Abstract
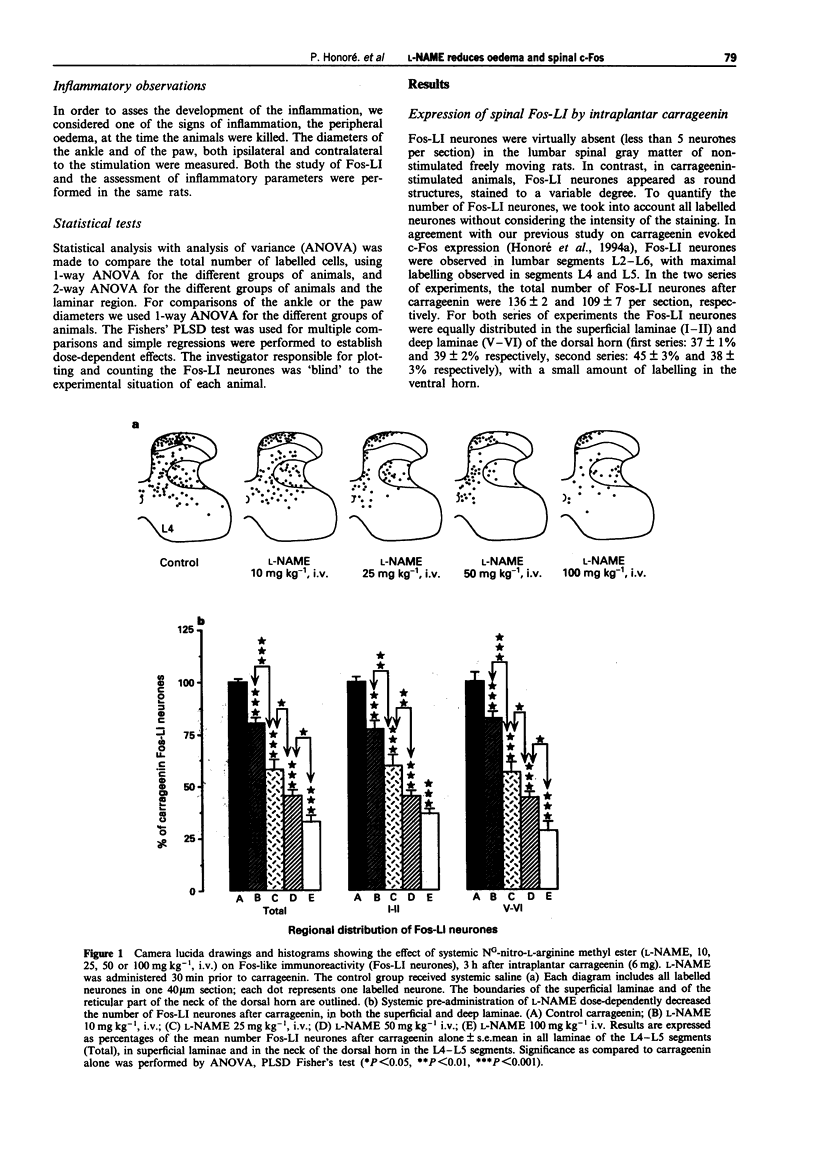
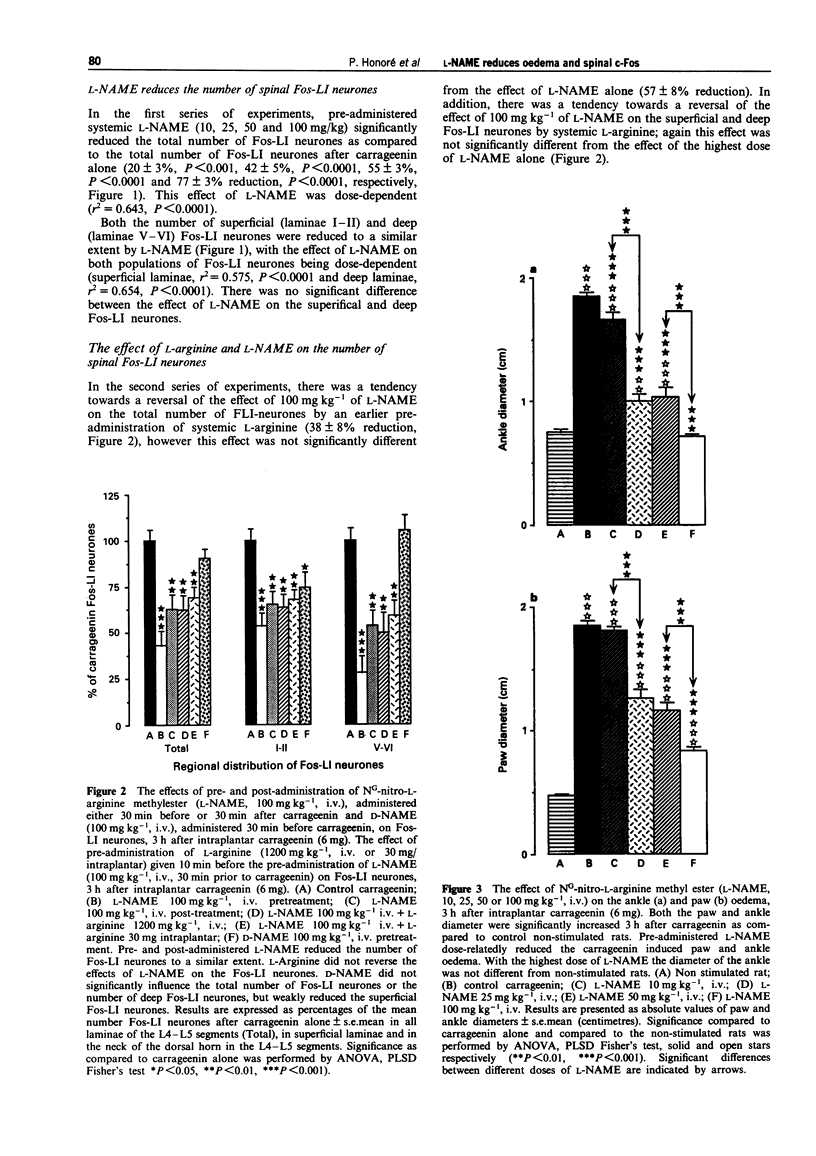
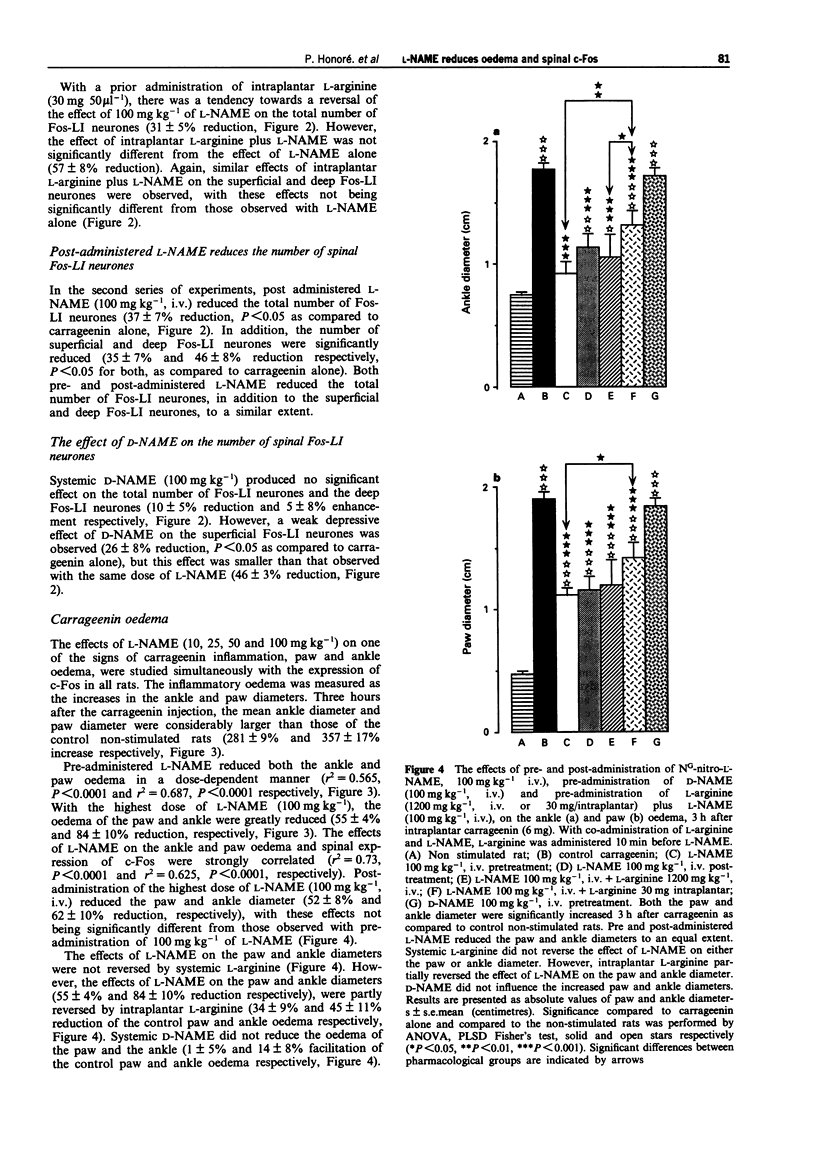
1. Three hours after intraplantar carrageenin (6 mg/150 microliters of saline) Fos-like immunoreactivity (Fos-LI) was mainly observed in L4 and L5 segments of the dorsal horn. Both superficial (I-II) and deep laminae (V-VI) neurones were labelled. 2. We have studied the effect of systemic administration of a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) on carrageenin evoked c-Fos expression and thus the contribution of nitric oxide to this expression. 3. Pre-administration of L-NAME (10, 25, 50, 100 mg kg-1, i.v.) dose-dependently reduced the number of superificial and deep laminae Fos-LI neurones, 100 mg kg-1 produced a 63 +/- 2% and 72 +/- 4% reduction of Fos-LI neurones respectively, P < 0.0001 for both superficial and deep neurones. 4. Pre-administered L-NAME dose-relatedly reduced the carrageenin-evoked paw and ankle oedema, with 100 mg kg-1 of L-NAME resulting in a 74 +/- 2% and 103 +/- 2% reduction respectively. 5. Post-administration of L-NAME (10 mg kg-1, i.v.) reduced the number of superficial and deep laminae Fos-LI neurones (65 +/- 7% and 53 +/- 8% reduction respectively, P < 0.01 for both superficial and deep neurones). 6. Post-administered L-NAME reduced both the paw and ankle oedema (52 +/- 8% and 62 +/- 10% reduction respectively, P < 0.0001 for both paw and ankle).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimi Y., Fujimura M., Vincent S. R., Kimura H. Localization of NADPH-diaphorase-containing neurons in sensory ganglia of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Apr 15;306(3):382–392. doi: 10.1002/cne.903060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson J. M., Chaouch A. Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jan;67(1):67–186. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draisci G., Iadarola M. J. Temporal analysis of increases in c-fos, preprodynorphin and preproenkephalin mRNAs in rat spinal cord. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Jul;6(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubner R., Ruda M. A. Activity-dependent neuronal plasticity following tissue injury and inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Mar;15(3):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Lorenzetti B. B., Poole S. Bradykinin initiates cytokine-mediated inflammatory hyperalgesia. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1227–1231. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Kemp P. A., Bennett T. Regional and cardiac haemodynamic effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester in conscious, Long Evans rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):625–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J. E., Dickenson A. H., Schachter M. Electrophysiological evidence for a role of nitric oxide in prolonged chemical nociception in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1992 Mar;31(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(92)90175-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herdegen T., Kovary K., Leah J., Bravo R. Specific temporal and spatial distribution of JUN, FOS, and KROX-24 proteins in spinal neurons following noxious transsynaptic stimulation. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Nov 1;313(1):178–191. doi: 10.1002/cne.903130113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herdegen T., Rüdiger S., Mayer B., Bravo R., Zimmermann M. Expression of nitric oxide synthase and colocalisation with Jun, Fos and Krox transcription factors in spinal cord neurons following noxious stimulation of the rat hindpaw. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Mar;22(1-4):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. R., Williams T. J., Brain S. D. Evidence that endogenous nitric oxide modulates oedema formation induced by substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):481–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94184-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ialenti A., Ianaro A., Moncada S., Di Rosa M. Modulation of acute inflammation by endogenous nitric oxide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90526-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris J., Costello A., Dubner R., Hargreaves K. M. Opiates suppress carrageenan-induced edema and hyperthermia at doses that inhibit hyperalgesia. Pain. 1990 Oct;43(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)90054-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil Z., Helme R. D. The quantitative contribution of nitric oxide and sensory nerves to bradykinin-induced inflammation in rat skin microvasculature. Brain Res. 1992 Aug 28;589(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91167-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher L., Anton F., Reeh P. W., Handwerker H. O. The effect of carrageenan-induced inflammation on the sensitivity of unmyelinated skin nociceptors in the rat. Pain. 1987 Jun;29(3):363–373. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Wilcox G. L., Beitz A. J. Nitric oxide mediates Fos expression in the spinal cord induced by mechanical noxious stimulation. Neuroreport. 1992 Oct;3(10):841–844. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199210000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippe I. T., Stabentheiner A., Holzer P. Participation of nitric oxide in the mustard oil-induced neurogenic inflammation of the rat paw skin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 23;232(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90735-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg A. B., Yaksh T. L. Spinal nitric oxide synthesis inhibition blocks NMDA-induced thermal hyperalgesia and produces antinociception in the formalin test in rats. Pain. 1993 Sep;54(3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(93)90028-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller S. T., Cummings C. P., Traub R. J., Gebhart G. F. The role of nitric oxide in the development and maintenance of the hyperalgesia produced by intraplantar injection of carrageenan in the rat. Neuroscience. 1994 May;60(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller S. T., Gebhart G. F. Nitric oxide (NO) and nociceptive processing in the spinal cord. Pain. 1993 Feb;52(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(93)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molander C., Xu Q., Grant G. The cytoarchitectonic organization of the spinal cord in the rat. I. The lower thoracic and lumbosacral cord. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Nov 20;230(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/cne.902300112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Babbedge R. C., Wallace P., Gaffen Z. A., Hart S. L. 7-Nitro indazole, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, exhibits anti-nociceptive activity in the mouse without increasing blood pressure. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):296–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Oluyomi A. O., Babbedge R. C., Wallace P., Hart S. L. L-NG-nitro arginine methyl ester exhibits antinociceptive activity in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):198–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi K., Dubner R., Ruda M. A. Preproenkephalin mRNA in spinal dorsal horn neurons is induced by peripheral inflammation and is co-localized with Fos and Fos-related proteins. Neuroscience. 1992;46(3):561–570. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90144-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi K., Kowalski K., Traub R., Solodkin A., Iadarola M. J., Ruda M. A. Dynorphin expression and Fos-like immunoreactivity following inflammation induced hyperalgesia are colocalized in spinal cord neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jun;10(3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan V., Henry J. L. L-NAME blocks responses to NMDA, substance P and noxious cutaneous stimuli in cat dorsal horn. Neuroreport. 1993 Mar;4(3):323–326. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199303000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito S., Kidd G. J., Trapp B. D., Dawson T. M., Bredt D. S., Wilson D. A., Traystman R. J., Snyder S. H., Hanley D. F. Rat spinal cord neurons contain nitric oxide synthase. Neuroscience. 1994 Mar;59(2):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90608-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira M. M., Williams T. J., Hellewell P. G. Role of prostaglandins and nitric oxide in acute inflammatory reactions in guinea-pig skin. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1515–1521. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13994.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. J., Solodkin A., Gebhart G. F. NADPH-diaphorase histochemistry provides evidence for a bilateral, somatotopically inappropriate response to unilateral hindpaw inflammation in the rat. Brain Res. 1994 May 30;647(1):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91405-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Mitchell J. A., Appleton I., Tomlinson A., Bishop-Bailey D., Croxtall J., Willoughby D. A. Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric-oxide synthase in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. A., RISLEY E. A., NUSS G. W. Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for antiiflammatory drugs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:544–547. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Shimoyama N., Mizuguchi T. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor blocks spinal sensitization induced by formalin injection into the rat paw. Anesth Analg. 1993 Nov;77(5):886–890. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199311000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Verge V., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Ju G., Bredt D., Synder S. H., Hökfelt T. Nitric oxide synthase-like immunoreactivity in lumbar dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord of rat and monkey and effect of peripheral axotomy. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Sep 22;335(4):563–575. doi: 10.1002/cne.903350408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Tölle T. R. The pharmacology of pain signalling. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Aug;3(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


