Abstract
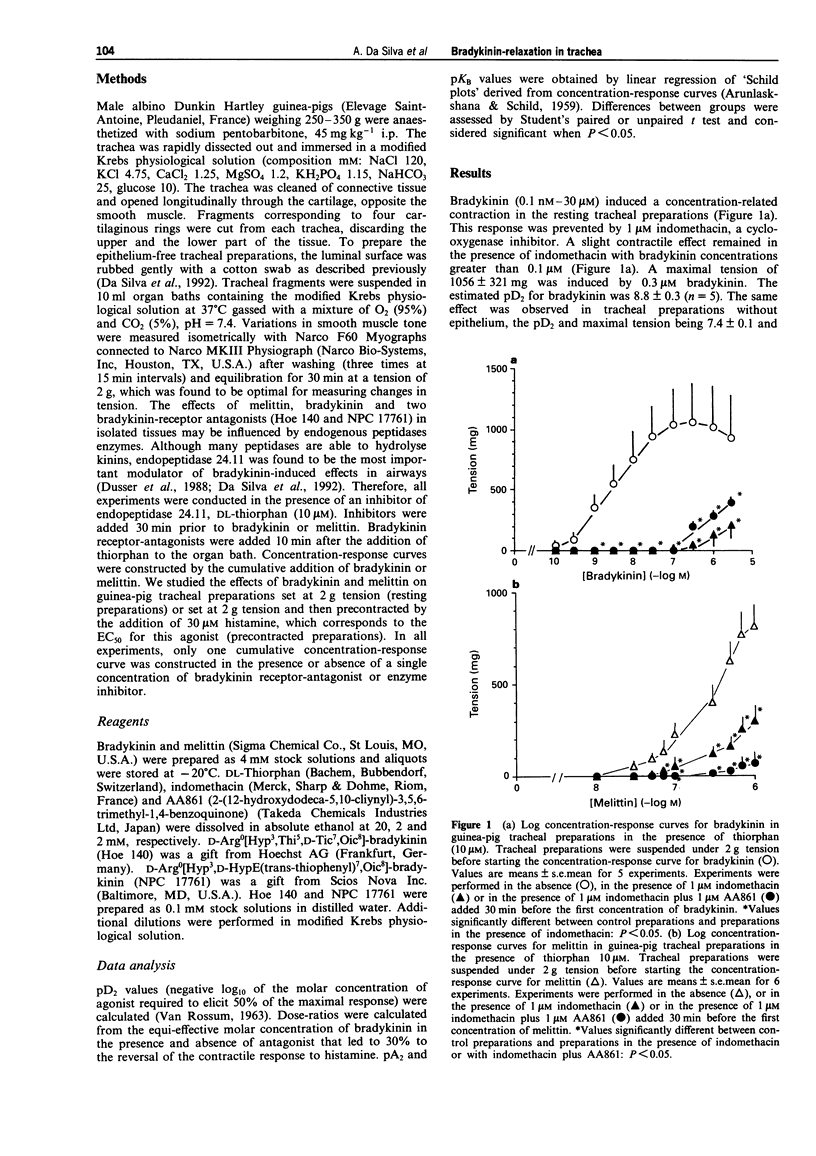
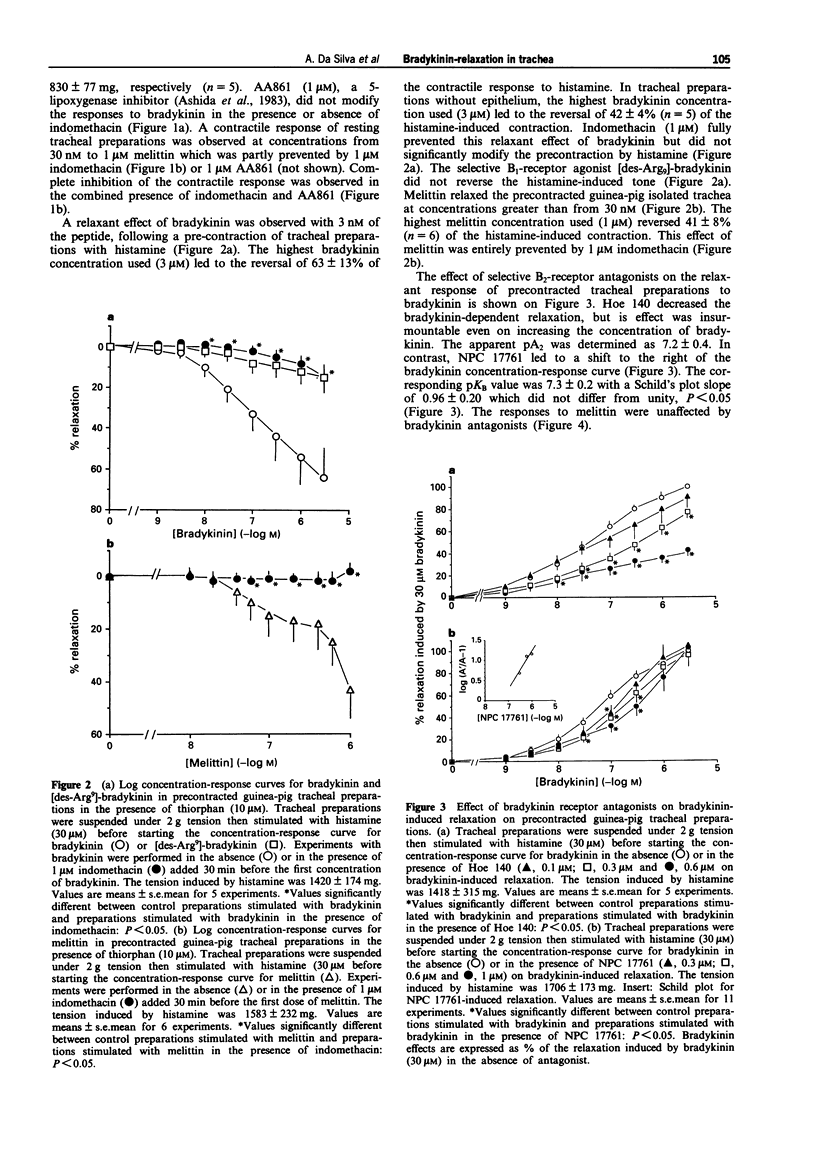
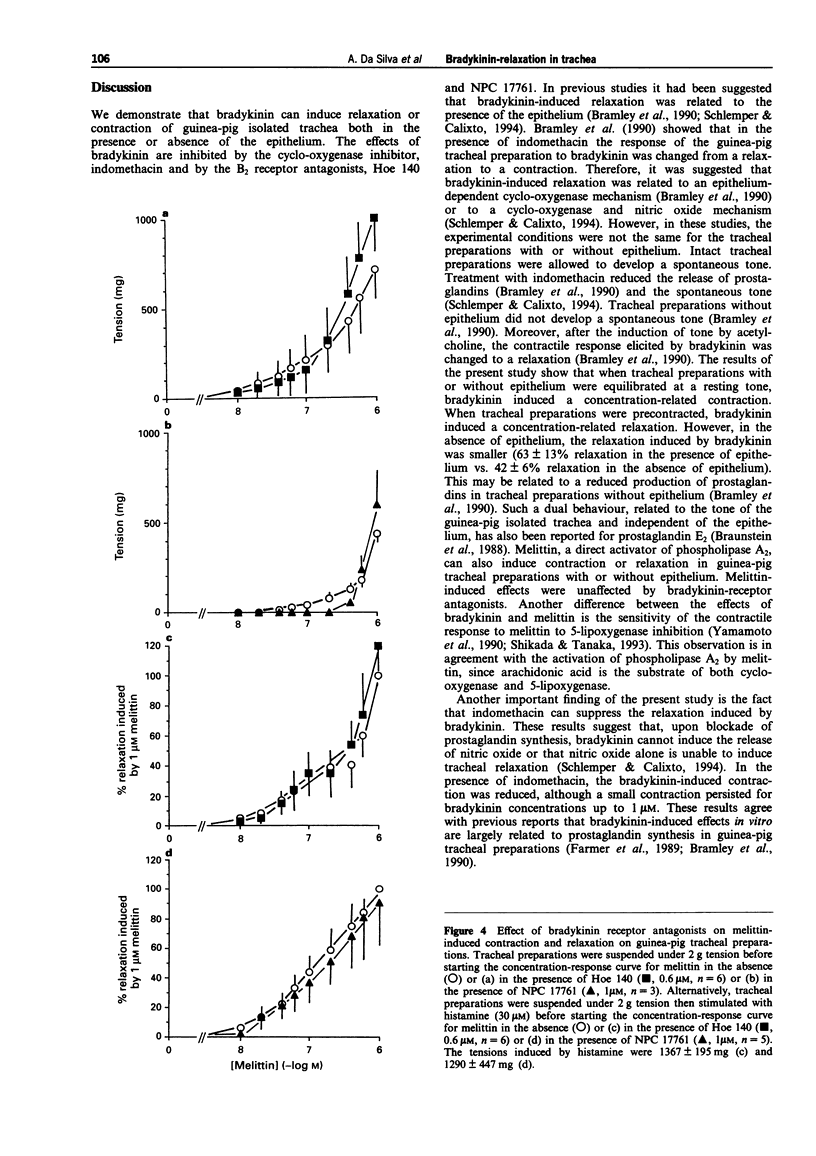
1. The aim of this study was to determine the receptor type and involvement of arachidonic acid metabolites in bradykinin-induced relaxation of the guinea-pig isolated trachea. 2. In the resting tracheal preparation, bradykinin (0.1 nM-30 microM induced a concentration-related contractile response (pD2 = 8.8 +/- 0.3). The maximal tension (1056 +/- 321 mg) was observed at 0.3 microM bradykinin. In contrast, when tracheal preparations were pre-contracted with histamine (30 microM leading to a half-maximum response), a concentration-related relaxation was observed with bradykinin. At the highest concentration of bradykinin used (3 microM), a reversal of 63 +/- 13% of the contractile response to histamine was observed. Both effects of bradykinin were inhibited by the cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, indomethacin (1 microM). In concentration-response curves, melittin (10 nM-1 microM), a direct activator of phospholipase A2, mimicked both effects of bradykinin. The highest concentration of melittin used (1 microM), induced a tension of 813 +/- 120 mg and led to the reversal of 41 +/- 8% of the contractile response to histamine. The contractile effect of melittin was inhibited in the presence of both indomethacin (1 microM) and AA861 (1 microM), a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. 3. [Des Arg9]-bradykinin (1 nM-3 microM), a B1-receptor agonist, was unable to relax precontracted guinea-pig tracheal preparations. The relaxation induced by bradykinin was antagonized by the B2 receptor antagonists, Hoe 140 (D-Arg0[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Oic8]bradykinin) and NPC 17761 (D-Arg0[Hyp3,D-HypE(trans-thiophenyl)7,Oic8]bradykinin ).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashida Y., Saijo T., Kuriki H., Makino H., Terao S., Maki Y. Pharmacological profile of AA-861, a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. Prostaglandins. 1983 Dec;26(6):955–972. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(83)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J. Bradykinin and asthma. Thorax. 1992 Nov;47(11):979–983. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.11.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramley A. M., Samhoun M. N., Piper P. J. Effect of a bradykinin B2 antagonist on responses of intact and rubbed guinea-pig trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98 (Suppl):786P–786P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramley A. M., Samhoun M. N., Piper P. J. The role of the epithelium in modulating the responses of guinea-pig trachea induced by bradykinin in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):762–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb13003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein G., Labat C., Brunelleschi S., Benveniste J., Marsac J., Brink C. Evidence that the histamine sensitivity and responsiveness of guinea-pig isolated trachea are modulated by epithelial prostaglandin E2 production. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):300–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16577.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva A., Dhuy J., Waeldelé F., Bertrand C., Landry Y. Endopeptidase 24.15 modulates bradykinin-induced contraction in guinea-pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 25;212(1):97–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90078-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction: inhibition by nedocromil sodium and sodium cromoglycate. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;27(6):831–836. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Nadel J. A., Sekizawa K., Graf P. D., Borson D. B. Neutral endopeptidase and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors potentiate kinin-induced contraction of ferret trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):531–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Kyle D. J., Martin J. A., Meeker S. N., Togo J. D-Arg[Hyp3-Thi5-D-Tic7-Tic8]-bradykinin, a potent antagonist of smooth muscle BK2 receptors and BK3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):785–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Meeker S. A., Wilkins D. E. Evidence for a pulmonary B3 bradykinin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., DeSiato M. A. Effects of a novel nonpeptide bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist on intestinal and airway smooth muscle: further evidence for the tracheal B3 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):461–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Ensor J. E., Burch R. M. Evidence that cultured airway smooth muscle cells contain bradykinin B2 and B3 receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;4(3):273–277. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. L., Hall J. M., Morton I. K. Bradykinin receptors in the guinea-pig taenia caeci are similar to proposed BK3 receptors in the guinea-pig trachea, and are blocked by HOE 140. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frossard N., Stretton C. D., Barnes P. J. Modulation of bradykinin responses in airway smooth muscle by epithelial enzymes. Agents Actions. 1990 Nov;31(3-4):204–209. doi: 10.1007/BF01997609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Dixon C. M., Cuss F. M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in humans. Mode of action. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):176–180. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M. Bradykinin receptors: pharmacological properties and biological roles. Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Nov;56(2):131–190. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90016-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Nakajima N., Takahashi T., Yamauchi H., Inoue H., Takishima T. Protection against bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatic patients by neurokinin receptor antagonist. Lancet. 1992 Nov 21;340(8830):1248–1251. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92948-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Ashton J., Schulz W. W., Erdös E. G. Neutral metalloendopeptidase in human lung tissue and cultured cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):564–568. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi J., D'Orléans-Juste P., Caranikas S., Regoli D. Effects of peptides and amines on isolated guinea pig tracheae as influenced by inhibitors of the metabolism of arachidonic acid. Pharmacology. 1982;25(6):320–326. doi: 10.1159/000137758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp F. P., Folkerts G. Reversal of arachidonic acid-induced guinea-pig tracheal relaxation into contraction after epithelium removal. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 19;131(2-3):315–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90591-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polosa R., Holgate S. T. Comparative airway response to inhaled bradykinin, kallidin, and [des-Arg9]bradykinin in normal and asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1367–1371. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Drapeau G. New selective bradykinin receptor antagonists and bradykinin B2 receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):156–161. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90067-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Drapeau G., Regoli D., Browne R. G. Bradykinin antagonism: differentiation between peptide antagonists and antiinflammatory agents. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 7;151(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90808-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Regoli D., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (HOE 140: D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Qic8]bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90661-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlemper V., Calixto J. B. Nitric oxide pathway-mediated relaxant effect of bradykinin in the guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier W. T. Activation of high levels of endogenous phospholipase A2 in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):195–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shikada K., Tanaka S. Influence of epithelium on the inhibition of melittin-induced contraction of guinea-pig isolated trachea by the potassium channel opener NIP-121. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1091–1096. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. M., Vavrek R. J. Kinin antagonists: design and activities. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 6):S69–S74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff A., Amrani Y., Landry Y., Gies J. P. Comparative action of new highly potent bradykinin receptor antagonists in the guinea-pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 3;239(1-3):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)91000-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff A., Da Silva A., Gies J. P. Kinins and respiratory tract diseases. Eur Respir J. 1993 Apr;6(4):576–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff A., Da Silva A., Landry Y., Gies J. P. Effect of Hoe 140, a new B2 noncompetitive antagonist, on guinea pig tracheal bradykinin receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Dec;263(3):1377–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschirhart E., Frossard N., Bertrand C., Landry Y. Arachidonic acid metabolites and airway epithelium-dependent relaxant factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):310–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ROSSUM J. M. Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;143:299–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. Competitive antagonists of bradykinin. Peptides. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Hock F. J., Albus U., Linz W., Alpermann H. G., Anagnostopoulos H., Henk S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):774–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Shikada K., Tanaka S. Arachidonate lipoxygenase inhibitors in guinea-pig isolated trachea. Effects on contractions to antigen and various agonists. Prostaglandins. 1990 Dec;40(6):615–625. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(90)90006-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


