Abstract
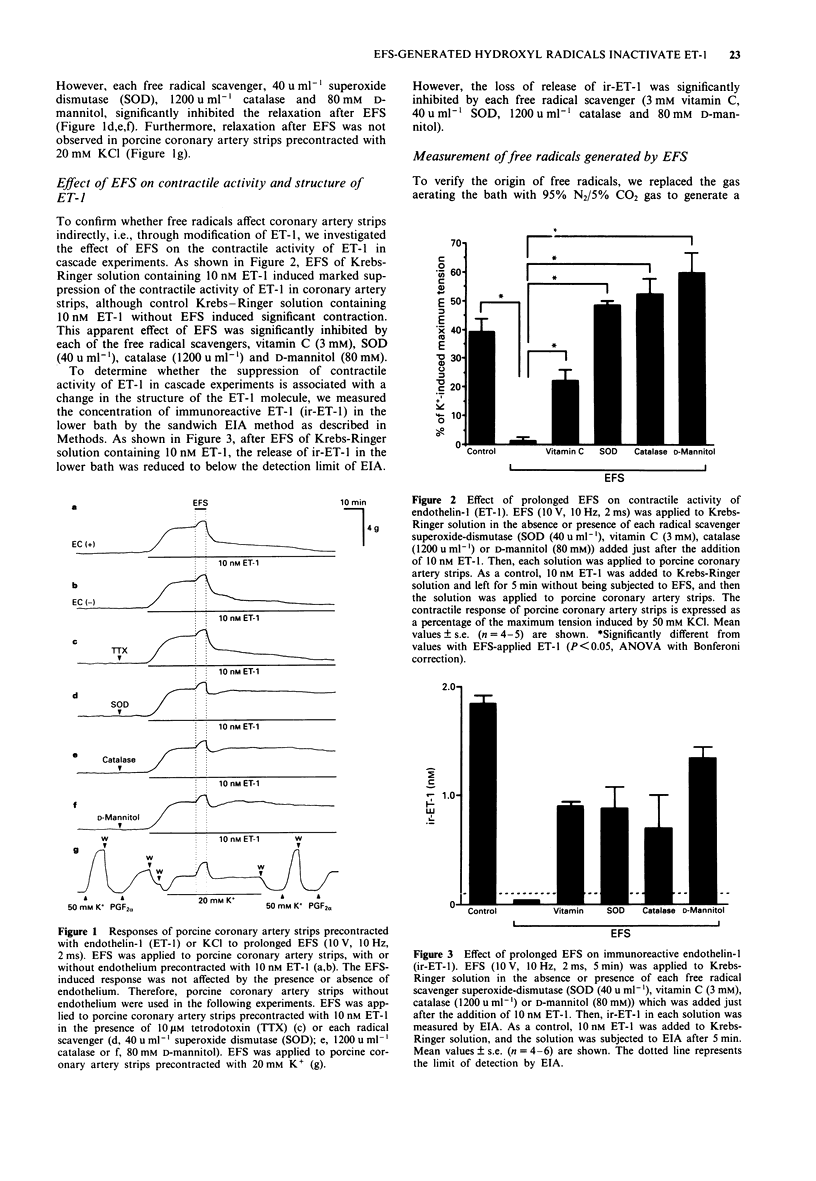
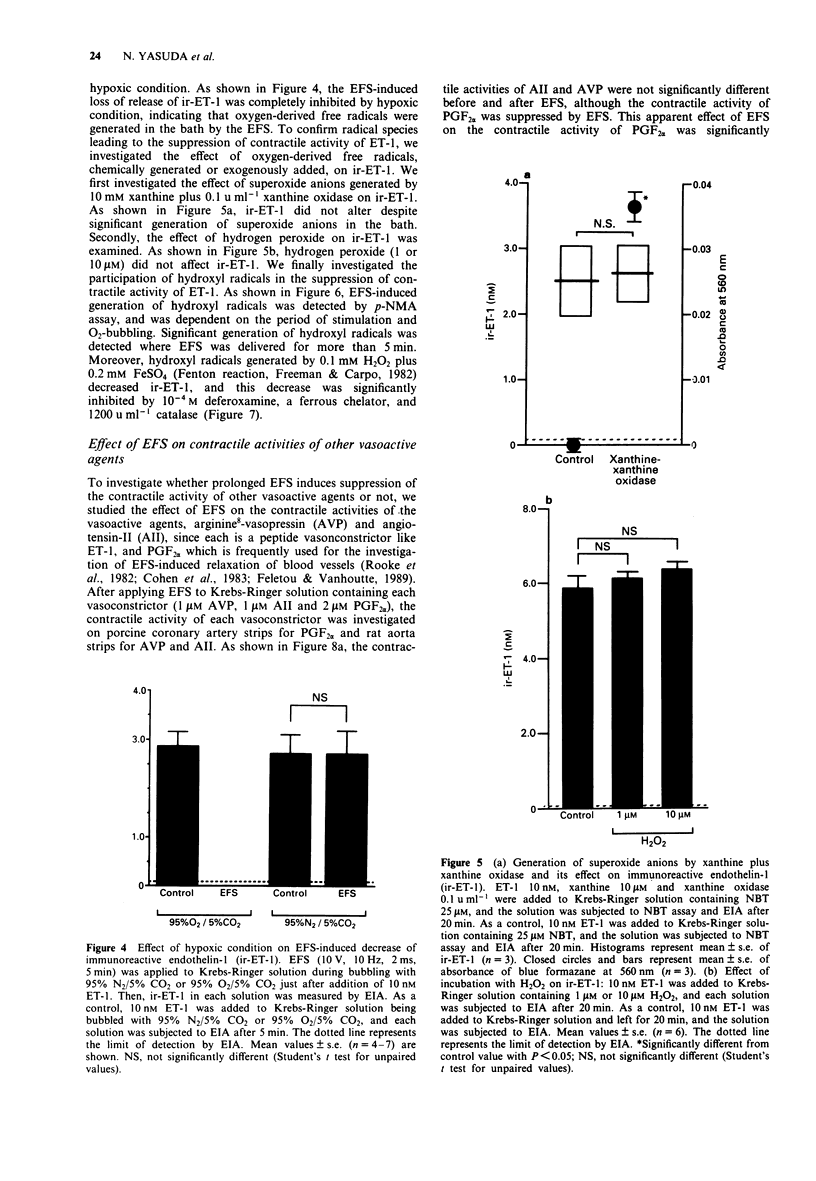
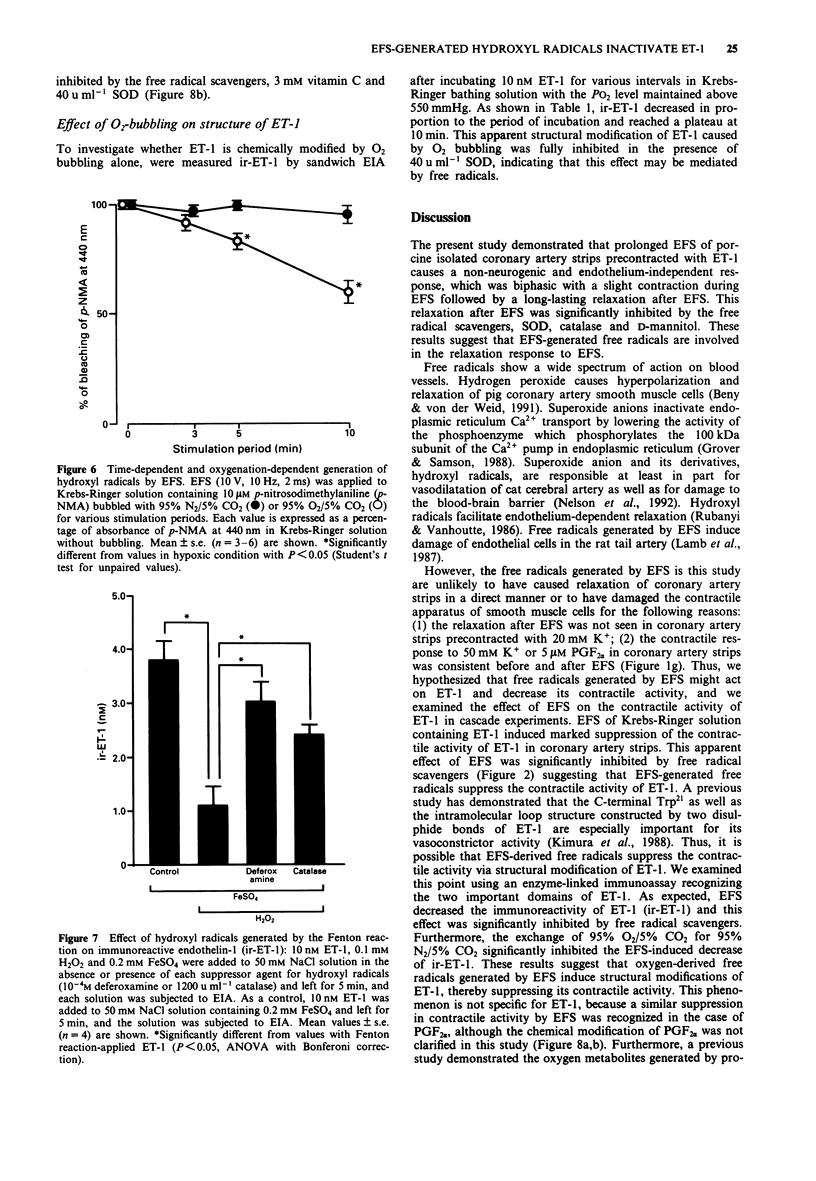
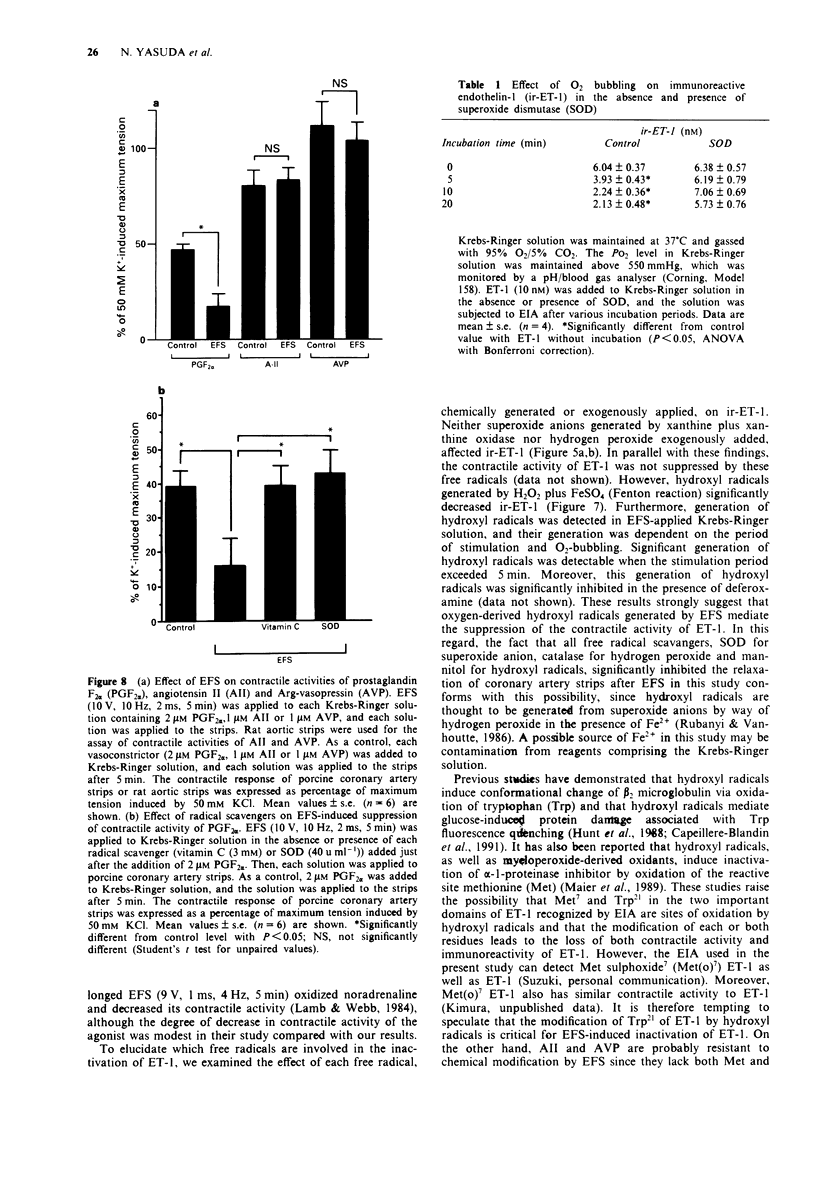
1. Electrical field stimulation (EFS; 10 V, 10 Hz, 2 ms) of porcine coronary artery strips precontracted with 10 nM endothelin-1 (ET-1) for 5 min caused a biphasic response, consisting of a slight contraction during EFS and a marked and irreversible relaxation just after EFS. This irreversible relaxation after EFS has never been investigated. In the present study, we have investigated the mechanism of the relaxation after EFS. 2. The EFS-induced response was not affected by the presence or absence of endothelium and was insensitive to 10 microM tetrodotoxin (TTX). 3. In the presence of free radical scavengers (40 u ml-1 superoxide dismutase (SOD), 1200 u ml-1 catalase or 80 mM D-mannitol), the relaxation after EFS was significantly inhibited. Moreover, relaxation after EFS was not observed in porcine coronary artery strips precontracted with 20 mM KCl. 4. In a cascade experiment, EFS of Krebs-Ringer solution containing 10 nM ET-1 induced marked suppression of the contractile activity of ET-1 in porcine coronary artery strips, which was in accord with the observed decrease in release of immunoreactive ET-1 (ir-ET-1). This effect of EFS was significantly inhibited by each of the free radical scavengers, 3 mM vitamin C, 40 u ml-1 SOD, 1200 u ml-1 catalase and 80 mM D-mannitol. 5. The exchange of 95% O2/5% CO2 gas for 95% N2/5% CO2 gas significantly inhibited the EFS-induced decrease in release of ir-ET-1.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auch-Schwelk W., Katusic Z. S., Vanhoutte P. M. Contractions to oxygen-derived free radicals are augmented in aorta of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1989 Jun;13(6 Pt 2):859–864. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.6.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aumelas A., Sakarellos C., Lintner K., Fermandjian S., Khosla M. C., Smeby R. R., Bumpus F. M. Studies on angiotensin II and analogs: impact of substitution in position 8 on conformation and activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1881–1885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balwierczak J. L., Hopkins M. F., Savage P., Martin L. L., Jeng A. Y. Decrease in immunoreactivity and vasoactivity of endothelin-1 after exposure to oxygen. Biochem Int. 1992 Sep;27(6):1111–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp C., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bors W., Michel C., Saran M. On the nature of biochemically generated hydroxyl radicals. Studies using the bleaching of p-nitrosodimethylaniline as a direct assay method. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):621–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buga G. M., Ignarro L. J. Electrical field stimulation causes endothelium-dependent and nitric oxide-mediated relaxation of pulmonary artery. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):H973–H979. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.4.H973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bény J. L., von der Weid P. Y. Hydrogen peroxide: an endogenous smooth muscle cell hyperpolarizing factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):378–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90935-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capeillere-Blandin C., Delaveau T., Descamps-Latscha B. Structural modifications of human beta 2 microglobulin treated with oxygen-derived radicals. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):175–182. doi: 10.1042/bj2770175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. A., Shepherd J. T., Vanhoutte P. M. Prejunctional and postjunctional actions of endogenous norepinephrine at the sympathetic neuroeffector junction in canine coronary arteries. Circ Res. 1983 Jan;52(1):16–25. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feletou M., Vanhoutte P. M. Relaxation of canine coronary artery to electrical stimulation: limited role of free radicals. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):H884–H889. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.4.H884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feletou M., Vanhoutte P. M. Tetrodotoxin-insensitive relaxation of coronary arterial smooth muscle to electrical stimulation: possible involvement of a dopaminergic mechanism. Blood Vessels. 1989;26(4):213–227. doi: 10.1159/000158769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):412–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori A., Saito A., Kimura S., Watanabe T., Uchiyama Y., Kawasaki H., Goto K. Neurogenic vasodilation and release of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) from perivascular nerves in the rat mesenteric artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1391–1398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg B., Rhoden K., Barnes P. J. Activated oxygen molecules generated by electrical stimulation affect vascular smooth muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1986 Sep;18(9):975–981. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(86)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover A. K., Samson S. E. Effect of superoxide radical on Ca2+ pumps of coronary artery. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):C297–C303. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.3.C297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Yoshimi H., Takaichi S., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Binding and receptor down-regulation of a novel vasoconstrictor endothelin in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. V., Dean R. T., Wolff S. P. Hydroxyl radical production and autoxidative glycosylation. Glucose autoxidation as the cause of protein damage in the experimental glycation model of diabetes mellitus and ageing. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):205–212. doi: 10.1042/bj2560205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S., Quillan M. Cholinergic contraction to field stimulation in coronary arteries of cattle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jun;249(3):785–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuya Y., Ishikawa T., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Mechanism of contraction to endothelin in isolated porcine coronary artery. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):H1828–H1835. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.6.H1828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuya Y., Takuwa Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Goto K. A pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism of endothelin action in porcine coronary artery smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):456–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12767.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Kasuya Y., Sawamura T., Shinmi O., Sugita Y., Yanagisawa M., Goto K., Masaki T. Structure-activity relationships of endothelin: importance of the C-terminal moiety. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1182–1186. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80757-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb F. S., Webb R. C. Vascular effects of free radicals generated by electrical stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):H709–H714. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.247.5.H709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier K. L., Matejkova E., Hinze H., Leuschel L., Weber H., Beck-Speier I. Different selectivities of oxidants during oxidation of methionine residues in the alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80725-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann W. A., Stassen F., Huffman W., Kinter L. B. Mechanism of action and structural requirements of vasopressin analog inhibition of transepithelial water flux in toad urinary bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):401–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch J., Edvinsson L. Cerebral circulatory and metabolic effects of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):H449–H456. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.238.4.H449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minotti G., Aust S. D. The requirement for iron (III) in the initiation of lipid peroxidation by iron (II) and hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1098–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. W., Wei E. P., Povlishock J. T., Kontos H. A., Moskowitz M. A. Oxygen radicals in cerebral ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):H1356–H1362. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.5.H1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke T., Cohen R. A., Verbeuren T. J., Vanhoutte P. M. Non-neurogenic inhibitory effect of electrical impulses in isolated canine coronary arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 May 21;80(2-3):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubanyi G. M., Vanhoutte P. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals, endothelium, and responsiveness of vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):H815–H821. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.5.H815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Molecular characterization of endothelin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Matsumoto H., Kitada C., Masaki T., Fujino M. A sensitive sandwich-enzyme immunoassay for human endothelin. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Mar 31;118(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N. Relaxant responses to transmural stimulation and nicotine of dog and monkey cerebral arteries. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):H145–H153. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.2.H145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Riper D. A., Bevan J. A. Electrical field stimulation-mediated relaxation of rabbit middle cerebral artery. Evidence of a cholinergic endothelium-dependent component. Circ Res. 1992 Jun;70(6):1104–1112. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.6.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A., Hirsch D. J., Glatt C. E., Ronnett G. V., Snyder S. H. Carbon monoxide: a putative neural messenger. Science. 1993 Jan 15;259(5093):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.7678352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


