Abstract
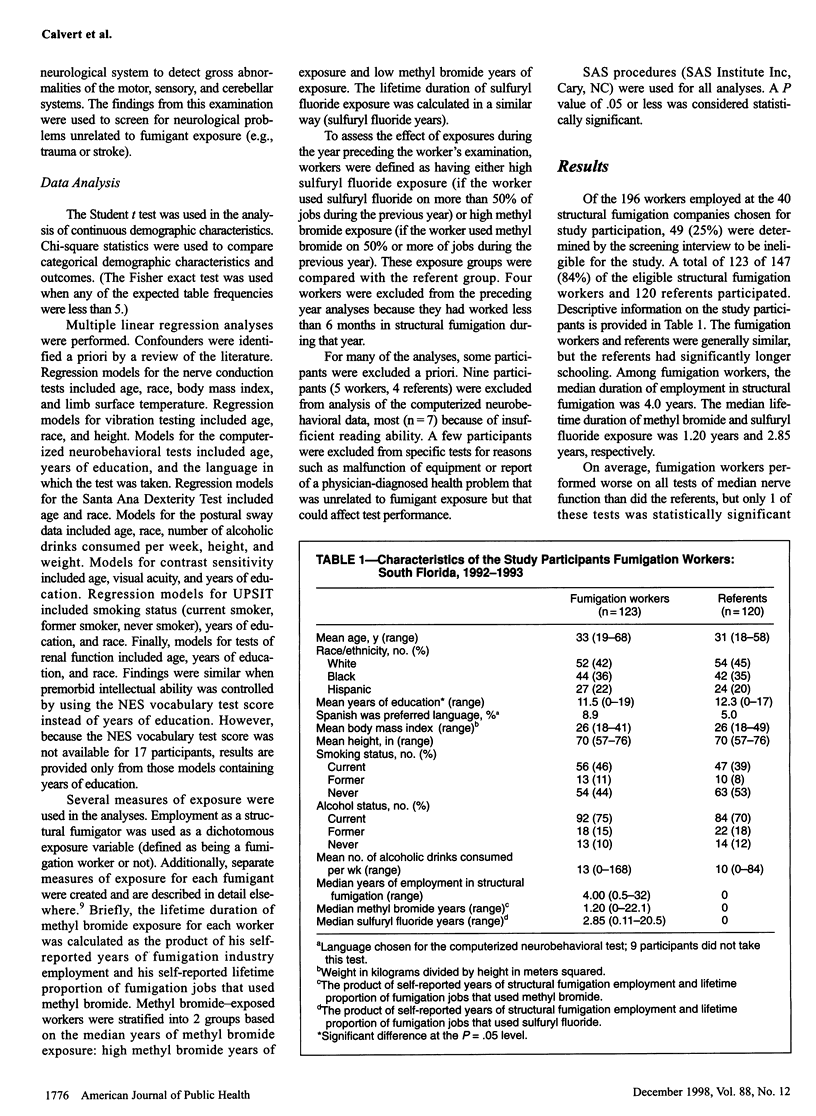
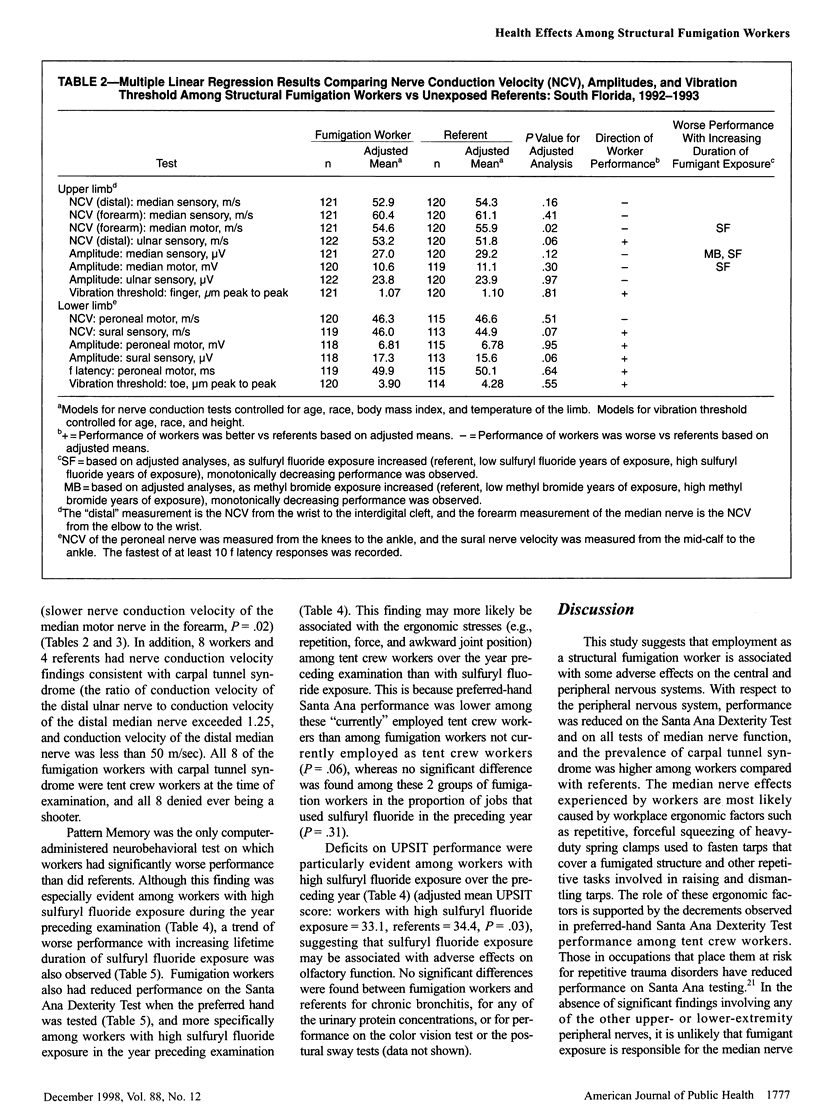
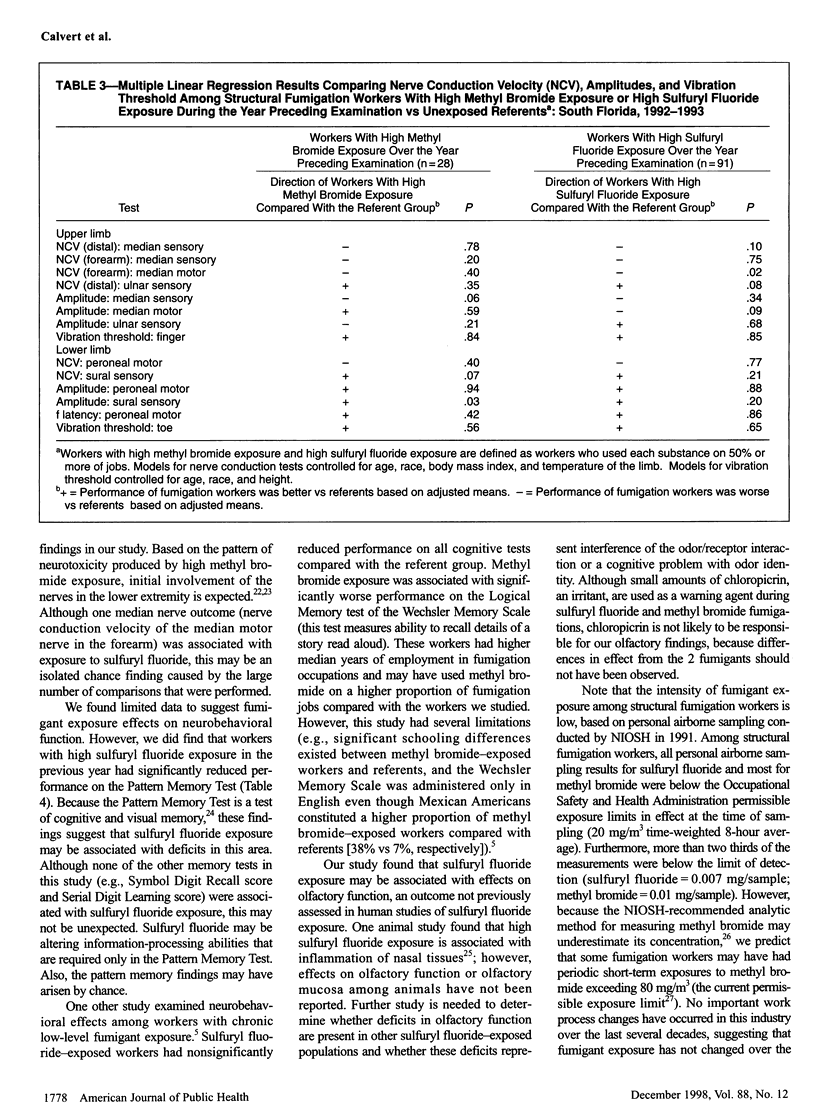
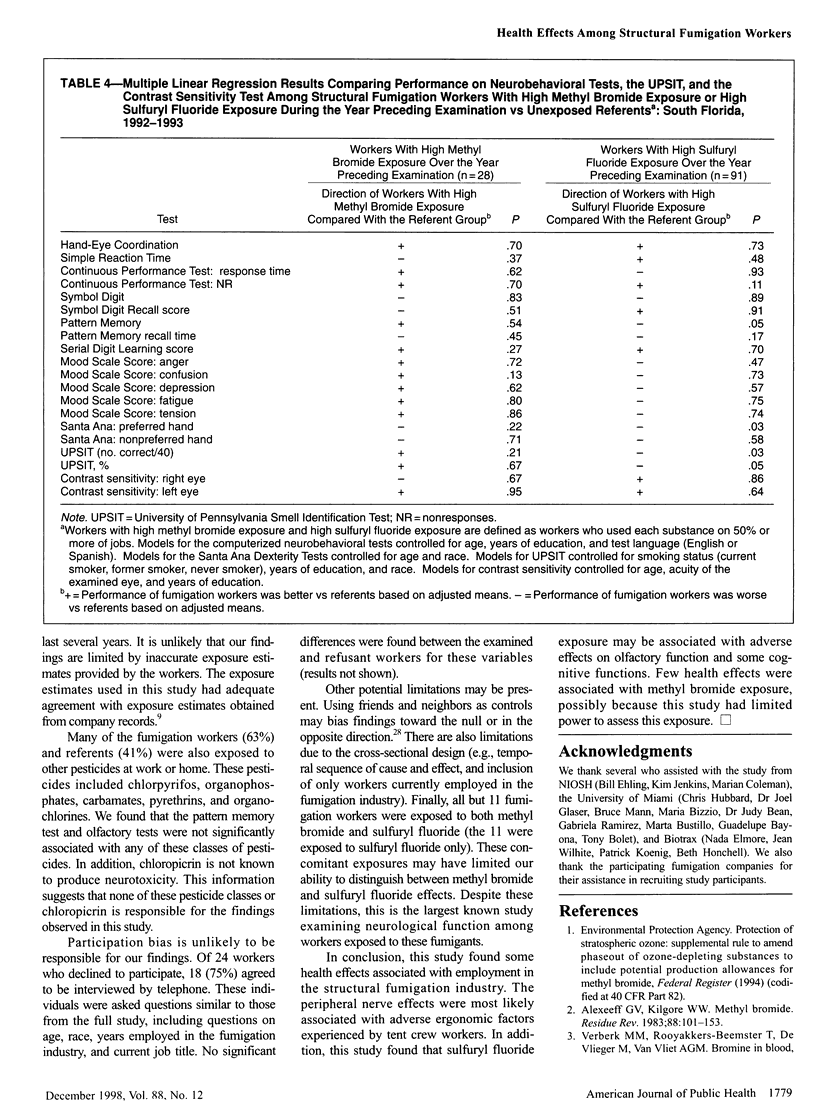
OBJECTIVES: This study assessed the health effects associated with occupational exposure to methyl bromide and sulfuryl fluoride among structural fumigation workers. METHODS: A cross-sectional study of 123 structural fumigation workers and 120 referents in south Florida was conducted. Nerve conduction, vibration, neurobehavioral, visual, olfactory, and renal function testing was included. RESULTS: The median lifetime duration of methyl bromide and sulfuryl fluoride exposure among workers was 1.20 years and 2.85 years, respectively. Sulfuryl fluoride exposure over the year preceding examination was associated with significantly reduced performance on the Pattern Memory Test and on olfactory testing. In addition, fumigation workers had significantly reduced performance on the Santa Ana Dexterity Test of the dominant hand and a nonsignificantly higher prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome than did the referents. CONCLUSIONS: Occupational sulfuryl fluoride exposures may be associated with subclinical effects on the central nervous system, including effects on olfactory and some cognitive functions. However, no widespread pattern of cognitive deficits was observed. The peripheral nerve effects were likely caused by ergonomic stresses experienced by the fumigation workers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexeeff G. V., Kilgore W. W. Methyl bromide. Residue Rev. 1983;88:101–153. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-5569-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anger W. K., Moody L., Burg J., Brightwell W. S., Taylor B. J., Russo J. M., Dickerson N., Setzer J. V., Johnson B. L., Hicks K. Neurobehavioral evaluation of soil and structural fumigators using methyl bromide and sulfuryl fluoride. Neurotoxicology. 1986 Fall;7(3):137–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvert G. M., Mueller C. A., O'Neill V. L., Fajen J. M., Briggle T., Fleming L. E. Agreement between company-recorded and self-reported estimates of duration and frequency of occupational fumigant exposure. Am J Ind Med. 1997 Oct;32(4):364–368. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0274(199710)32:4<364::aid-ajim7>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalleri F., Galassi G., Ferrari S., Merelli E., Volpi G., Gobba F., Del Carlo G., De Iaco A., Botticelli A. R., Rizzuto N. Methyl bromide induced neuropathy: a clinical, neurophysiological, and morphological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Mar;58(3):383–383. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.3.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick R. B., Bhattacharya A., Shukla R. Use of a computerized postural sway measurement system for neurobehavioral toxicology. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(90)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doty R. L., Shaman P., Dann M. Development of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test: a standardized microencapsulated test of olfactory function. Physiol Behav. 1984 Mar;32(3):489–502. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(84)90269-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbrandt D. L., Nitschke K. D. Inhalation toxicity of sulfuryl fluoride in rats and rabbits. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1989 Apr;12(3):540–557. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(89)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerr F. E., Letz R. Reliability of a widely used test of peripheral cutaneous vibration sensitivity and a comparison of two testing protocols. Br J Ind Med. 1988 Sep;45(9):635–639. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.9.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerr F., Letz R. Vibrotactile threshold testing in occupational health: a review of current issues and limitations. Environ Res. 1993 Jan;60(1):145–159. doi: 10.1006/enrs.1993.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTARJIAN A. D., SHAHEEN A. S. METHYL BROMIDE POISONING WITH NERVOUS SYSTEM MANIFESTATIONS RESEMBLING POLYNEUROPATHY. Neurology. 1963 Dec;13:1054–1058. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.12.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linksz A. The Farnsworth panel D-15 test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966 Jul;62(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(66)91673-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson J. L., Albee R. R., Eisenbrandt D. L., Chang L. W. Subchronic neurotoxicity in rats of the structural fumigant, sulfuryl fluoride. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0892-0362(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D., Linz D., Shukla R., Rice C., Bhattacharya A., Suskind R. Health status of pesticide applicators: postural stability assessments. J Occup Med. 1993 Dec;35(12):1196–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuerman E. H. Suicide by exposure to sulfuryl fluoride. J Forensic Sci. 1986 Jul;31(3):1154–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenland K., Jenkins B., Ames R. G., O'Malley M., Chrislip D., Russo J. Chronic neurological sequelae to organophosphate pesticide poisoning. Am J Public Health. 1994 May;84(5):731–736. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



