Abstract
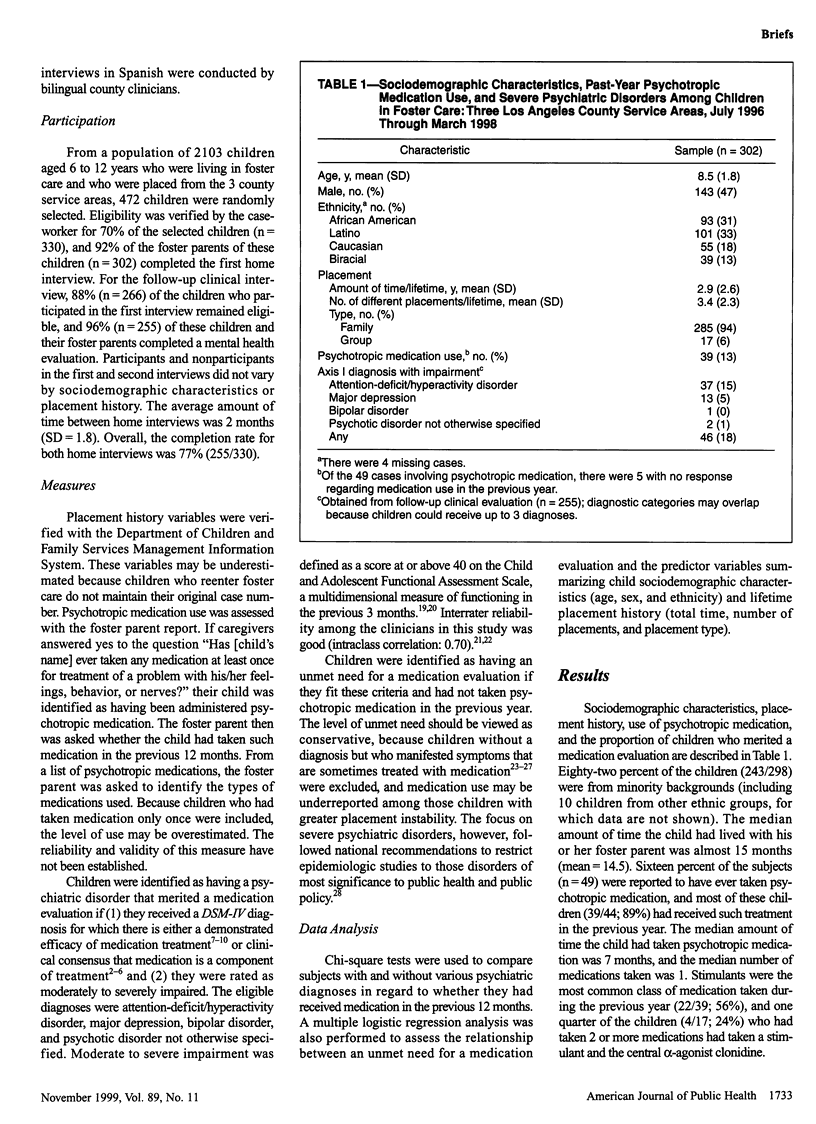
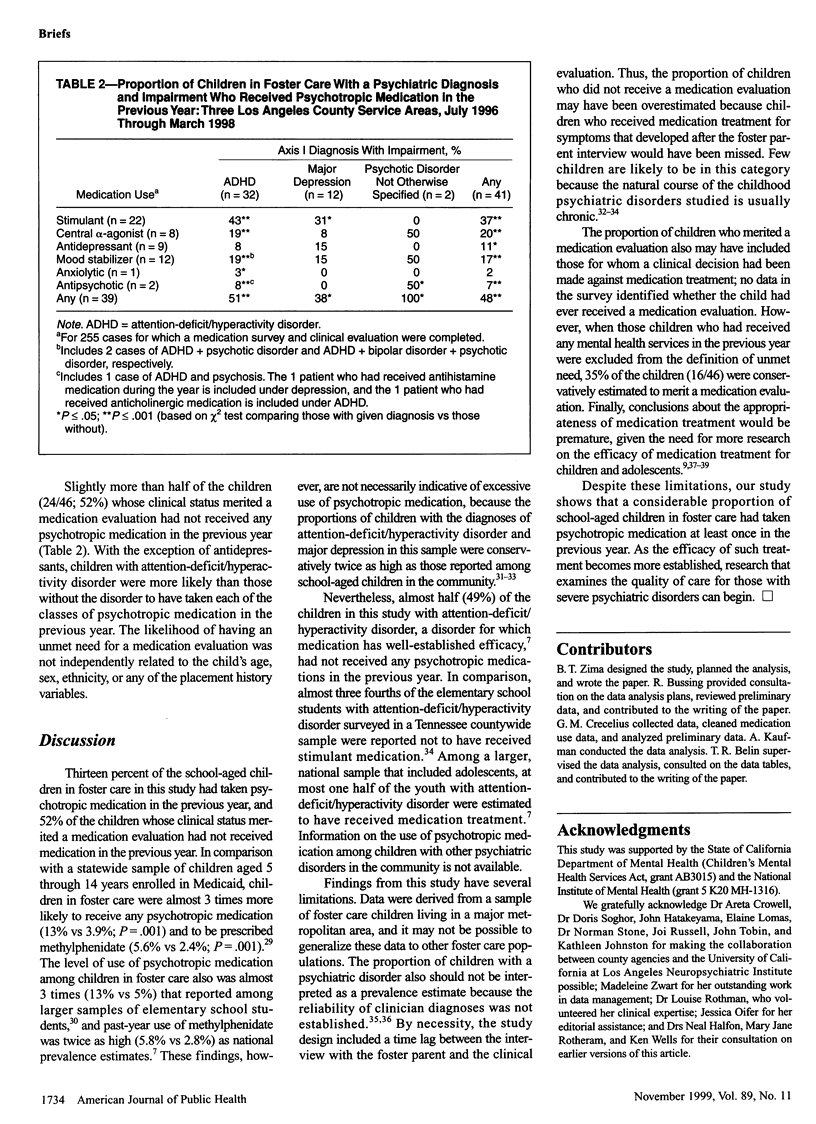
OBJECTIVES: This study sought to describe the level of psychotropic medication use and its relationship to severe psychiatric disorders among school-aged children in foster care. METHODS: Home interviews with 302 foster parents and children aged 6 to 12 years and 266 follow-up clinical evaluations were conducted. RESULTS: Thirteen percent of the children had taken psychotropic medication in the previous year, and 52% of those whose clinical status merited a medication evaluation had not received medication in the previous year. CONCLUSIONS: As the efficacy of psychotropic medication treatment for severe child psychiatric disorders becomes more established, research on the appropriateness of such care can begin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. J., Leonard H., Swedo S. E. Current knowledge of medications for the treatment of childhood anxiety disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1995 Aug;34(8):976–986. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199508000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. S., Peterson N. L., Meier J. H. Variables associated with disrupted placement in a select sample of abused and neglected children. Child Abuse Negl. 1987;11(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(87)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emslie G. J., Rush A. J., Weinberg W. A., Kowatch R. A., Hughes C. W., Carmody T., Rintelmann J. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of fluoxetine in children and adolescents with depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997 Nov;54(11):1031–1037. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830230069010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England M. J., Cole R. F. Building systems of care for youth with serious mental illness. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1992 Jun;43(6):630–633. doi: 10.1176/ps.43.6.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findling R. L., Dogin J. W. Psychopharmacology of ADHD: children and adolescents. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59 (Suppl 7):42–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittelman-Klein R., Klein D. F. School phobia: diagnostic considerations in the light of imipramine effects. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1973 Mar;156(3):199–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L. S., Genel M., Bezman R. J., Slanetz P. J. Diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association. JAMA. 1998 Apr 8;279(14):1100–1107. doi: 10.1001/jama.279.14.1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges K., Gust J. Measures of impairment for children and adolescents. J Ment Health Adm. 1995 Fall;22(4):403–413. doi: 10.1007/BF02518634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. S., Vitiello B., Leonard H., Laughren T. P. Design and methodology issues for clinical treatment trials in children and adolescents. Child and adolescent psychopharmacology: expanding the research base. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1994;30(1):3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Simms R. M., Busner J. Prescribing practices of outpatient child psychiatrists. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1994 Jan;33(1):35–44. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199401000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumra S., Frazier J. A., Jacobsen L. K., McKenna K., Gordon C. T., Lenane M. C., Hamburger S. D., Smith A. K., Albus K. E., Alaghband-Rad J. Childhood-onset schizophrenia. A double-blind clozapine-haloperidol comparison. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1996 Dec;53(12):1090–1097. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1996.01830120020005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardeck J. T. A profile of the child likely to experience unstable foster care. Adolescence. 1985 Fall;20(79):689–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piacentini J., Shaffer D., Fisher P., Schwab-Stone M., Davies M., Gioia P. The Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children-Revised Version (DISC-R): III. Concurrent criterion validity. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1993 May;32(3):658–665. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199305000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier D. A., Kaelber C. T., Rae D. S., Farmer M. E., Knauper B., Kessler R. C., Norquist G. S. Limitations of diagnostic criteria and assessment instruments for mental disorders. Implications for research and policy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998 Feb;55(2):109–115. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.55.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins L. N. Epidemiology: reflections on testing the validity of psychiatric interviews. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 Sep;42(9):918–924. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790320090013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D. J., Krager J. M. The increased rate of stimulant treatment for hyperactive/inattentive students in secondary schools. Pediatrics. 1994 Oct;94(4 Pt 1):462–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeon J. G. Challenges to pediatric psychopharmacology. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1997 Jan;22(1):15–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swire M. R., Kavaler F. The health status of foster children. Child Welfare. 1977 Dec;56(10):635–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkmar F. R. Childhood and adolescent psychosis: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1996 Jul;35(7):843–851. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199607000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolraich M. L., Lindgren S., Stromquist A., Milich R., Davis C., Watson D. Stimulant medication use by primary care physicians in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics. 1990 Jul;86(1):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zito J. M., Safer D. J., dosReis S., Riddle M. A. Racial disparity in psychotropic medications prescribed for youths with Medicaid insurance in Maryland. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1998 Feb;37(2):179–184. doi: 10.1097/00004583-199802000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


