Abstract
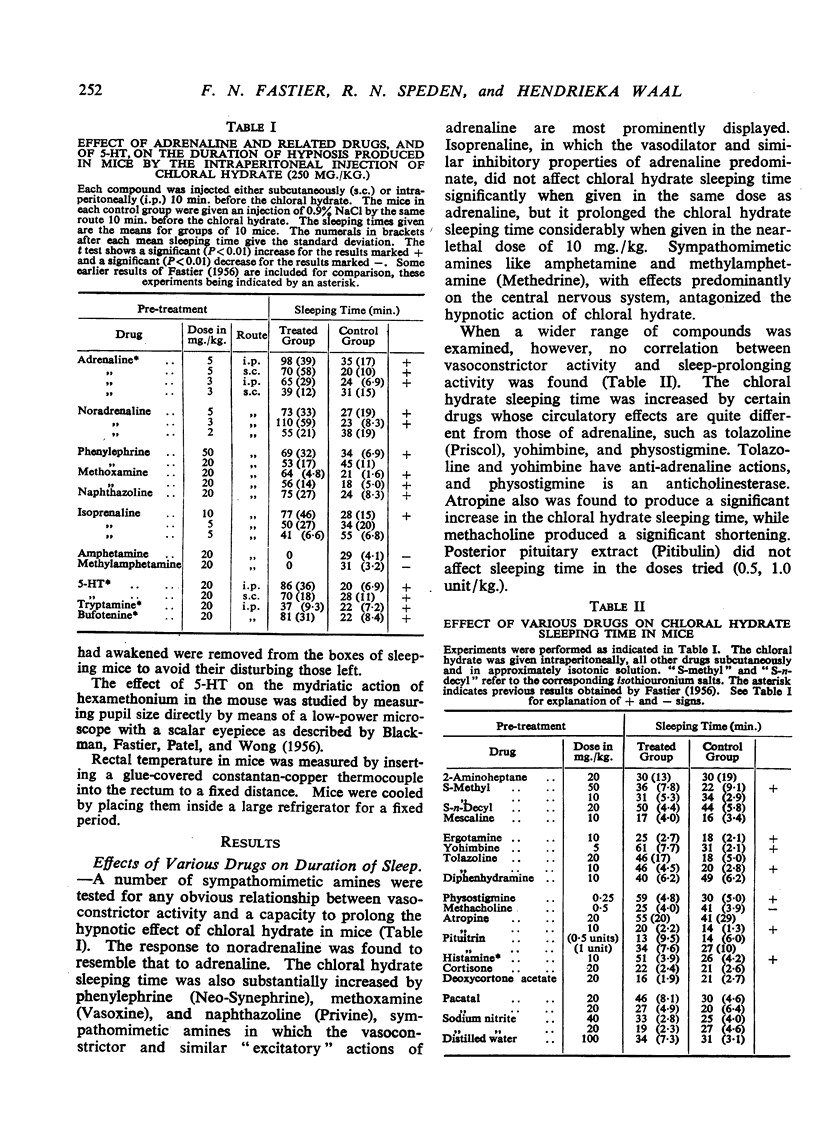
Various drugs have been tested for a capacity to prolong the hypnotic effect of chloral hydrate in mice. Amongst the compounds which, when injected subcutaneously in substantial amount shortly before the chloral hydrate (250 mg./kg. intraperitoneally), increased sleeping time significantly were adrenaline, noradrenaline, phenylephrine, methoxamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), histamine, ergotamine, yohimbine, and atropine. The ability of these drugs to prolong chloral hydrate sleeping time could not be related to any common circulatory property, but most of the active drugs are known to lower body temperature under comparable conditions. It was found that mice which have been pre-treated with 5-hydroxytryptamine or adrenaline suffer a much greater fall of body temperature when chloral hydrate is given subsequently than do mice which have been given chloral hydrate alone. It is suggested that some, at least, of the drugs which prolong the effects of hypnotics do so by virtue of a hypothermic action.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKMAN J. G., FASTIER F. N., PATEL C. M., WONG L. C. Assessment of depressor activity and mydriatic activity of hexamethonium analogues. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Sep;11(3):282–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb01067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FABINYI-SZEBEHELY M., SZEBEHELY J. The influence of antihistamines on the effect of histamine upon body temperature and oxygen consumption in mice and rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;27(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FASTIER F. N. Prolongation of hypnosis by 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Experientia. 1956 Sep 15;12(9):351–351. doi: 10.1007/BF02165348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLACKE W., MULKE G., SCHULZ R. Beitrag zur Wirkung von Pharmaka auf die Unterdrucktoleranz. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;220(6):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORNAROLI P., KOLLER M. 5-Ossitriptamina e barbiturici. Farmaco Sci. 1954;9(10):546–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITH F. R., Jr Fact and theory regarding the calorigenic action of adrenaline. Physiol Rev. 1951 Apr;31(2):151–187. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1951.31.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GYERMEK L. Die Wirkung des Histamins auf den Gasstoffwechsel und die Körper-temperatur. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1950;209(4-5):456–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORWITZ O., MONTGOMERY H. Effects of vasodilator drugs and other procedures on digital cutaneous blood flow, cardiac output, blood pressure, pulse rate, body temperature, and metabolic rate. Am J Med Sci. 1949 Dec;218(6):669–682. doi: 10.1097/00000441-194921860-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALOW W. Urinary excretion of d-tubocurarine in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Sep;109(1):74–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIND L. S. Antagonism of cortisone to body temperature reducing effect of histamine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Feb;85(2):371–372. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH D. F. The distribution, metabolism, and excretion of d-tubocurarine chloride and related compounds in man and other animals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Jul;105(3):299–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. M., ZAIMIS E. The methonium. Pharmacol Rev. 1952 Sep;4(3):219–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS R. K., TAYLOR J. D. Some factors influencing distribution, metabolism and action of barbiturates; a review. Anesthesiology. 1956 May;17(3):414–458. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195605000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMOIRAGHI G. C., SOLLERO L., PAGE I. H. Blockade by brom-lysergic-acid-diethylamide (BOL) of the potentiating action of serotonin and reserpine on hexobarbital hypnosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 Jun;117(2):166–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., SILVER S. L., BRODIE B. B. Interaction of serotonin and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in the central nervous system. Experientia. 1955 Jul 15;11(7):272–273. doi: 10.1007/BF02161252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


