Abstract
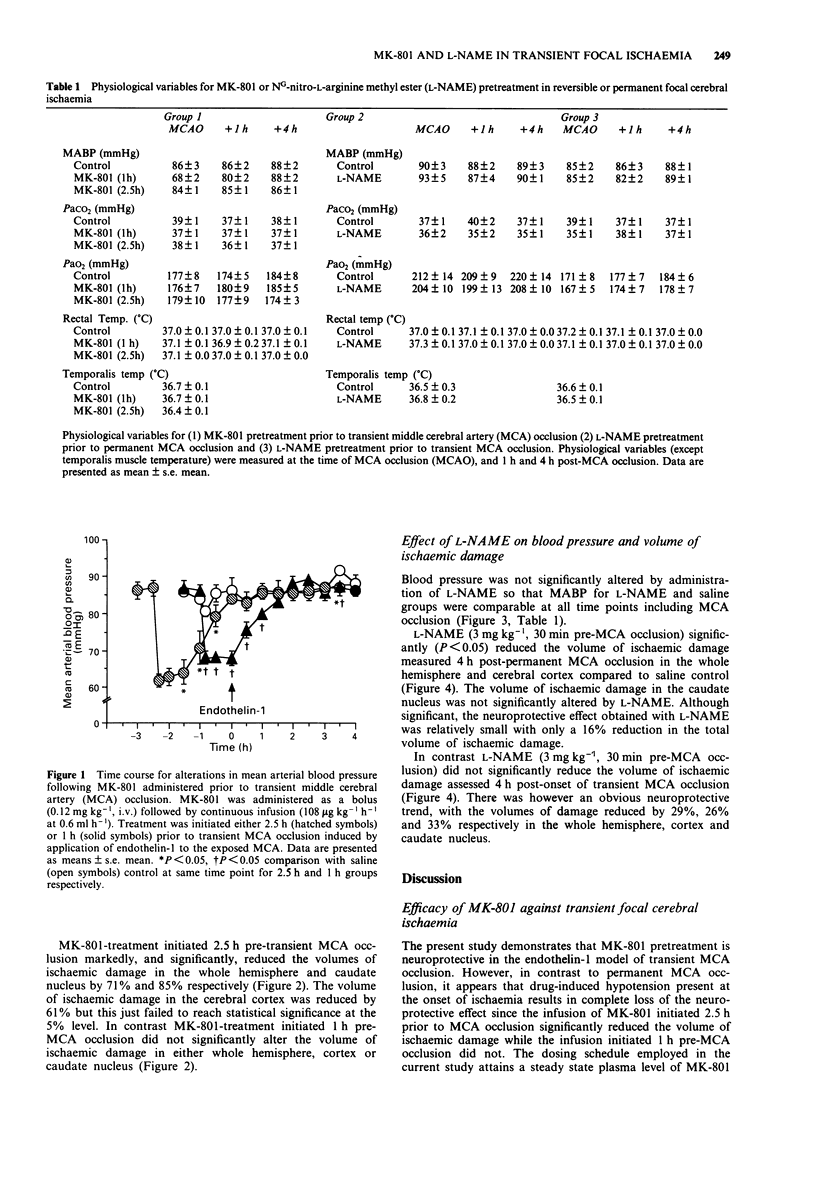
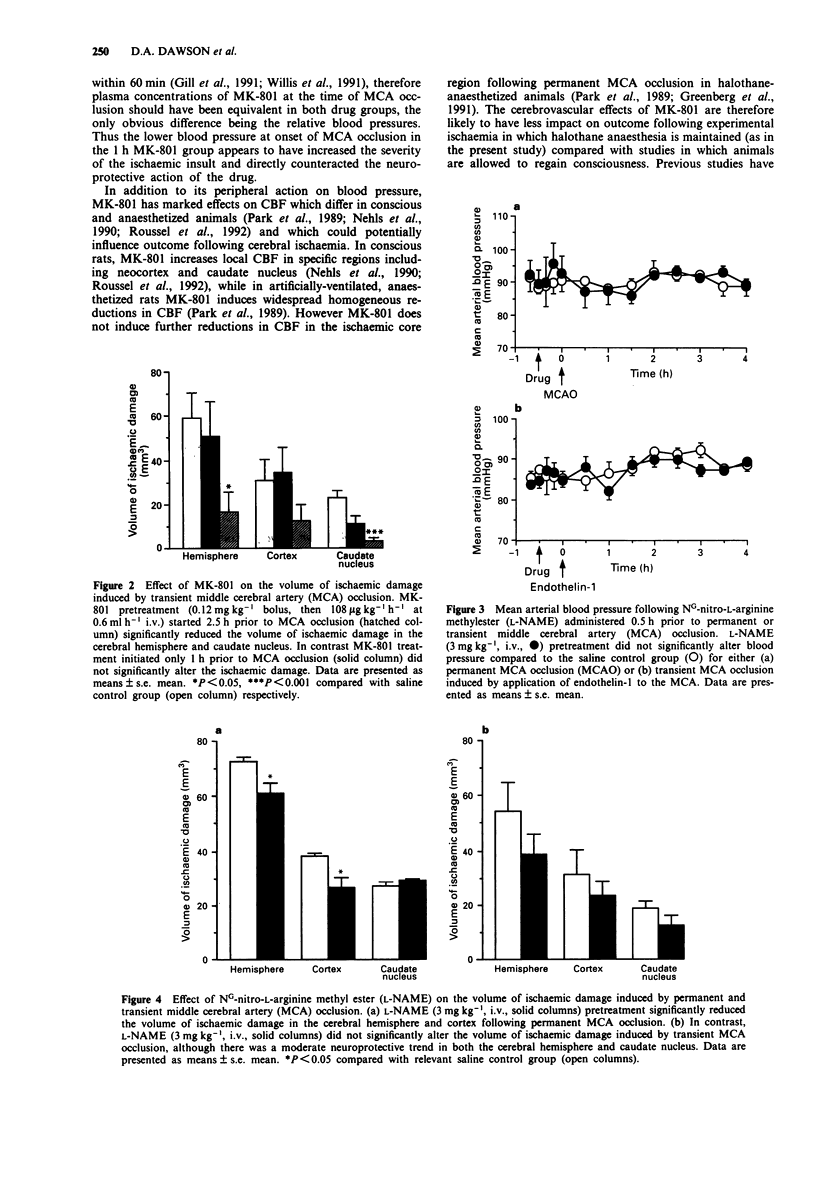
1. We have recently developed a new model of transient focal ischaemia in the rat utilising topical application of endothelin-1 to the left middle cerebral artery (MCA). In order to validate this approach the present study assessed the neuroprotective efficacy of the NMDA receptor antagonist dizocilpine (MK-801) in the endothelin-1 model. The anti-ischaemic efficacy of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) was subsequently evaluated, and contrasted with its efficacy against permanent focal ischaemia, to determine the utility of the endothelin-1 model for identification of novel pharmacoprotective agents. 2. MK-801 (0.12 mg kg-1 bolus, 108 micrograms kg-1 h-1 infusion i.v., either 1 or 2.5 h pre-transient MCA occlusion (MCAO)) induced hypotension that persisted for approximately 1.5 h so that mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) at the time of MCAO was significantly lower in the 1 h group compared with control (MABP: 86 +/- 11, 68 +/- 6 and 84 +/- 4 mmHg (mean +/- s.d.) for saline, 1 h MK-801 and 2.5 h MK-801 groups respectively). The 2.5 h pretreatment schedule resulted in significant reduction (71%) in the volume of hemispheric damage (assessed 4 h post onset of ischaemia) while the 1 h pretreatment schedule did not (volumes of hemispheric damage: 59 +/- 38, 51 +/- 51 and 17 +/- 28 mm3 for saline, 1 h and 2.5 h MK-801 groups). 3. Thus the considerable neuroprotective effect of MK-801 in the endothelin-1 model of transient focal cerebral ischaemia was highly sensitive to drug-induced hypotension.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A. W. Structural abnormalities in neurones. J Clin Pathol Suppl (R Coll Pathol) 1977;11:155–169. doi: 10.1136/jcp.s3-11.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A. M., Slivka A., Xue D. The effect of the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 on cerebral blood flow and infarct volume in experimental focal stroke. Brain Res. 1992 Mar 6;574(1-2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90814-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisson A., Plotkine M., Boulu R. G. The neuroprotective effect of a nitric oxide inhibitor in a rat model of focal cerebral ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):766–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock R., Fujisawa H. The role of glutamate antagonists for the treatment of CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. 1992 May;9 (Suppl 2):S443–S462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. A., Kusumoto K., Graham D. I., McCulloch J., Macrae I. M. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis does not reduce infarct volume in a rat model of focal cerebral ischaemia. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Aug 17;142(2):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90361-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M., London E. D., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6368–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezsi L., Greenberg J. H., Hamar J., Sladky J., Karp A., Reivich M. Acute improvement in histological outcome by MK-801 following focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in the cat independent of blood flow changes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 May;12(3):390–399. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa H., Dawson D., Browne S. E., MacKay K. B., Bullock R., McCulloch J. Pharmacological modification of glutamate neurotoxicity in vivo. Brain Res. 1993 Nov 26;629(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90483-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Brazell C., Woodruff G. N., Kemp J. A. The neuroprotective action of dizocilpine (MK-801) in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model of focal ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):2030–2036. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. H., Uematsu D., Araki N., Reivich M. Intracellular calcium and pathophysiological changes in cerebral ischemia. Arzneimittelforschung. 1991 Mar;41(3A):324–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kader A., Frazzini V. I., Solomon R. A., Trifiletti R. R. Nitric oxide production during focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1993 Nov;24(11):1709–1716. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.11.1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuluz J. W., Prado R. J., Dietrich W. D., Schleien C. L., Watson B. D. The effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on infarct volume after reversible focal cerebral ischemia in conscious rats. Stroke. 1993 Dec;24(12):2023–2029. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.12.2023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Choi Y. B., Pan Z. H., Lei S. Z., Chen H. S., Sucher N. J., Loscalzo J., Singel D. J., Stamler J. S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):626–632. doi: 10.1038/364626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrae I. M., Dawson D. A., Norrie J. D., McCulloch J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis: effects on cerebral blood flow and glucose utilisation in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 Nov;13(6):985–992. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrae I. M., Robinson M. J., Graham D. I., Reid J. L., McCulloch J. Endothelin-1-induced reductions in cerebral blood flow: dose dependency, time course, and neuropathological consequences. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 Mar;13(2):276–284. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinski T., Bailey F., Zhang Z. G., Chopp M. Nitric oxide measured by a porphyrinic microsensor in rat brain after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 May;13(3):355–358. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mhairi Macrae I. New models of focal cerebral ischaemia. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;34(4):302–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb05634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Babbedge R. C., Wallace P., Gaffen Z. A., Hart S. L. 7-Nitro indazole, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, exhibits anti-nociceptive activity in the mouse without increasing blood pressure. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):296–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa E., Ginsberg M. D., Dietrich W. D., Duncan R. C., Kraydieh S., Globus M. Y., Busto R. The significance of brain temperature in focal cerebral ischemia: histopathological consequences of middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 May;12(3):380–389. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa E., Huang Z., Moskowitz M. A. L-arginine decreases infarct size caused by middle cerebral arterial occlusion in SHR. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):H1632–H1635. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.5.H1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa E., Rosenblatt S., Moskowitz M. A. L-arginine dilates rat pial arterioles by nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms and increases blood flow during focal cerebral ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):905–907. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuji T., Matsui T., Koide T., Asano T. Blockade of nitric oxide formation by N omega-nitro-L-arginine mitigates ischemic brain edema and subsequent cerebral infarction in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Dec 7;147(2):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90584-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehls D. G., Park C. K., MacCormack A. G., McCulloch J. The effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade with MK-801 upon the relationship between cerebral blood flow and glucose utilisation. Brain Res. 1990 Mar 19;511(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki J. P., Duval D., Poignet H., Scatton B. Nitric oxide mediates neuronal death after focal cerebral ischemia in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 12;204(3):339–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90862-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne K. A., Shigeno T., Balarsky A. M., Ford I., McCulloch J., Teasdale G. M., Graham D. I. Quantitative assessment of early brain damage in a rat model of focal cerebral ischaemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Apr;50(4):402–410. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.4.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. K., Nehls D. G., Graham D. I., Teasdale G. M., McCulloch J. The glutamate antagonist MK-801 reduces focal ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1988 Oct;24(4):543–551. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. K., Nehls D. G., Teasdale G. M., McCulloch J. Effect of the NMDA antagonist MK-801 on local cerebral blood flow in focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Oct;9(5):617–622. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringelstein E. B., Biniek R., Weiller C., Ammeling B., Nolte P. N., Thron A. Type and extent of hemispheric brain infarctions and clinical outcome in early and delayed middle cerebral artery recanalization. Neurology. 1992 Feb;42(2):289–298. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel S., Pinard E., Seylaz J. The acute effects of MK-801 on cerebral blood flow and tissue partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in conscious and alpha-chloralose anaesthetized rats. Neuroscience. 1992;47(4):959–965. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey J., Ritchie I. M., Kelly P. A. Perivascular microapplication of endothelin-1: a new model of focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 Sep;13(5):865–871. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Graham D. I., McCulloch J., Teasdale G. M. Focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat: 1. Description of technique and early neuropathological consequences following middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):53–60. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Gotoh F., Gomi S., Takashima S., Mihara B., Shirai T., Nogawa S., Nagata E. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis induces a significant reduction in local cerebral blood flow in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jun 10;127(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90911-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga T., Sato S., Ohnishi T., Ohnishi S. T. Potentiation of nitric oxide formation following bilateral carotid occlusion and focal cerebral ischemia in the rat: in vivo detection of the nitric oxide radical by electron paramagnetic resonance spin trapping. Brain Res. 1993 Jun 18;614(1-2):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91053-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis C. L., Brazell C., Foster A. C. Plasma and CSF levels of dizocilpine (MK-801) required for neuroprotection in the quinolinate-injected rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 24;196(3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90441-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Golanov E. V., Berger S. B., Reis D. J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis increases focal ischemic infarction in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 Sep;12(5):717–726. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Iadecola C. Nitroprusside improves blood flow and reduces brain damage after focal ischemia. Neuroreport. 1993 May;4(5):559–562. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199305000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Benveniste H., Piantadosi C. A. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase increases extracellular cerebral glutamate concentration after global ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Jul 23;157(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90731-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


