Abstract
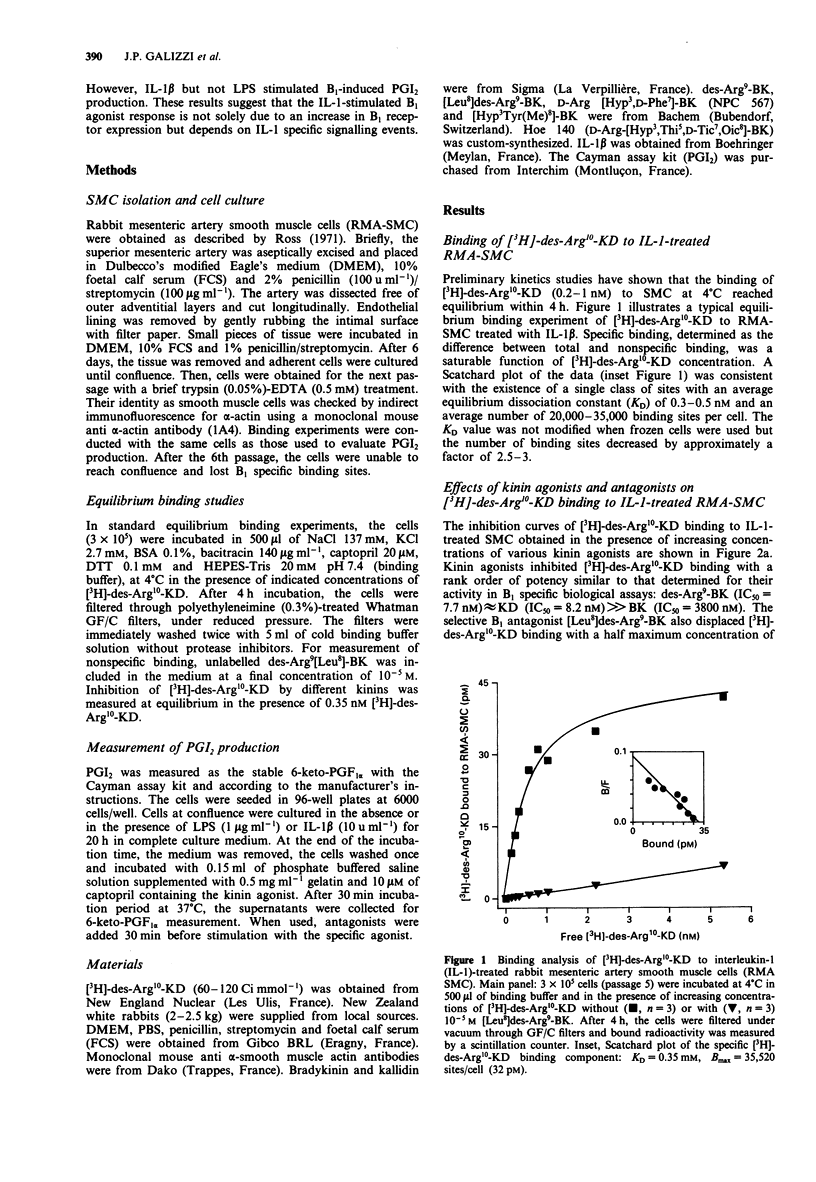
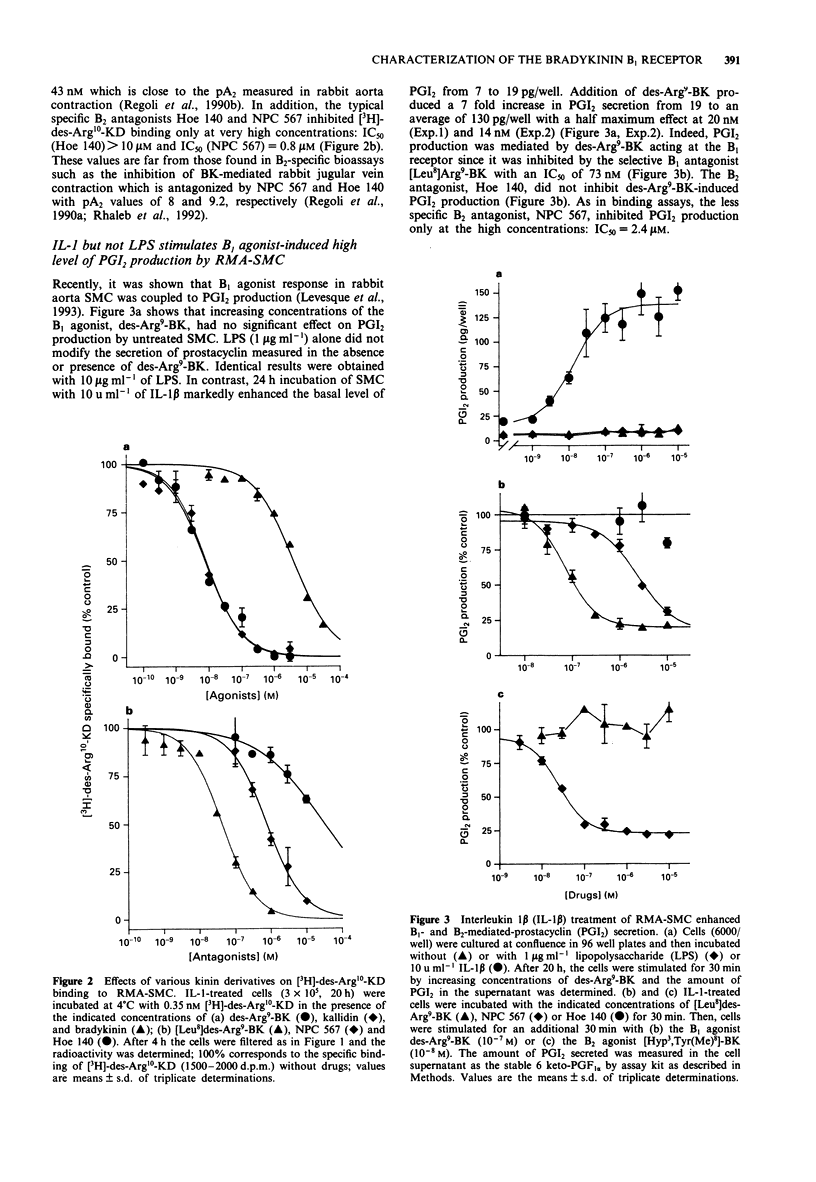
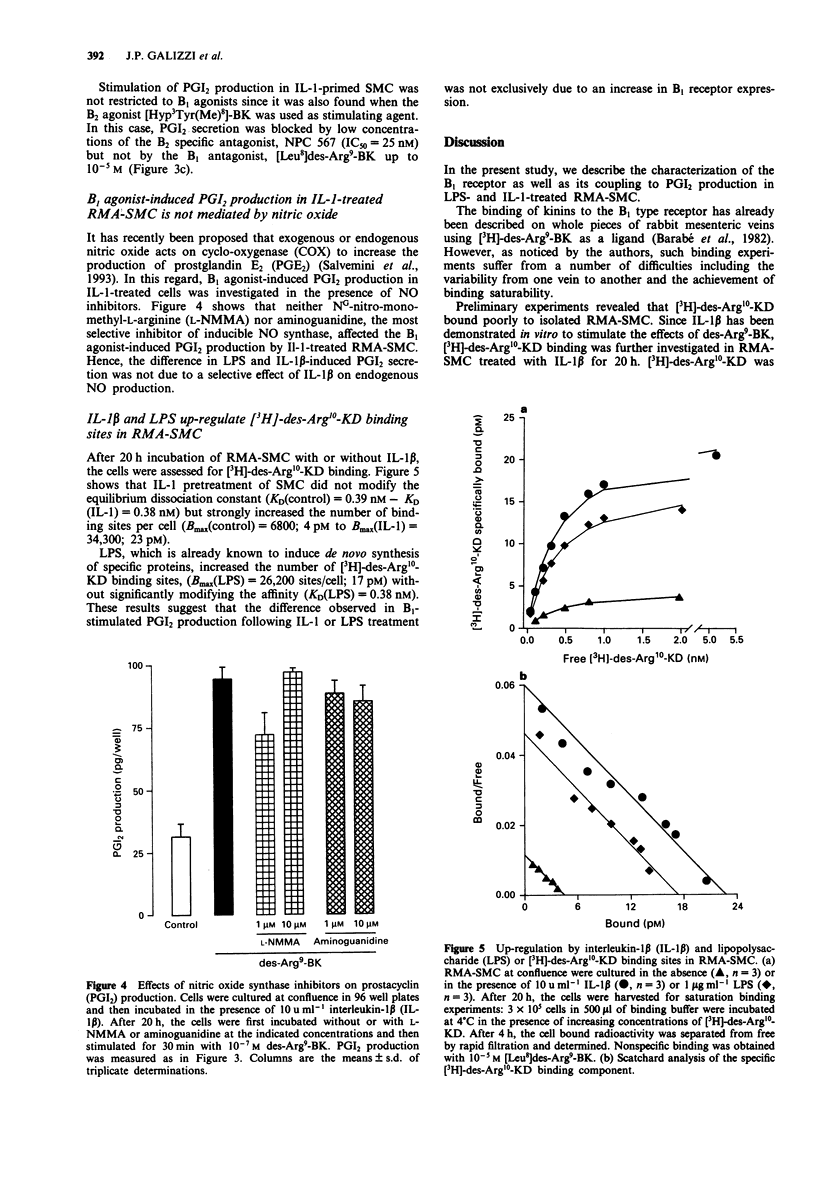
1. Binding of the specific bradykinin B1 receptor agonist, [3H]-des-Arg10-kallidin (-KD) was investigated in smooth muscle cells (SMC) isolated from rabbit mesenteric arteries (RMA). 2. [3H]-des-Arg10-KD specifically bound to interleukin-1 (IL-1)-treated RMA-SMC in a saturable fashion with an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of 0.3-0.5 nM. The number of binding sites per cell was 20,000-35,000. Kinins inhibited [3H]-des-Arg10-KD binding to RMA-SMC with an order of potency very similar to that observed in typical B1 specific bioassays: des-Arg9-bradykinin (BK) approximately KD >> BK. Furthermore, the B1 receptor antagonist [Leu8]des-Arg9-BK inhibited [3H]-des-Arg10-KD binding with an IC50 of 43 nM as expected for its effect at B1 receptors. The B2 receptor antagonists, NPC 567 and Hoe 140 only affected [3H]-des-Arg10-KD binding at very high concentrations (IC50 = 0.8 microM and IC50 > 10 microM, respectively). 3. Des-Arg9-BK (B1 agonist) and [Hyp3]Tyr(Me)8-BK (B2 agonist) did not induce prostacyclin (PGI2) production by RMA-SMC. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment of the cells did not affect the B1 agonist response whereas IL-1 beta treatment produced a 7 fold increase in des-Arg9-BK-stimulated PGI2 production. IL-1 beta also stimulated the response to B2 agonists. 4. Des-Arg9-BK-induced PGI2 secretion in IL-1-primed RMA-SMC was mediated by B1 receptors since it was inhibited by [Leu8]des-Arg9-BK (IC50 = 56-73 nM) but not by Hoe 140.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barabé J., Babiuk C., Regoli D. Binding of [3H]des-Arg9-BK to rabbit anterior mesenteric vein. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;60(12):1551–1555. doi: 10.1139/y82-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschcov P., Paiva A. C., Paiva T. B., Shimuta S. I. Further evidence for the existence of two receptor sites for bradykinin responsible for the diphasic effect in the rat isolated duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthillier J., Deblois D., Marceau F. Studies on the induction of pharmacological responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;92(2):257–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Clark B. D., Wingfield P., Schmeissner U., Losberger C., Dinarello C. A., Shaw A. R. Rabbit IL-1. Cloning, expression, biologic properties, and transcription during endotoxemia. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill L., Ward P. E. Relaxation of isolated mesenteric arteries by des-Arg9-bradykinin stimulation of B1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couture R., Mizrahi J., Regoli D., Devroede G. Peptides and the human colon: an in vitro pharmacological study. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;59(9):957–964. doi: 10.1139/y81-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deblois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Effect of glucocorticoids, monokines and growth factors on the spontaneously developing responses of the rabbit isolated aorta to des-Arg9-bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;93(4):969–977. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deblois D., Marceau F. The ability of des-Arg9-bradykinin to relax rabbit isolated mesenteric arteries is acquired during in vitro incubation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 6;142(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90664-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., deBlois D., Marceau F. Hypotensive effects of Lys-des-Arg9-bradykinin and metabolically protected agonists of B1 receptors for kinins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):997–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Perkins M. Bradykinin and inflammatory pain. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Mar;16(3):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M. Biochemical and molecular pharmacology of kinin receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:511–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.002455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib A., Créminon C., Frobert Y., Grassi J., Pradelles P., Maclouf J. Demonstration of an inducible cyclooxygenase in human endothelial cells using antibodies raised against the carboxyl-terminal region of the cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23448–23454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque L., Drapeau G., Grose J. H., Rioux F., Marceau F. Vascular mode of action of kinin B1 receptors and development of a cellular model for the investigation of these receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1254–1262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Ordovas J. M., Auger K. R., Robbins A. H., Birinyi L. K., Dinarello C. A. Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor induce interleukin-1 gene expression in adult human vascular endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1986 Aug;124(2):179–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Ordovas J. M., Birinyi L. K., Auger K. R., Dinarello C. A. Inducible interleukin-1 gene expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1432–1438. doi: 10.1172/JCI112732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Barabé J., St-Pierre S., Regoli D. Kinin receptors in experimental inflammation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 May;58(5):536–542. doi: 10.1139/y80-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Lussier A., St-Pierre S. Selective induction of cardiovascular responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin by bacterial endotoxin. Pharmacology. 1984;29(2):70–74. doi: 10.1159/000137994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Banion M. K., Winn V. D., Young D. A. cDNA cloning and functional activity of a glucocorticoid-regulated inflammatory cyclooxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4888–4892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruneau D., Bélichard P. Induction of bradykinin B1 receptor-mediated relaxation in the isolated rabbit carotid artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 3;239(1-3):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90976-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D. C., Marceau F., Lavigne J. Induction of beta 1-receptors for kinins in the rabbit by a bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90391-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Drapeau G. New selective bradykinin receptor antagonists and bradykinin B2 receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90067-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Rhaleb N. E., Drapeau G., Dion S. Kinin receptor subtypes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 6):S30–S38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Barabé J., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Receptors for kinins in isolated arterial vessels of dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 29;162(3):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Regoli D., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (HOE 140: D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Qic8]bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90661-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The smooth muscle cell. II. Growth of smooth muscle in culture and formation of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):172–186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Misko T. P., Masferrer J. L., Seibert K., Currie M. G., Needleman P. Nitric oxide activates cyclooxygenase enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7240–7244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneck K. A., Hess J. F., Stonesifer G. Y., Ransom R. W. Bradykinin B1 receptors in rabbit aorta smooth muscle cells in culture. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb 15;266(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabó C., Wu C. C., Gross S. S., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Interleukin-1 contributes to the induction of nitric oxide synthase by endotoxin in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 30;250(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90634-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiffany C. W., Burch R. M. Bradykinin stimulates tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 release from macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropea M. M., Gummelt D., Herzig M. S., Leeb-Lundberg L. M. B1 and B2 kinin receptors on cultured rabbit superior mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells: receptor-specific stimulation of inositol phosphate formation and arachidonic acid release by des-Arg9-bradykinin and bradykinin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):930–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBlois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Pharmacological modulation of the up-regulated responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin in vivo and in vitro. Immunopharmacology. 1989 May-Jun;17(3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(89)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBlois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Pulse exposure to protein synthesis inhibitors enhances vascular responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin: possible role of interleukin-1. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1057–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


