Abstract
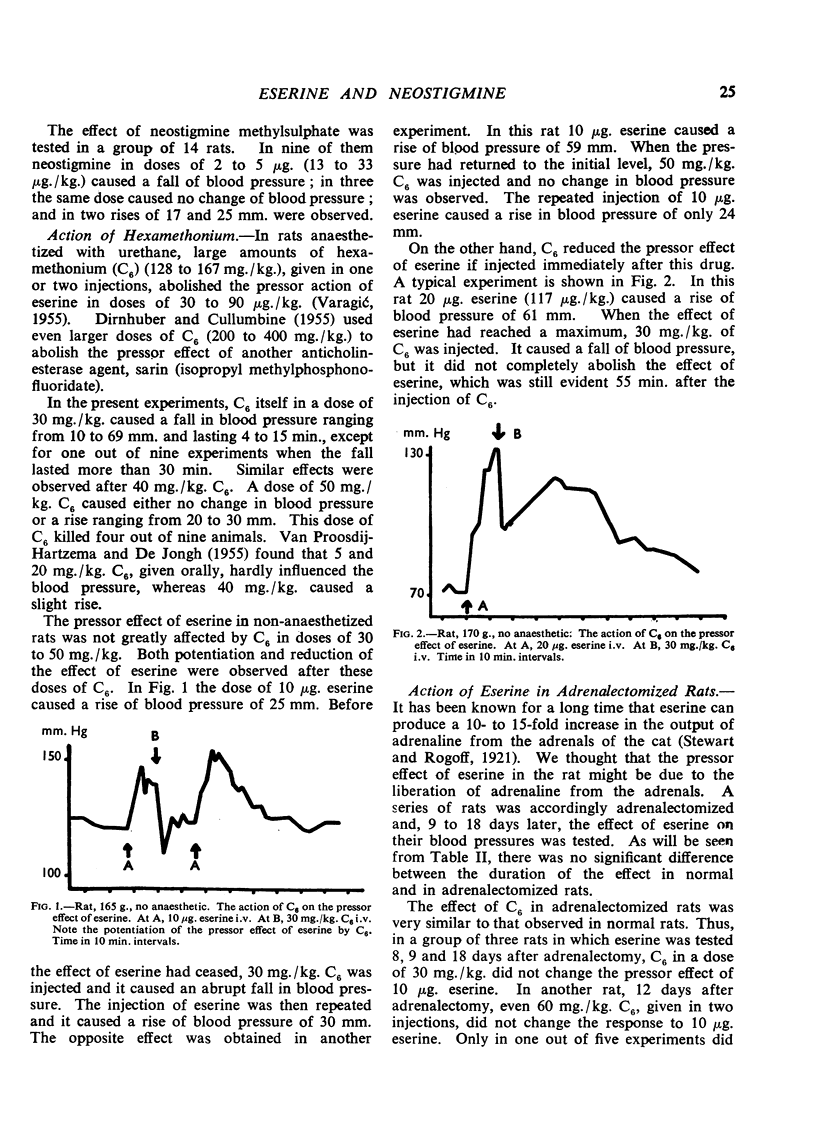
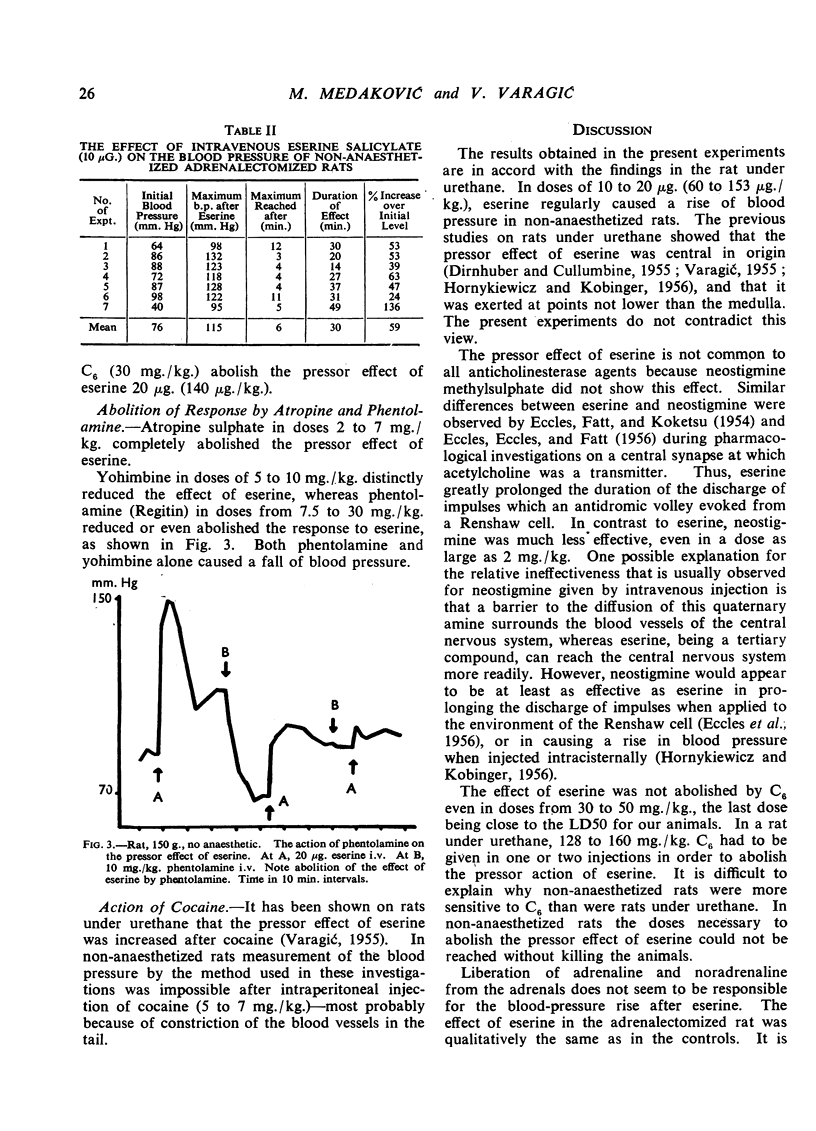
Small amounts of eserine salicylate (10 to 20 μg.) regularly caused a rise of blood pressure in non-anaesthetized rats. Neostigmine methylsulphate in doses from 1 to 10 μg./animal usually caused a fall of blood pressure, or no change was observed; only in a few experiments was a rise of blood pressure noted. The pressor effect of eserine was abolished by atropine and reduced or abolished by yohimbine and phentolamine. Adrenalectomy did not change the response to eserine. The present experiments do not contradict earlier statements that the pressor effect of eserine was due to the discharge of impulses from a centre or centres in the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAHEN R. L., TVEDE K. M. Action of atropine on sympathetic ganglia. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1953 Jun;94(2):248–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIRNHUBER P., CULLUMBINE H. The effect of anti-cholinesterase agents on the rat's blood pressure. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Mar;10(1):12–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES D. M., FATT P. Pharmacological investigations on a central synapse operated by acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1956 Jan 27;131(1):154–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNYKIEWICZ O., KOBINGER W. Uber den Einfluss von Eserin, Tetraäthylpyrophosphat (TEPP) und Neostigmin auf den Blutdruck und die pressorischen Carotissinusreflexe der Ratte. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1956;228(5):493–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN PROOSDIJ-HARTZEMA E. G. Indirect measurement of the blood pressure in the rat. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Neerl. 1954;3(4):472–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


