Abstract
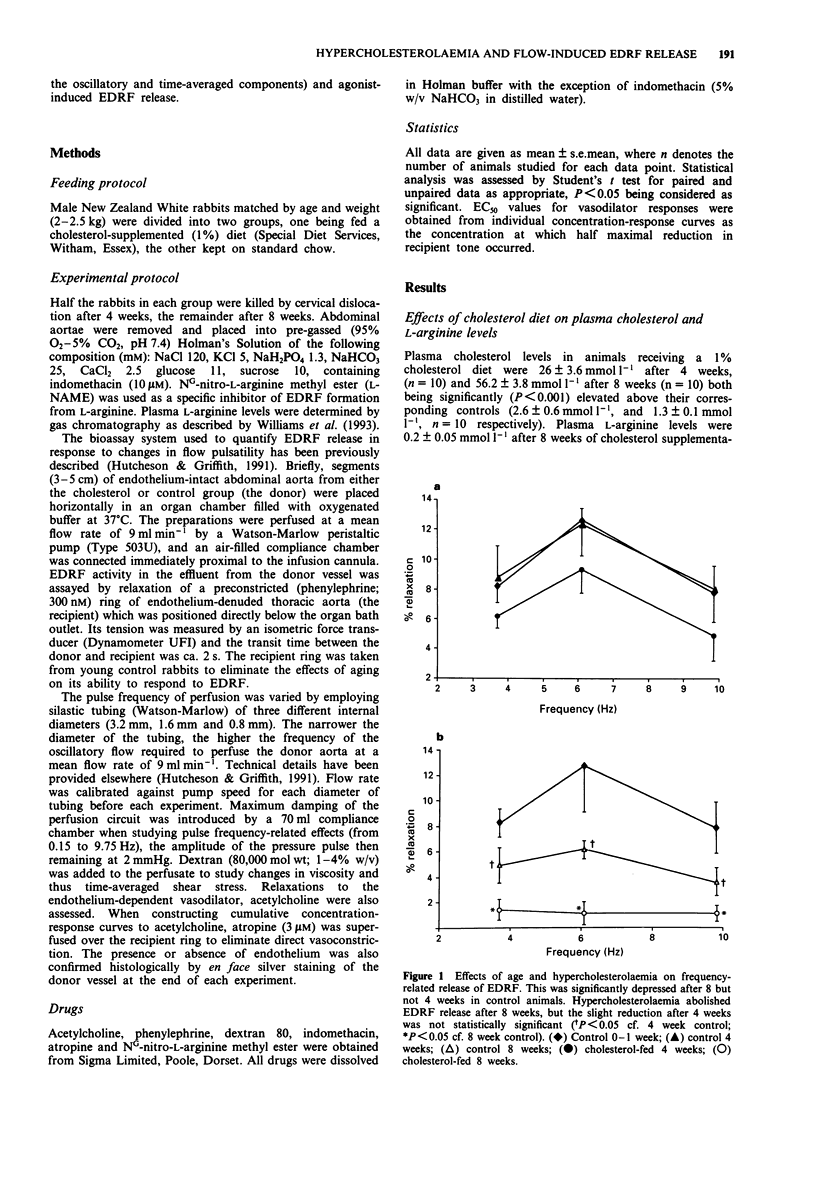
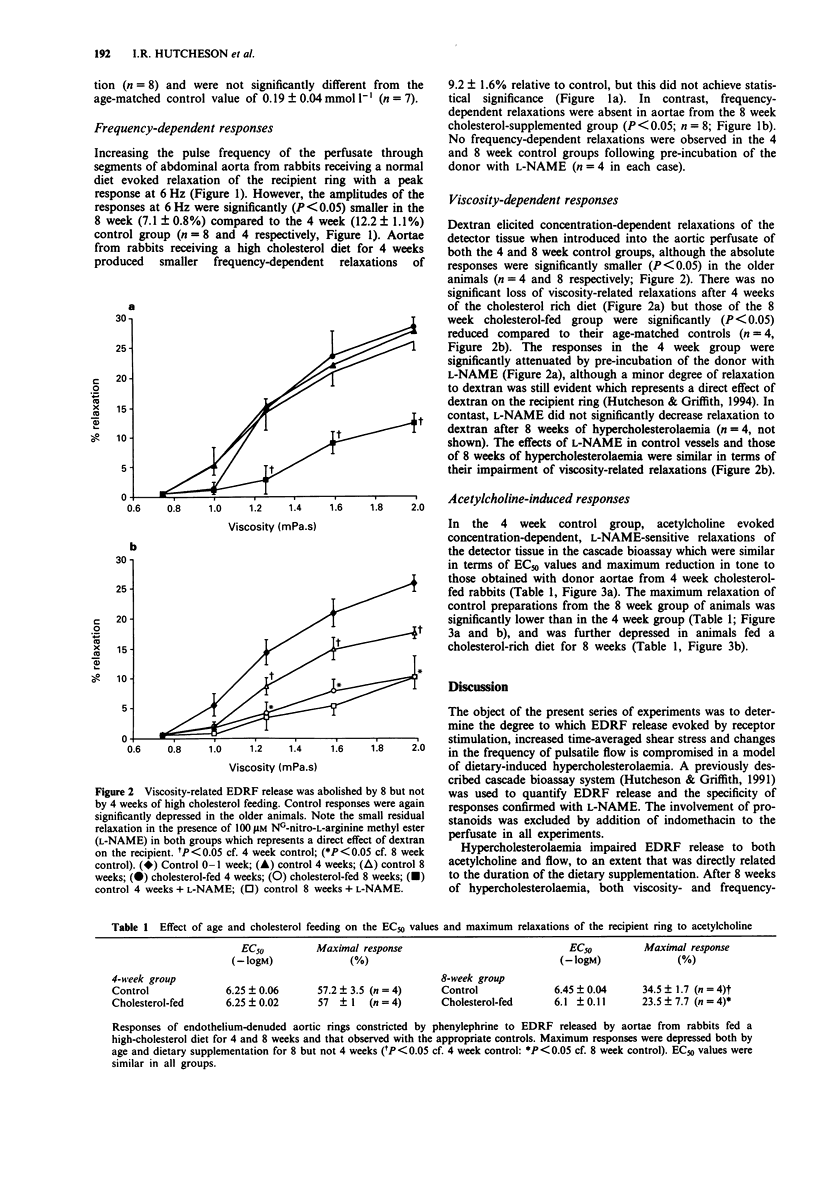
1. We have used a pulsatile cascade bioassay system to investigate the effects of dietary-induced hypercholesterolaemia on EDRF release evoked by acetylcholine and by the oscillatory and time-averaged components of flow, in isolated segments of rabbit abdominal aorta. 2. Flow pulsatility (frequency range 0.1-10 Hz) was studied with constant flow (9 ml min-1) at a pulse pressure amplitude of 2 mmHg. Frequency-related EDRF release, maximal at 6 Hz, was slightly attenuated after 4 weeks and abolished after 8 weeks of cholesterol feeding. 3. Time-averaged shear stress was manipulated with dextran (1-4% w/v, 80000 mol. wt.), to increase perfusate viscosity. EDRF release induced by increased perfusate viscosity was unaffected after 4 weeks but abolished after 8 weeks of cholesterol feeding. 4. Endothelium-dependent relaxations to acetylcholine (0.1-10 microM) were not influenced after 4 weeks and only partially attenuated (by 60% of the maximal response, EC50 unchanged at 6.45 +/- 0.04 vs. 6.4 +/- 0.1 microM) after 8 weeks of cholesterol feeding. 5. Blood cholesterol levels were significantly (P < 0.001) increased after 4 weeks (26 +/- 3.6 vs 2.6 +/- 0.6 mmol l-1) and 8 weeks (56.2 +/- 3.8 vs 1.3 +/- 0.1 mmol l-1) of cholesterol feeding but after 8 weeks plasma L-arginine levels were not significantly different from the age-matched controls (0.2 +/- 0.05 vs. 0.19 +/- 0.04 mmol l-1). 6. We conclude that hypercholesterolaemia impairs flow-related (pulsatile- and time-averaged shear-induced) EDRF release earlier than acetylcholine-induced relaxation in rabbit aorta.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
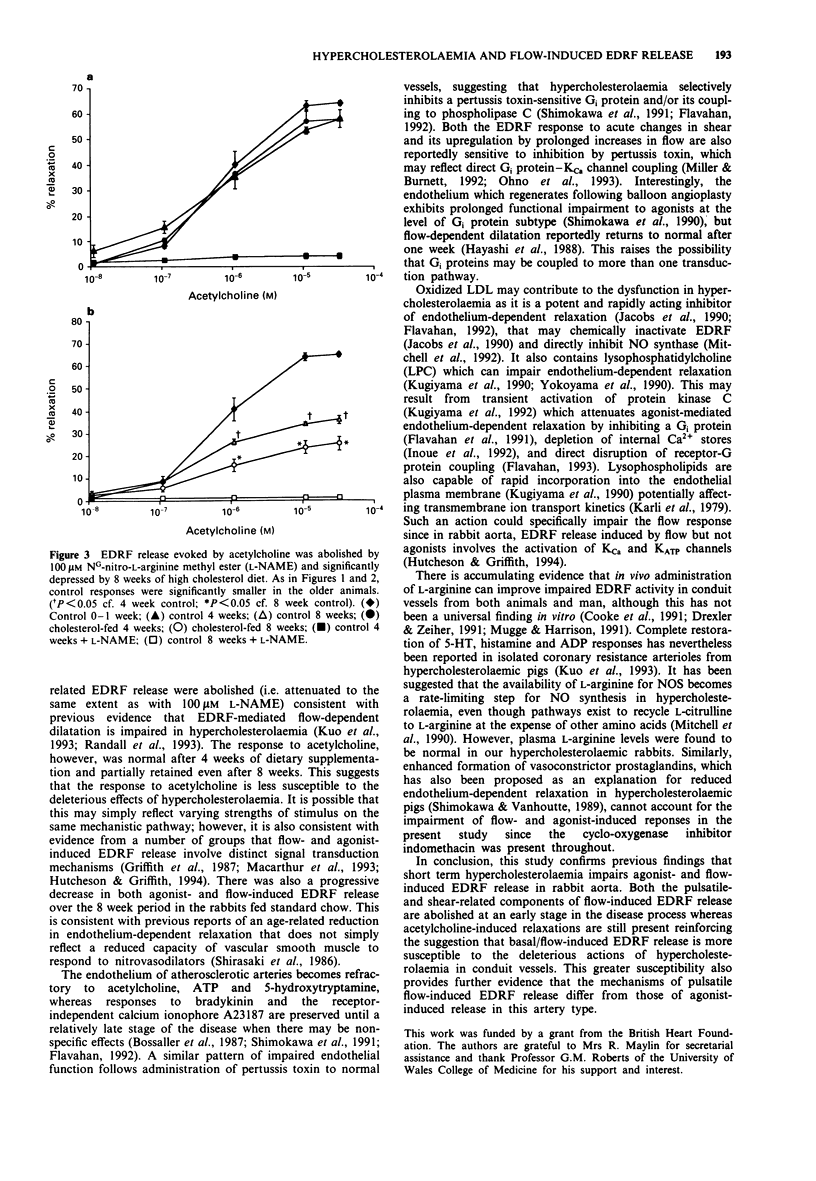

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bath P. M., Hassall D. G., Gladwin A. M., Palmer R. M., Martin J. F. Nitric oxide and prostacyclin. Divergence of inhibitory effects on monocyte chemotaxis and adhesion to endothelium in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Mar-Apr;11(2):254–260. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossaller C., Habib G. B., Yamamoto H., Williams C., Wells S., Henry P. D. Impaired muscarinic endothelium-dependent relaxation and cyclic guanosine 5'-monophosphate formation in atherosclerotic human coronary artery and rabbit aorta. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):170–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI112779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. P., Andon N. A., Girerd X. J., Hirsch A. T., Creager M. A. Arginine restores cholinergic relaxation of hypercholesterolemic rabbit thoracic aorta. Circulation. 1991 Mar;83(3):1057–1062. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.3.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. A., Vita J. A., Treasure C. B., Fish R. D., Alexander R. W., Ganz P., Selwyn A. P. Atherosclerosis impairs flow-mediated dilation of coronary arteries in humans. Circulation. 1989 Sep;80(3):458–465. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.3.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A. Atherosclerosis or lipoprotein-induced endothelial dysfunction. Potential mechanisms underlying reduction in EDRF/nitric oxide activity. Circulation. 1992 May;85(5):1927–1938. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.5.1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A. Lysophosphatidylcholine modifies G protein-dependent signaling in porcine endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):H722–H727. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.3.H722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A., Shimokawa H., Vanhoutte P. M. Inhibition of endothelium-dependent relaxations by phorbol myristate acetate in canine coronary arteries: role of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jan;256(1):50–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Mügge A., Alheid U., Haverich A., Frölich J. C. Selective attenuation of endothelium-mediated vasodilation in atherosclerotic human coronary arteries. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):185–190. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg U. C., Hassid A. Nitric oxide-generating vasodilators and 8-bromo-cyclic guanosine monophosphate inhibit mitogenesis and proliferation of cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1774–1777. doi: 10.1172/JCI114081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Henderson A. H. Unstimulated release of endothelium derived relaxing factor is independent of mitochondrial ATP generation. Cardiovasc Res. 1987 Aug;21(8):565–568. doi: 10.1093/cvr/21.8.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Tomoike H., Nagasawa K., Yamada A., Nishijima H., Adachi H., Nakamura M. Functional and anatomical recovery of endothelium after denudation of coronary artery. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 2):H1081–H1090. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.6.H1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutcheson I. R., Griffith T. M. Heterogeneous populations of K+ channels mediate EDRF release to flow but not agonists in rabbit aorta. Am J Physiol. 1994 Feb;266(2 Pt 2):H590–H596. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.2.H590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutcheson I. R., Griffith T. M. Release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor is modulated both by frequency and amplitude of pulsatile flow. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 2):H257–H262. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.1.H257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue N., Hirata K., Yamada M., Hamamori Y., Matsuda Y., Akita H., Yokoyama M. Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits bradykinin-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis and calcium transients in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1992 Dec;71(6):1410–1421. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.6.1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Plane F., Bruckdorfer K. R. Native and oxidized low-density lipoproteins have different inhibitory effects on endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the rabbit aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):21–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karli J. N., Karikas G. A., Hatzipavlou P. K., Levis G. M., Moulopoulos S. N. The inhibition of Na+ and K+ stimulated ATPase activity of rabbit and dog heart sarcolemma by lysophosphatidyl choline. Life Sci. 1979 May 14;24(20):1869–1875. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku D. N., Giddens D. P., Zarins C. K., Glagov S. Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):293–302. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugiyama K., Kerns S. A., Morrisett J. D., Roberts R., Henry P. D. Impairment of endothelium-dependent arterial relaxation by lysolecithin in modified low-density lipoproteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):160–162. doi: 10.1038/344160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugiyama K., Ohgushi M., Sugiyama S., Murohara T., Fukunaga K., Miyamoto E., Yasue H. Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits surface receptor-mediated intracellular signals in endothelial cells by a pathway involving protein kinase C activation. Circ Res. 1992 Dec;71(6):1422–1428. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.6.1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo L., Davis M. J., Cannon M. S., Chilian W. M. Pathophysiological consequences of atherosclerosis extend into the coronary microcirculation. Restoration of endothelium-dependent responses by L-arginine. Circ Res. 1992 Mar;70(3):465–476. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macarthur H., Hecker M., Busse R., Vane J. R. Selective inhibition of agonist-induced but not shear stress-dependent release of endothelial autacoids by thapsigargin. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):100–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLenachan J. M., Vita J., Fish D. R., Treasure C. B., Cox D. A., Ganz P., Selwyn A. P. Early evidence of endothelial vasodilator dysfunction at coronary branch points. Circulation. 1990 Oct;82(4):1169–1173. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.4.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. M., Burnett J. C., Jr Modulation of NO and endothelin by chronic increases in blood flow in canine femoral arteries. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 2):H103–H108. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.1.H103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. A., Hecker M., Anggård E. E., Vane J. R. Cultured endothelial cells maintain their L-arginine level despite the continuous release of EDRF. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 17;182(3):573–576. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90058-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Identification as nitric oxide and role in the control of vascular tone and platelet function. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 1;37(13):2495–2501. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mügge A., Harrison D. G. L-arginine does not restore endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic rabbit aorta in vitro. Blood Vessels. 1991;28(5):354–357. doi: 10.1159/000158881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Gibbons G. H., Dzau V. J., Cooke J. P. Shear stress elevates endothelial cGMP. Role of a potassium channel and G protein coupling. Circulation. 1993 Jul;88(1):193–197. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragazzi E., Froldi G., Pandolfo L., Chinellato A., De Biasi M., Prosdocimi M., Caparrotta L., Fassina G. Segmental impairment of endothelium-mediated relaxation in thoracic aortas from atherosclerotic rabbits. Comparison to cholesterol infiltration and energy metabolism. Artery. 1989;16(6):327–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall M. D., Smith J. A., Griffith T. M. Hypercholesterolaemia severely impairs EDRF-dependent collateral perfusion following acute arterial occlusion in rabbit isolated ear. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):838–844. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa H., Aarhus L. L., Vanhoutte P. M. Porcine coronary arteries with regenerated endothelium have a reduced endothelium-dependent responsiveness to aggregating platelets and serotonin. Circ Res. 1987 Aug;61(2):256–270. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa H., Flavahan N. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Loss of endothelial pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein function in atherosclerotic porcine coronary arteries. Circulation. 1991 Feb;83(2):652–660. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.2.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa H., Flavahan N. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Natural course of the impairment of endothelium-dependent relaxations after balloon endothelium removal in porcine coronary arteries. Possible dysfunction of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Circ Res. 1989 Sep;65(3):740–753. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.3.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasaki Y., Su C., Lee T. J., Kolm P., Cline W. H., Jr, Nickols G. A. Endothelial modulation of vascular relaxation to nitrovasodilators in aging and hypertension. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):861–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeuren T. J., Jordaens F. H., Zonnekeyn L. L., Van Hove C. E., Coene M. C., Herman A. G. Effect of hypercholesterolemia on vascular reactivity in the rabbit. I. Endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent contractions and relaxations in isolated arteries of control and hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):552–564. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L. Role of oxidised low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. Br Heart J. 1993 Jan;69(1 Suppl):S12–S18. doi: 10.1136/hrt.69.1_suppl.s12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Bossaller C., Cartwright J., Jr, Henry P. D. Videomicroscopic demonstration of defective cholinergic arteriolar vasodilation in atherosclerotic rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1752–1758. doi: 10.1172/JCI113516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama M., Hirata K., Miyake R., Akita H., Ishikawa Y., Fukuzaki H. Lysophosphatidylcholine: essential role in the inhibition of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by oxidized low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91708-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


