., Colditz G. A., Willett W. C. Body size and fat distribution as predictors of coronary heart disease among middle-aged and older US men. Am J Epidemiol. 1995 Jun 15;141(12):1117–1127. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum M., Leibel R. L., Hirsch J. Obesity. N Engl J Med. 1997 Aug 7;337(6):396–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199708073370606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotte D. E., Stunkard A. J. The effects of weight reduction on blood pressure in 301 obese patients. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Aug;150(8):1701–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M. J., Maclure K. M., Colditz G. A., Manson J. E., Willett W. C. Risk of symptomatic gallstones in women with severe obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Mar;55(3):652–658. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/55.3.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassertheil-Smoller S., Blaufox M. D., Oberman A. S., Langford H. G., Davis B. R., Wylie-Rosett J. The Trial of Antihypertensive Interventions and Management (TAIM) study. Adequate weight loss, alone and combined with drug therapy in the treatment of mild hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 1992 Jan;152(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. C., Siegel J. E., Gold M. R., Kamlet M. S., Russell L. B. Recommendations of the Panel on Cost-effectiveness in Health and Medicine. JAMA. 1996 Oct 16;276(15):1253–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. F., Pamuk E., Thun M., Flanders D., Byers T., Heath C. Prospective study of intentional weight loss and mortality in never-smoking overweight US white women aged 40-64 years. Am J Epidemiol. 1995 Jun 15;141(12):1128–1141. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R. R., Koeske R., Epstein L. H., Nowalk M. P., Gooding W., Becker D. Long-term effects of modest weight loss in type II diabetic patients. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Oct;147(10):1749–1753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf A. M., Colditz G. A. The cost of obesity: the US perspective. Pharmacoeconomics. 1994;5(Suppl 1):34–37. doi: 10.2165/00019053-199400051-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C., Seeley R. J., Porte D., Jr, Schwartz M. W. Signals that regulate food intake and energy homeostasis. Science. 1998 May 29;280(5368):1378–1383. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5368.1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



