Abstract
1. The involvement of nitric oxide in the acute inhibitory effects of low doses of endotoxin, following intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) or intravenous (i.v.) administration, on gastric acid secretion stimulated by distension or i.v. infusion of pentagastrin has been investigated in the continuously perfused stomach of the anaesthetized rat. 2. The i.c.v. administration of E. coli endotoxin (800 ng kg-1) abolished the acid secretory response induced by gastric distension (20 cm water intragastric pressure) within 30 min of administration. 3. By contrast, submaximal rates of acid secretion induced by i.v. infusion of pentagastrin (8 micrograms kg-1 h-1) were not inhibited by i.c.v. administration of endotoxin (800 ng kg-1). 4. Prior i.c.v. administration of the NO synthase inhibitor, NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 800 micrograms kg-1) restored the acid secretory responses to distension in rats treated with endotoxin (i.c.v.). 5. Likewise, i.v. administration of endotoxin (5 micrograms kg-1) abolished the acid secretory response induced by gastric distension within 30 min of administration. Prior i.c.v. injection of L-NAME (800 micrograms kg-1) or its i.v. administration (10 mg kg-1) restored acid secretory responses in rats receiving i.v. endotoxin. 6. The reversal by L-NAME (i.v.) of the acid inhibitory effects of endotoxin (i.v.) was prevented by L-arginine (12 mg kg-1, i.c.v. or 100 mg kg-1, i.v.), but not by its enantiomer D-arginine. 7. The present results imply the existence of an acute response to endotoxin involving NO synthesis in the brain.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
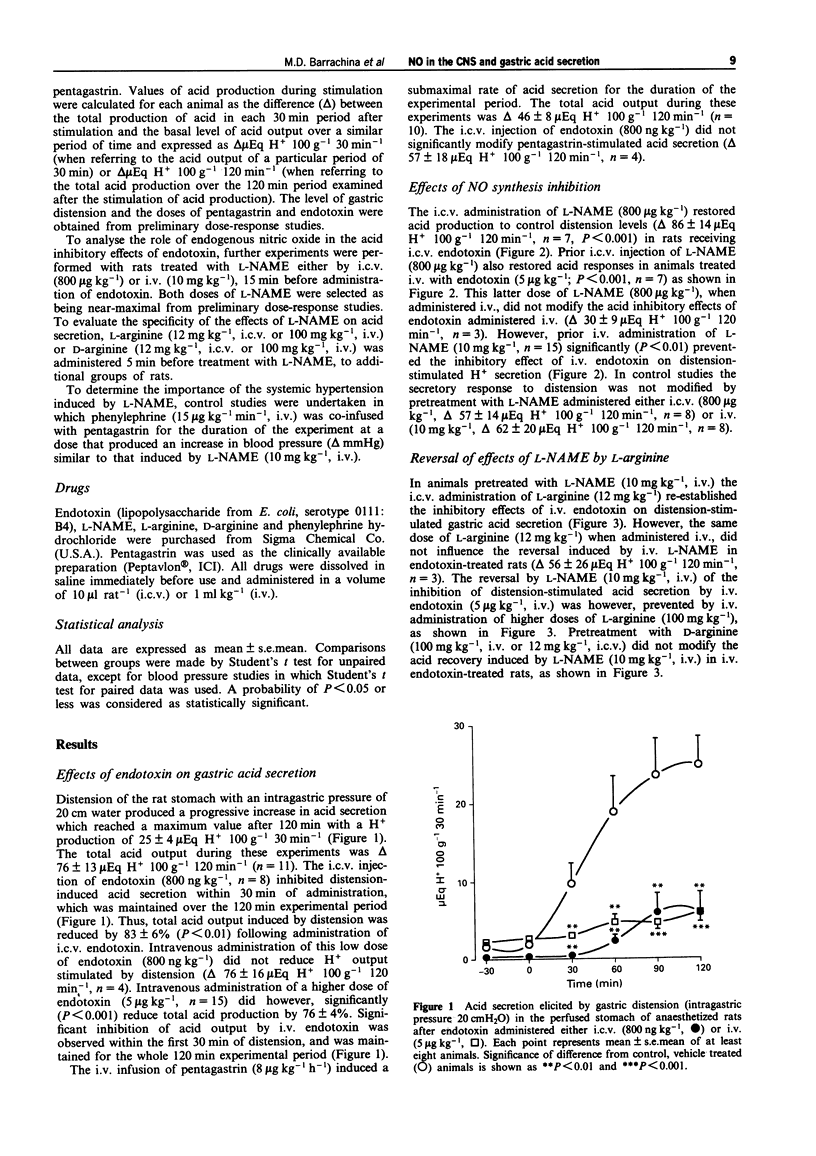
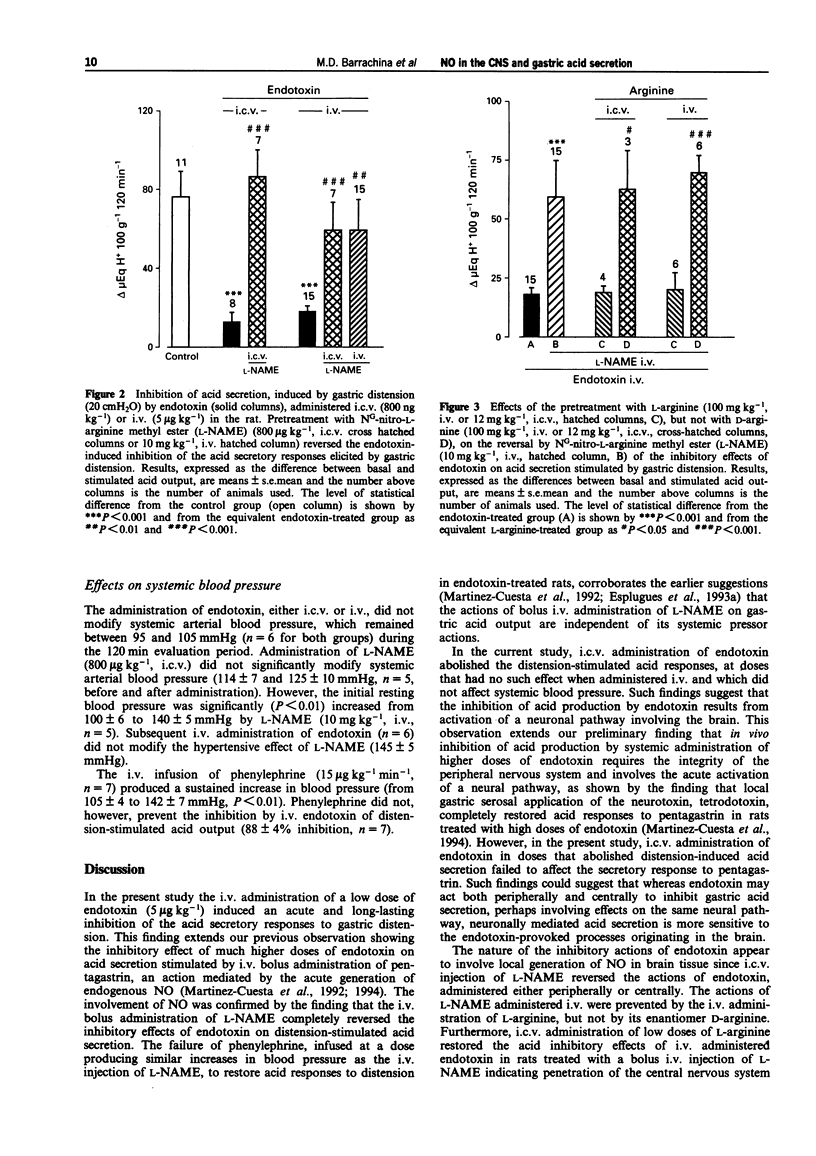


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Mülsch A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81445-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esplugues J. V., Barrachina M. D., Calatayud S., Pique J. M., Whittle B. J. Nitric oxide mediates the inhibition by interleukin-1 beta of pentagastrin-stimulated rat gastric acid secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):9–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esplugues J. V., Barrachina M. D., Esplugues J. Modulation by peripheral opioids of basal and distension-stimulated gastric acid secretion in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esplugues J. V., Ramos E. G., Gil L., Esplugues J. Influence of capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurones on the acid secretory responses of the rat stomach in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):491–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Calmodulin-dependent endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase activity is present in the particulate and cytosolic fractions of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1788–1792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Garthwaite G., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. NMDA receptor activation induces nitric oxide synthesis from arginine in rat brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 17;172(4-5):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z., Rachlin E. M. Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julou-Schaeffer G., Gray G. A., Fleming I., Schott C., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Loss of vascular responsiveness induced by endotoxin involves L-arginine pathway. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):H1038–H1043. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.4.H1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Gross S. S., Jubran A., Adams J., Griffith O. W., Levi R., Lodato R. F. NG-methyl-L-arginine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced hypotension: implications for the involvement of nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3629–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: a transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5159–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Salter M., Brooks S. L., Moncada S. Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids inhibit the induction by endotoxin of nitric oxide synthase in the lung, liver and aorta of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1042–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Cuesta M. A., Barrachina M. D., Piqué J. M., Whittle B. J., Esplugues J. V. The role of nitric oxide and platelet-activating factor in the inhibition by endotoxin of pentagastrin-stimulated gastric acid secretion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug 6;218(2-3):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. A., Sheng H., Förstermann U., Murad F. Characterization of nitric oxide synthases in non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerve containing tissue from the rat anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):289–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):2002–2012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols K., Staines W., Krantis A. Nitric oxide synthase distribution in the rat intestine: a histochemical analysis. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1651–1661. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91060-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida K., Harrison D. G., Navas J. P., Fisher A. A., Dockery S. P., Uematsu M., Nerem R. M., Alexander R. W., Murphy T. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of the constitutive bovine aortic endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2092–2096. doi: 10.1172/JCI116092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M., Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Widespread tissue distribution, species distribution and changes in activity of Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent nitric oxide synthases. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81123-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Korbut R., Anggård E., Vane J. Immediate release of a nitric oxide-like factor from bovine aortic endothelial cells by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Ward S. M. Nitric oxide as a mediator of nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurotransmission. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):G379–G392. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.3.G379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Radomski M. W., Moncada S. Nitric oxide mediates the vascular actions of cytokines in septic shock. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;22(6):438–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1992.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Vane J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis reduces the hypotension induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in the rat in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 17;182(3):591–595. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90062-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J. Thirteenth Gaddum Memorial Lecture. Neuronal and endothelium-derived mediators in the modulation of the gastric microcirculation: integrity in the balance. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):3–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


